Jinning Li
SCRAG: Social Computing-Based Retrieval Augmented Generation for Community Response Forecasting in Social Media Environments
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces SCRAG, a prediction framework inspired by social computing, designed to forecast community responses to real or hypothetical social media posts. SCRAG can be used by public relations specialists (e.g., to craft messaging in ways that avoid unintended misinterpretations) or public figures and influencers (e.g., to anticipate social responses), among other applications related to public sentiment prediction, crisis management, and social what-if analysis. While large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success in generating coherent and contextually rich text, their reliance on static training data and susceptibility to hallucinations limit their effectiveness at response forecasting in dynamic social media environments. SCRAG overcomes these challenges by integrating LLMs with a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technique rooted in social computing. Specifically, our framework retrieves (i) historical responses from the target community to capture their ideological, semantic, and emotional makeup, and (ii) external knowledge from sources such as news articles to inject time-sensitive context. This information is then jointly used to forecast the responses of the target community to new posts or narratives. Extensive experiments across six scenarios on the X platform (formerly Twitter), tested with various embedding models and LLMs, demonstrate over 10% improvements on average in key evaluation metrics. A concrete example further shows its effectiveness in capturing diverse ideologies and nuances. Our work provides a social computing tool for applications where accurate and concrete insights into community responses are crucial.
Perturbation-based Graph Active Learning for Weakly-Supervised Belief Representation Learning
Oct 24, 2024



Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of optimizing the allocation of labeling resources for semi-supervised belief representation learning in social networks. The objective is to strategically identify valuable messages on social media graphs that are worth labeling within a constrained budget, ultimately maximizing the task's performance. Despite the progress in unsupervised or semi-supervised methods in advancing belief and ideology representation learning on social networks and the remarkable efficacy of graph learning techniques, the availability of high-quality curated labeled social data can greatly benefit and further improve performances. Consequently, allocating labeling efforts is a critical research problem in scenarios where labeling resources are limited. This paper proposes a graph data augmentation-inspired perturbation-based active learning strategy (PerbALGraph) that progressively selects messages for labeling according to an automatic estimator, obviating human guidance. This estimator is based on the principle that messages in the network that exhibit heightened sensitivity to structural features of the observational data indicate landmark quality that significantly influences semi-supervision processes. We design the estimator to be the prediction variance under a set of designed graph perturbations, which is model-agnostic and application-independent. Extensive experiment results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed strategy for belief representation learning tasks.
Adaptive Prediction Ensemble: Improving Out-of-Distribution Generalization of Motion Forecasting
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:Deep learning-based trajectory prediction models for autonomous driving often struggle with generalization to out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios, sometimes performing worse than simple rule-based models. To address this limitation, we propose a novel framework, Adaptive Prediction Ensemble (APE), which integrates deep learning and rule-based prediction experts. A learned routing function, trained concurrently with the deep learning model, dynamically selects the most reliable prediction based on the input scenario. Our experiments on large-scale datasets, including Waymo Open Motion Dataset (WOMD) and Argoverse, demonstrate improvement in zero-shot generalization across datasets. We show that our method outperforms individual prediction models and other variants, particularly in long-horizon prediction and scenarios with a high proportion of OOD data. This work highlights the potential of hybrid approaches for robust and generalizable motion prediction in autonomous driving.
Decoding the Silent Majority: Inducing Belief Augmented Social Graph with Large Language Model for Response Forecasting
Oct 20, 2023



Abstract:Automatic response forecasting for news media plays a crucial role in enabling content producers to efficiently predict the impact of news releases and prevent unexpected negative outcomes such as social conflict and moral injury. To effectively forecast responses, it is essential to develop measures that leverage the social dynamics and contextual information surrounding individuals, especially in cases where explicit profiles or historical actions of the users are limited (referred to as lurkers). As shown in a previous study, 97% of all tweets are produced by only the most active 25% of users. However, existing approaches have limited exploration of how to best process and utilize these important features. To address this gap, we propose a novel framework, named SocialSense, that leverages a large language model to induce a belief-centered graph on top of an existent social network, along with graph-based propagation to capture social dynamics. We hypothesize that the induced graph that bridges the gap between distant users who share similar beliefs allows the model to effectively capture the response patterns. Our method surpasses existing state-of-the-art in experimental evaluations for both zero-shot and supervised settings, demonstrating its effectiveness in response forecasting. Moreover, the analysis reveals the framework's capability to effectively handle unseen user and lurker scenarios, further highlighting its robustness and practical applicability.
Quantifying Agent Interaction in Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning for Cost-efficient Generalization
Oct 11, 2023
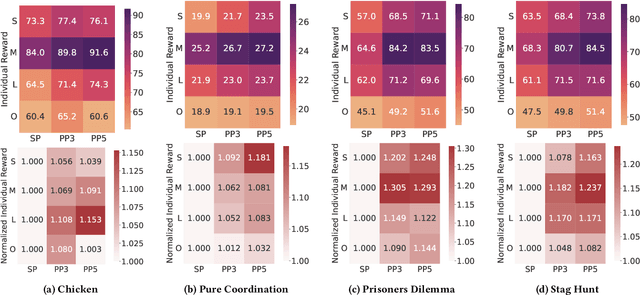

Abstract:Generalization poses a significant challenge in Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL). The extent to which an agent is influenced by unseen co-players depends on the agent's policy and the specific scenario. A quantitative examination of this relationship sheds light on effectively training agents for diverse scenarios. In this study, we present the Level of Influence (LoI), a metric quantifying the interaction intensity among agents within a given scenario and environment. We observe that, generally, a more diverse set of co-play agents during training enhances the generalization performance of the ego agent; however, this improvement varies across distinct scenarios and environments. LoI proves effective in predicting these improvement disparities within specific scenarios. Furthermore, we introduce a LoI-guided resource allocation method tailored to train a set of policies for diverse scenarios under a constrained budget. Our results demonstrate that strategic resource allocation based on LoI can achieve higher performance than uniform allocation under the same computation budget.
Guided Online Distillation: Promoting Safe Reinforcement Learning by Offline Demonstration
Sep 18, 2023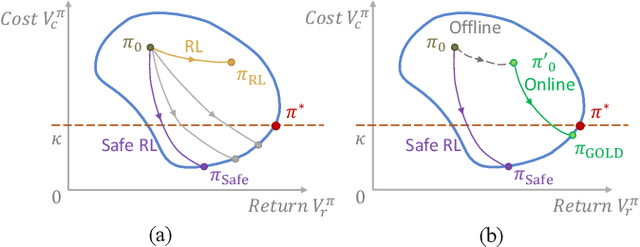
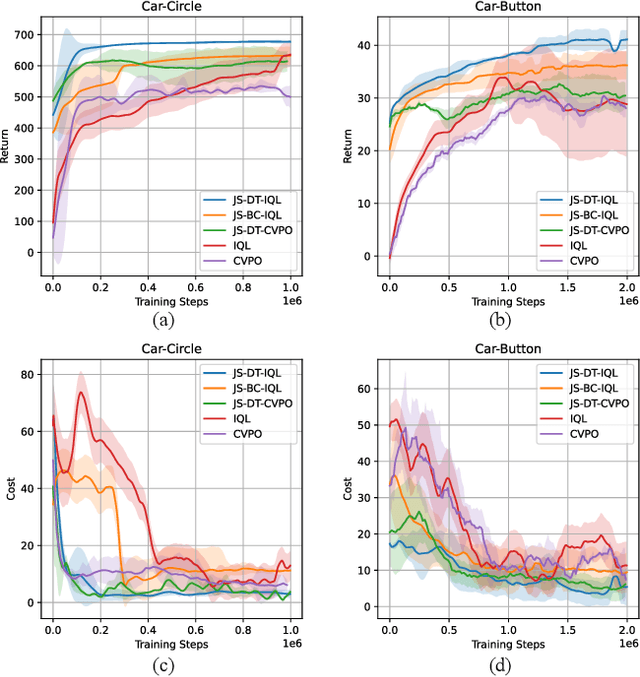
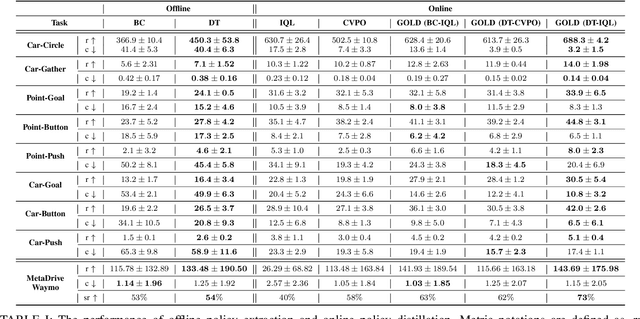
Abstract:Safe Reinforcement Learning (RL) aims to find a policy that achieves high rewards while satisfying cost constraints. When learning from scratch, safe RL agents tend to be overly conservative, which impedes exploration and restrains the overall performance. In many realistic tasks, e.g. autonomous driving, large-scale expert demonstration data are available. We argue that extracting expert policy from offline data to guide online exploration is a promising solution to mitigate the conserveness issue. Large-capacity models, e.g. decision transformers (DT), have been proven to be competent in offline policy learning. However, data collected in real-world scenarios rarely contain dangerous cases (e.g., collisions), which makes it prohibitive for the policies to learn safety concepts. Besides, these bulk policy networks cannot meet the computation speed requirements at inference time on real-world tasks such as autonomous driving. To this end, we propose Guided Online Distillation (GOLD), an offline-to-online safe RL framework. GOLD distills an offline DT policy into a lightweight policy network through guided online safe RL training, which outperforms both the offline DT policy and online safe RL algorithms. Experiments in both benchmark safe RL tasks and real-world driving tasks based on the Waymo Open Motion Dataset (WOMD) demonstrate that GOLD can successfully distill lightweight policies and solve decision-making problems in challenging safety-critical scenarios.
Noisy Positive-Unlabeled Learning with Self-Training for Speculative Knowledge Graph Reasoning
Jun 13, 2023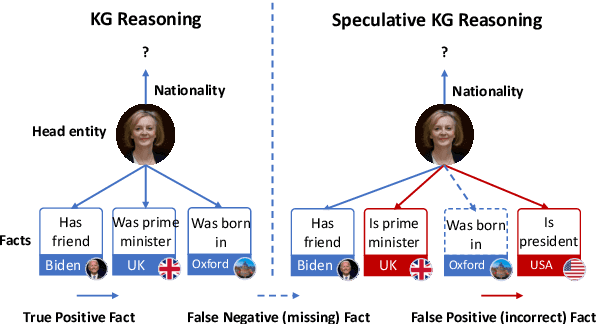
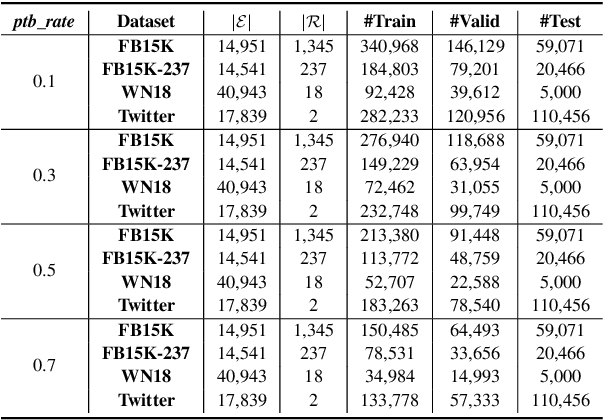
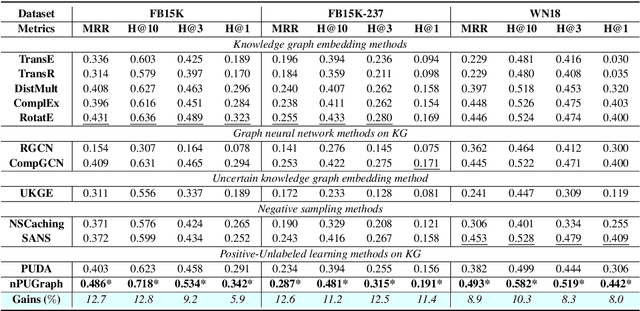
Abstract:This paper studies speculative reasoning task on real-world knowledge graphs (KG) that contain both \textit{false negative issue} (i.e., potential true facts being excluded) and \textit{false positive issue} (i.e., unreliable or outdated facts being included). State-of-the-art methods fall short in the speculative reasoning ability, as they assume the correctness of a fact is solely determined by its presence in KG, making them vulnerable to false negative/positive issues. The new reasoning task is formulated as a noisy Positive-Unlabeled learning problem. We propose a variational framework, namely nPUGraph, that jointly estimates the correctness of both collected and uncollected facts (which we call \textit{label posterior}) and updates model parameters during training. The label posterior estimation facilitates speculative reasoning from two perspectives. First, it improves the robustness of a label posterior-aware graph encoder against false positive links. Second, it identifies missing facts to provide high-quality grounds of reasoning. They are unified in a simple yet effective self-training procedure. Empirically, extensive experiments on three benchmark KG and one Twitter dataset with various degrees of false negative/positive cases demonstrate the effectiveness of nPUGraph.
Measuring the Effect of Influential Messages on Varying Personas
May 25, 2023Abstract:Predicting how a user responds to news events enables important applications such as allowing intelligent agents or content producers to estimate the effect on different communities and revise unreleased messages to prevent unexpected bad outcomes such as social conflict and moral injury. We present a new task, Response Forecasting on Personas for News Media, to estimate the response a persona (characterizing an individual or a group) might have upon seeing a news message. Compared to the previous efforts which only predict generic comments to news, the proposed task not only introduces personalization in the modeling but also predicts the sentiment polarity and intensity of each response. This enables more accurate and comprehensive inference on the mental state of the persona. Meanwhile, the generated sentiment dimensions make the evaluation and application more reliable. We create the first benchmark dataset, which consists of 13,357 responses to 3,847 news headlines from Twitter. We further evaluate the SOTA neural language models with our dataset. The empirical results suggest that the included persona attributes are helpful for the performance of all response dimensions. Our analysis shows that the best-performing models are capable of predicting responses that are consistent with the personas, and as a byproduct, the task formulation also enables many interesting applications in the analysis of social network groups and their opinions, such as the discovery of extreme opinion groups.
NTULM: Enriching Social Media Text Representations with Non-Textual Units
Oct 29, 2022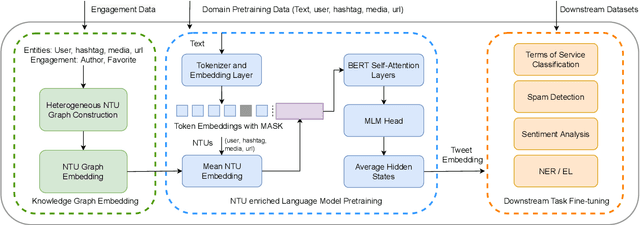
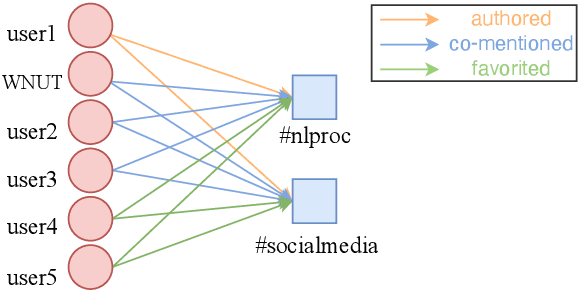
Abstract:On social media, additional context is often present in the form of annotations and meta-data such as the post's author, mentions, Hashtags, and hyperlinks. We refer to these annotations as Non-Textual Units (NTUs). We posit that NTUs provide social context beyond their textual semantics and leveraging these units can enrich social media text representations. In this work we construct an NTU-centric social heterogeneous network to co-embed NTUs. We then principally integrate these NTU embeddings into a large pretrained language model by fine-tuning with these additional units. This adds context to noisy short-text social media. Experiments show that utilizing NTU-augmented text representations significantly outperforms existing text-only baselines by 2-5\% relative points on many downstream tasks highlighting the importance of context to social media NLP. We also highlight that including NTU context into the initial layers of language model alongside text is better than using it after the text embedding is generated. Our work leads to the generation of holistic general purpose social media content embedding.
Learning to Sample and Aggregate: Few-shot Reasoning over Temporal Knowledge Graphs
Oct 16, 2022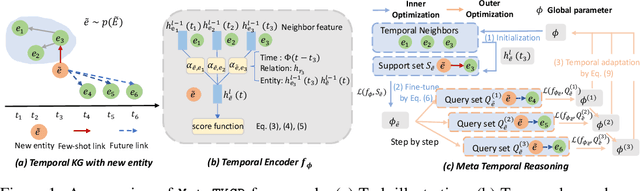
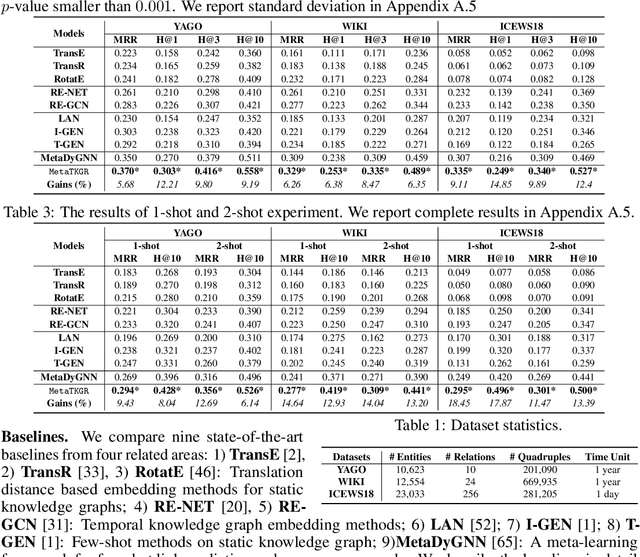
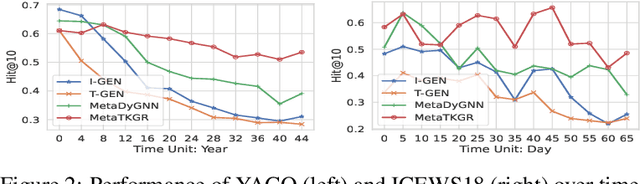
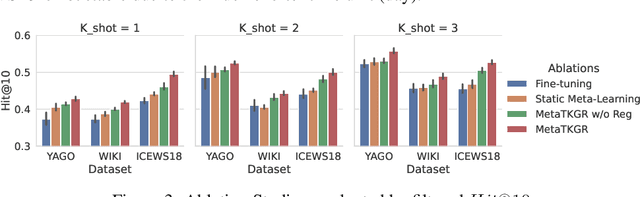
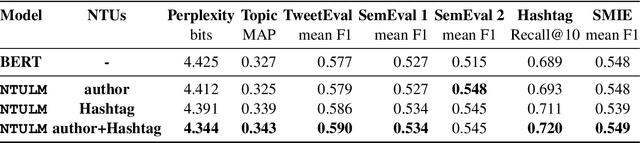
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate a realistic but underexplored problem, called few-shot temporal knowledge graph reasoning, that aims to predict future facts for newly emerging entities based on extremely limited observations in evolving graphs. It offers practical value in applications that need to derive instant new knowledge about new entities in temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs) with minimal supervision. The challenges mainly come from the few-shot and time shift properties of new entities. First, the limited observations associated with them are insufficient for training a model from scratch. Second, the potentially dynamic distributions from the initially observable facts to the future facts ask for explicitly modeling the evolving characteristics of new entities. We correspondingly propose a novel Meta Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning (MetaTKGR) framework. Unlike prior work that relies on rigid neighborhood aggregation schemes to enhance low-data entity representation, MetaTKGR dynamically adjusts the strategies of sampling and aggregating neighbors from recent facts for new entities, through temporally supervised signals on future facts as instant feedback. Besides, such a meta temporal reasoning procedure goes beyond existing meta-learning paradigms on static knowledge graphs that fail to handle temporal adaptation with large entity variance. We further provide a theoretical analysis and propose a temporal adaptation regularizer to stabilize the meta temporal reasoning over time. Empirically, extensive experiments on three real-world TKGs demonstrate the superiority of MetaTKGR over state-of-the-art baselines by a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge