Yichen Lu
a Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering of Ministry of Education, Tongji University, Shanghai, China
ViDove: A Translation Agent System with Multimodal Context and Memory-Augmented Reasoning
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:LLM-based translation agents have achieved highly human-like translation results and are capable of handling longer and more complex contexts with greater efficiency. However, they are typically limited to text-only inputs. In this paper, we introduce ViDove, a translation agent system designed for multimodal input. Inspired by the workflow of human translators, ViDove leverages visual and contextual background information to enhance the translation process. Additionally, we integrate a multimodal memory system and long-short term memory modules enriched with domain-specific knowledge, enabling the agent to perform more accurately and adaptively in real-world scenarios. As a result, ViDove achieves significantly higher translation quality in both subtitle generation and general translation tasks, with a 28% improvement in BLEU scores and a 15% improvement in SubER compared to previous state-of-the-art baselines. Moreover, we introduce DoveBench, a new benchmark for long-form automatic video subtitling and translation, featuring 17 hours of high-quality, human-annotated data. Our code is available here: https://github.com/pigeonai-org/ViDove
Enhancing Audiovisual Speech Recognition through Bifocal Preference Optimization
Dec 26, 2024



Abstract:Audiovisual Automatic Speech Recognition (AV-ASR) aims to improve speech recognition accuracy by leveraging visual signals. It is particularly challenging in unconstrained real-world scenarios across various domains due to noisy acoustic environments, spontaneous speech, and the uncertain use of visual information. Most previous works fine-tune audio-only ASR models on audiovisual datasets, optimizing them for conventional ASR objectives. However, they often neglect visual features and common errors in unconstrained video scenarios. In this paper, we propose using a preference optimization strategy to improve speech recognition accuracy for real-world videos. First, we create preference data via simulating common errors that occurred in AV-ASR from two focals: manipulating the audio or vision input and rewriting the output transcript. Second, we propose BPO-AVASR, a Bifocal Preference Optimization method to improve AV-ASR models by leveraging both input-side and output-side preference. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly improves speech recognition accuracy across various domains, outperforming previous state-of-the-art models on real-world video speech recognition.
FastAdaSP: Multitask-Adapted Efficient Inference for Large Speech Language Model
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:In this study, we aim to explore Multitask Speech Language Model (SpeechLM) efficient inference via token reduction. Unlike other modalities such as vision or text, speech has unique temporal dependencies, making previous efficient inference works on other modalities not directly applicable. Furthermore, methods for efficient SpeechLM inference on long sequence and sparse signals remain largely unexplored. Then we propose FastAdaSP, a weighted token merging framework specifically designed for various speech-related tasks to improve the trade-off between efficiency and performance. Experimental results on WavLLM and Qwen-Audio show that our method achieves the state-of-the-art (SOTA) efficiency-performance trade-off compared with other baseline methods. Specifically, FastAdaSP achieved 7x memory efficiency and 1.83x decoding throughput without any degradation on tasks like Emotion Recognition (ER) and Spoken Question Answering (SQA). The code will be available at https://github.com/yichen14/FastAdaSP
SynesLM: A Unified Approach for Audio-visual Speech Recognition and Translation via Language Model and Synthetic Data
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:In this work, we present SynesLM, an unified model which can perform three multimodal language understanding tasks: audio-visual automatic speech recognition(AV-ASR) and visual-aided speech/machine translation(VST/VMT). Unlike previous research that focused on lip motion as visual cues for speech signals, our work explores more general visual information within entire frames, such as objects and actions. Additionally, we use synthetic image data to enhance the correlation between image and speech data. We benchmark SynesLM against the How2 dataset, demonstrating performance on par with state-of-the-art (SOTA) models dedicated to AV-ASR while maintaining our multitasking framework. Remarkably, for zero-shot AV-ASR, SynesLM achieved SOTA performance by lowering the Word Error Rate (WER) from 43.4% to 39.4% on the VisSpeech Dataset. Furthermore, our results in VST and VMT outperform the previous results, improving the BLEU score to 43.5 from 37.2 for VST, and to 54.8 from 54.4 for VMT.
Exploring Speech Recognition, Translation, and Understanding with Discrete Speech Units: A Comparative Study
Sep 27, 2023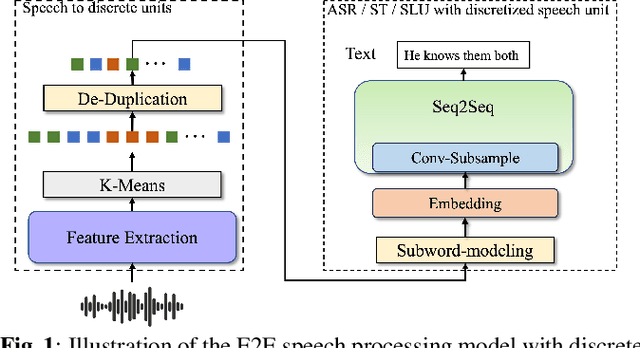
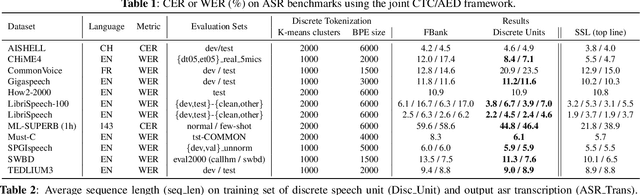
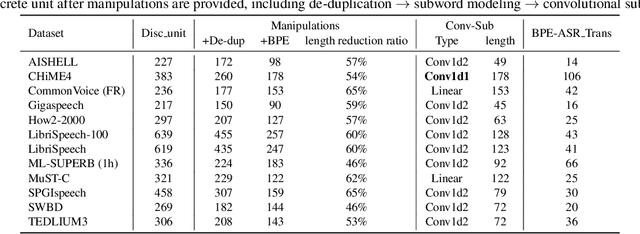
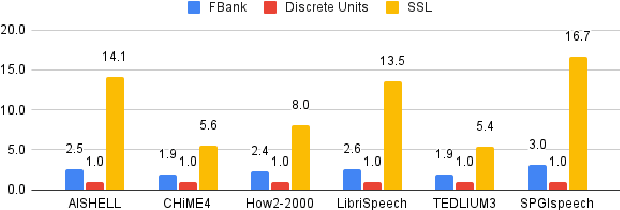
Abstract:Speech signals, typically sampled at rates in the tens of thousands per second, contain redundancies, evoking inefficiencies in sequence modeling. High-dimensional speech features such as spectrograms are often used as the input for the subsequent model. However, they can still be redundant. Recent investigations proposed the use of discrete speech units derived from self-supervised learning representations, which significantly compresses the size of speech data. Applying various methods, such as de-duplication and subword modeling, can further compress the speech sequence length. Hence, training time is significantly reduced while retaining notable performance. In this study, we undertake a comprehensive and systematic exploration into the application of discrete units within end-to-end speech processing models. Experiments on 12 automatic speech recognition, 3 speech translation, and 1 spoken language understanding corpora demonstrate that discrete units achieve reasonably good results in almost all the settings. We intend to release our configurations and trained models to foster future research efforts.
Noisy Positive-Unlabeled Learning with Self-Training for Speculative Knowledge Graph Reasoning
Jun 13, 2023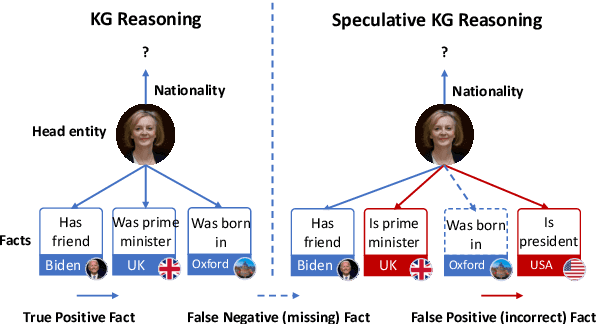
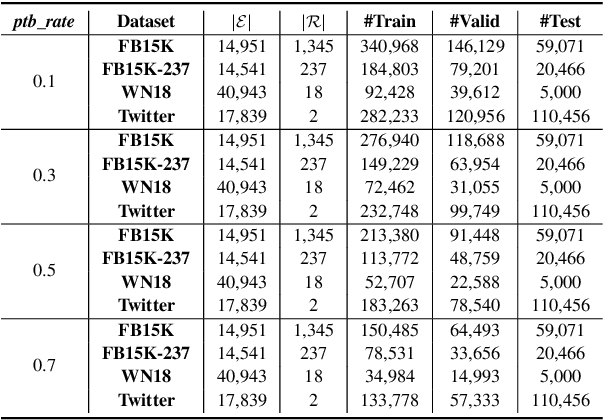
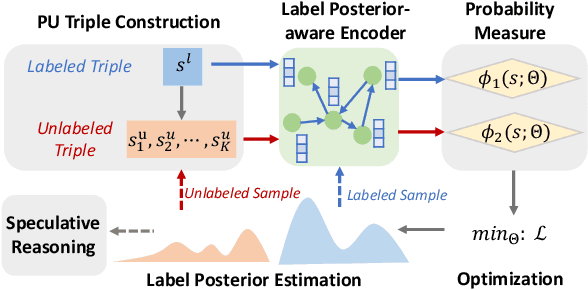
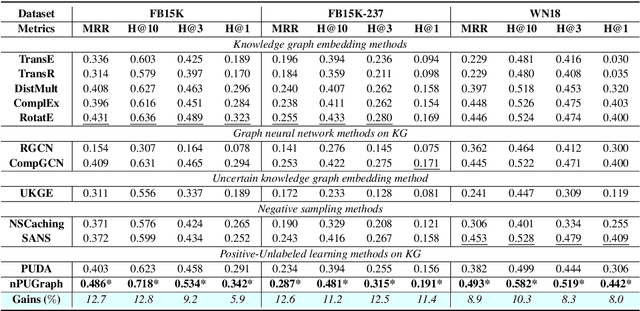
Abstract:This paper studies speculative reasoning task on real-world knowledge graphs (KG) that contain both \textit{false negative issue} (i.e., potential true facts being excluded) and \textit{false positive issue} (i.e., unreliable or outdated facts being included). State-of-the-art methods fall short in the speculative reasoning ability, as they assume the correctness of a fact is solely determined by its presence in KG, making them vulnerable to false negative/positive issues. The new reasoning task is formulated as a noisy Positive-Unlabeled learning problem. We propose a variational framework, namely nPUGraph, that jointly estimates the correctness of both collected and uncollected facts (which we call \textit{label posterior}) and updates model parameters during training. The label posterior estimation facilitates speculative reasoning from two perspectives. First, it improves the robustness of a label posterior-aware graph encoder against false positive links. Second, it identifies missing facts to provide high-quality grounds of reasoning. They are unified in a simple yet effective self-training procedure. Empirically, extensive experiments on three benchmark KG and one Twitter dataset with various degrees of false negative/positive cases demonstrate the effectiveness of nPUGraph.
Avatar Knowledge Distillation: Self-ensemble Teacher Paradigm with Uncertainty
May 04, 2023Abstract:Knowledge distillation is an effective paradigm for boosting the performance of pocket-size model, especially when multiple teacher models are available, the student would break the upper limit again. However, it is not economical to train diverse teacher models for the disposable distillation. In this paper, we introduce a new concept dubbed Avatars for distillation, which are the inference ensemble models derived from the teacher. Concretely, (1) For each iteration of distillation training, various Avatars are generated by a perturbation transformation. We validate that Avatars own higher upper limit of working capacity and teaching ability, aiding the student model in learning diverse and receptive knowledge perspectives from the teacher model. (2) During the distillation, we propose an uncertainty-aware factor from the variance of statistical differences between the vanilla teacher and Avatars, to adjust Avatars' contribution on knowledge transfer adaptively. Avatar Knowledge Distillation AKD is fundamentally different from existing methods and refines with the innovative view of unequal training. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our Avatars mechanism, which polishes up the state-of-the-art distillation methods for dense prediction without more extra computational cost. The AKD brings at most 0.7 AP gains on COCO 2017 for Object Detection and 1.83 mIoU gains on Cityscapes for Semantic Segmentation, respectively.
Dive into the Resolution Augmentations and Metrics in Low Resolution Face Recognition: A Plain yet Effective New Baseline
Feb 11, 2023



Abstract:Although deep learning has significantly improved Face Recognition (FR), dramatic performance deterioration may occur when processing Low Resolution (LR) faces. To alleviate this, approaches based on unified feature space are proposed with the sacrifice under High Resolution (HR) circumstances. To deal with the huge domain gap between HR and LR domains and achieve the best on both domains, we first took a closer look at the impacts of several resolution augmentations and then analyzed the difficulty of LR samples from the perspective of the model gradient produced by different resolution samples. Besides, we also find that the introduction of some resolutions could help the learning of lower resolutions. Based on these, we divide the LR samples into three difficulties according to the resolution and propose a more effective Multi-Resolution Augmentation. Then, due to the rapidly increasing domain gap as the resolution decreases, we carefully design a novel and effective metric loss based on a LogExp distance function that provides decent gradients to prevent oscillation near the convergence point or tolerance to small distance errors; it could also dynamically adjust the penalty for errors in different dimensions, allowing for more optimization of dimensions with large errors. Combining these two insights, our model could learn more general knowledge in a wide resolution range of images and balanced results can be achieved by our extremely simple framework. Moreover, the augmentations and metrics are the cornerstones of LRFR, so our method could be considered a new baseline for the LRFR task. Experiments on the LRFR datasets: SCface, XQLFW, and large-scale LRFR dataset: TinyFace demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods, while the degradation on HRFR datasets is significantly reduced.
Analysis of lane-change conflict between cars and trucks at merging section using UAV video data
Jan 05, 2022Abstract:The freeway on-ramp merging section is often identified as a crash-prone spot due to the high frequency of traffic conflicts. Very few traffic conflict analysis studies comprehensively consider different vehicle types at freeway merging section. Thus, the main objective of this study is to analyse conflicts between different vehicle types at freeway merging section. Field data are collected by Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) at merging areas in Shanghai, China. Vehicle extraction method is utilized to obtain vehicle trajectories. Time-to-collision (TTC) is utilized as the surrogate safety measure. TTC of car-car conflicts are the smallest while TTC of truck-truck conflicts are the largest. Traffic conflicts frequently occur at on-ramp and acceleration lane. Results show the spatial distribution of lane-change conflicts is significantly different between different vehicle types, suggesting that vehicle drivers should maintain safe distance especially car drivers. Besides, in order to decrease lane-change conflict at merging area, traffic management agencies are suggested to change dotted lie to solid lane at the beginning of acceleration lane.
The Future will be Different than Today: Model Evaluation Considerations when Developing Translational Clinical Biomarker
Jul 13, 2021



Abstract:Finding translational biomarkers stands center stage of the future of personalized medicine in healthcare. We observed notable challenges in identifying robust biomarkers as some with great performance in one scenario often fail to perform well in new trials (e.g. different population, indications). With rapid development in the clinical trial world (e.g. assay, disease definition), new trials very likely differ from legacy ones in many perspectives and in development of biomarkers this heterogeneity should be considered. In response, we recommend considering building in the heterogeneity when evaluating biomarkers. In this paper, we present one evaluation strategy by using leave-one-study-out (LOSO) in place of conventional cross-validation (cv) methods to account for the potential heterogeneity across trials used for building and testing the biomarkers. To demonstrate the performance of K-fold vs LOSO cv in estimating the effect size of biomarkers, we leveraged data from clinical trials and simulation studies. In our assessment, LOSO cv provided a more objective estimate of the future performance. This conclusion remained true across different evaluation metrics and different statistical methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge