Yuchen Yan
University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
TSAQA: Time Series Analysis Question And Answering Benchmark
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Time series data are integral to critical applications across domains such as finance, healthcare, transportation, and environmental science. While recent work has begun to explore multi-task time series question answering (QA), current benchmarks remain limited to forecasting and anomaly detection tasks. We introduce TSAQA, a novel unified benchmark designed to broaden task coverage and evaluate diverse temporal analysis capabilities. TSAQA integrates six diverse tasks under a single framework ranging from conventional analysis, including anomaly detection and classification, to advanced analysis, such as characterization, comparison, data transformation, and temporal relationship analysis. Spanning 210k samples across 13 domains, the dataset employs diverse formats, including true-or-false (TF), multiple-choice (MC), and a novel puzzling (PZ), to comprehensively assess time series analysis. Zero-shot evaluation demonstrates that these tasks are challenging for current Large Language Models (LLMs): the best-performing commercial LLM, Gemini-2.5-Flash, achieves an average score of only 65.08. Although instruction tuning boosts open-source performance: the best-performing open-source model, LLaMA-3.1-8B, shows significant room for improvement, highlighting the complexity of temporal analysis for LLMs.
Subspace Alignment for Vision-Language Model Test-time Adaptation
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs), despite their extraordinary zero-shot capabilities, are vulnerable to distribution shifts. Test-time adaptation (TTA) emerges as a predominant strategy to adapt VLMs to unlabeled test data on the fly. However, existing TTA methods heavily rely on zero-shot predictions as pseudo-labels for self-training, which can be unreliable under distribution shifts and misguide adaptation due to two fundamental limitations. First (Modality Gap), distribution shifts induce gaps between visual and textual modalities, making cross-modal relations inaccurate. Second (Visual Nuisance), visual embeddings encode rich but task-irrelevant noise that often overwhelms task-specific semantics under distribution shifts. To address these limitations, we propose SubTTA, which aligns the semantic subspaces of both modalities to enhance zero-shot predictions to better guide the TTA process. To bridge the modality gap, SubTTA extracts the principal subspaces of both modalities and aligns the visual manifold to the textual semantic anchor by minimizing their chordal distance. To eliminate visual nuisance, SubTTA projects the aligned visual features onto the task-specific textual subspace, which filters out task-irrelevant noise by constraining visual embeddings within the valid semantic span, and standard TTA is further performed on the purified space to refine the decision boundaries. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks and VLM architectures demonstrate the effectiveness of SubTTA, yielding an average improvement of 2.24% over state-of-the-art TTA methods.
Every Step Evolves: Scaling Reinforcement Learning for Trillion-Scale Thinking Model
Oct 21, 2025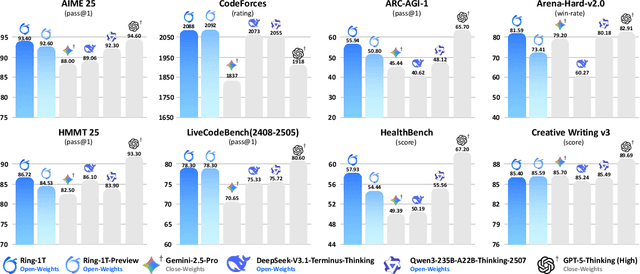
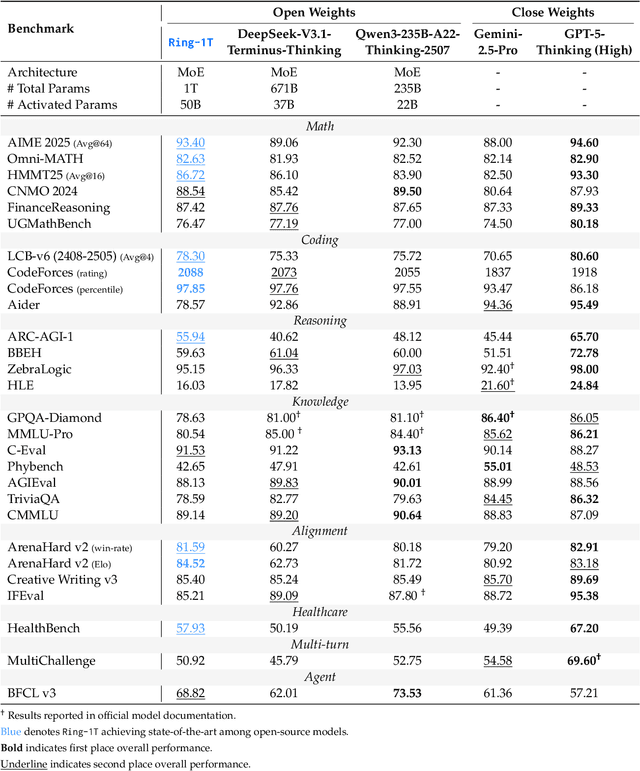
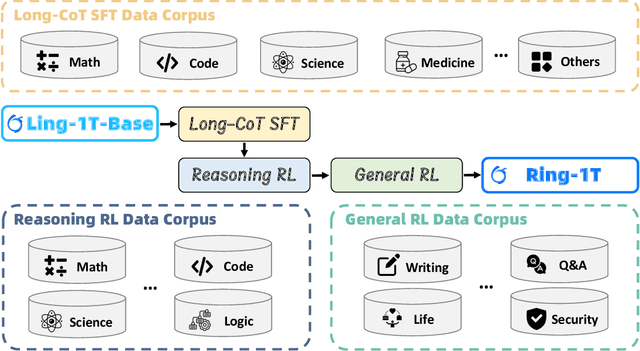
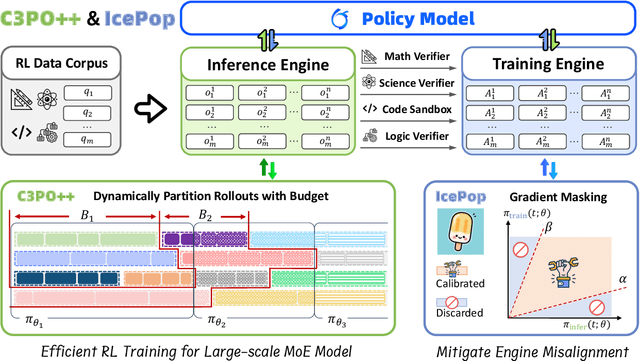
Abstract:We present Ring-1T, the first open-source, state-of-the-art thinking model with a trillion-scale parameter. It features 1 trillion total parameters and activates approximately 50 billion per token. Training such models at a trillion-parameter scale introduces unprecedented challenges, including train-inference misalignment, inefficiencies in rollout processing, and bottlenecks in the RL system. To address these, we pioneer three interconnected innovations: (1) IcePop stabilizes RL training via token-level discrepancy masking and clipping, resolving instability from training-inference mismatches; (2) C3PO++ improves resource utilization for long rollouts under a token budget by dynamically partitioning them, thereby obtaining high time efficiency; and (3) ASystem, a high-performance RL framework designed to overcome the systemic bottlenecks that impede trillion-parameter model training. Ring-1T delivers breakthrough results across critical benchmarks: 93.4 on AIME-2025, 86.72 on HMMT-2025, 2088 on CodeForces, and 55.94 on ARC-AGI-v1. Notably, it attains a silver medal-level result on the IMO-2025, underscoring its exceptional reasoning capabilities. By releasing the complete 1T parameter MoE model to the community, we provide the research community with direct access to cutting-edge reasoning capabilities. This contribution marks a significant milestone in democratizing large-scale reasoning intelligence and establishes a new baseline for open-source model performance.
OmniEAR: Benchmarking Agent Reasoning in Embodied Tasks
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Large language models excel at abstract reasoning but their capacity for embodied agent reasoning remains largely unexplored. We present OmniEAR, a comprehensive framework for evaluating how language models reason about physical interactions, tool usage, and multi-agent coordination in embodied tasks. Unlike existing benchmarks that provide predefined tool sets or explicit collaboration directives, OmniEAR requires agents to dynamically acquire capabilities and autonomously determine coordination strategies based on task demands. Through text-based environment representation, we model continuous physical properties and complex spatial relationships across 1,500 scenarios spanning household and industrial domains. Our systematic evaluation reveals severe performance degradation when models must reason from constraints: while achieving 85-96% success with explicit instructions, performance drops to 56-85% for tool reasoning and 63-85% for implicit collaboration, with compound tasks showing over 50% failure rates. Surprisingly, complete environmental information degrades coordination performance, indicating models cannot filter task-relevant constraints. Fine-tuning improves single-agent tasks dramatically (0.6% to 76.3%) but yields minimal multi-agent gains (1.5% to 5.5%), exposing fundamental architectural limitations. These findings demonstrate that embodied reasoning poses fundamentally different challenges than current models can address, establishing OmniEAR as a rigorous benchmark for evaluating and advancing embodied AI systems. Our code and data are included in the supplementary materials and will be open-sourced upon acceptance.
Test-Time Reinforcement Learning for GUI Grounding via Region Consistency
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Graphical User Interface (GUI) grounding, the task of mapping natural language instructions to precise screen coordinates, is fundamental to autonomous GUI agents. While existing methods achieve strong performance through extensive supervised training or reinforcement learning with labeled rewards, they remain constrained by the cost and availability of pixel-level annotations. We observe that when models generate multiple predictions for the same GUI element, the spatial overlap patterns reveal implicit confidence signals that can guide more accurate localization. Leveraging this insight, we propose GUI-RC (Region Consistency), a test-time scaling method that constructs spatial voting grids from multiple sampled predictions to identify consensus regions where models show highest agreement. Without any training, GUI-RC improves accuracy by 2-3% across various architectures on ScreenSpot benchmarks. We further introduce GUI-RCPO (Region Consistency Policy Optimization), which transforms these consistency patterns into rewards for test-time reinforcement learning. By computing how well each prediction aligns with the collective consensus, GUI-RCPO enables models to iteratively refine their outputs on unlabeled data during inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate the generality of our approach: GUI-RC boosts Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct from 80.11% to 83.57% on ScreenSpot-v2, while GUI-RCPO further improves it to 85.14% through self-supervised optimization. Our approach reveals the untapped potential of test-time scaling and test-time reinforcement learning for GUI grounding, offering a promising path toward more robust and data-efficient GUI agents.
Cooper: Co-Optimizing Policy and Reward Models in Reinforcement Learning for Large Language Models
Aug 07, 2025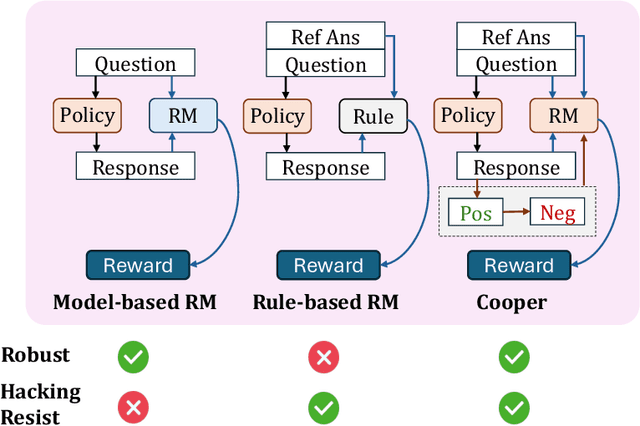



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in reasoning tasks, where reinforcement learning (RL) serves as a key algorithm for enhancing their reasoning capabilities. Currently, there are two mainstream reward paradigms: model-based rewards and rule-based rewards. However, both approaches suffer from limitations: rule-based rewards lack robustness, while model-based rewards are vulnerable to reward hacking. To address these issues, we propose Cooper(Co-optimizing Policy Model and Reward Model), a RL framework that jointly optimizes both the policy model and the reward model. Cooper leverages the high precision of rule-based rewards when identifying correct responses, and dynamically constructs and selects positive-negative sample pairs for continued training the reward model. This design enhances robustness and mitigates the risk of reward hacking. To further support Cooper, we introduce a hybrid annotation strategy that efficiently and accurately generates training data for the reward model. We also propose a reference-based reward modeling paradigm, where the reward model takes a reference answer as input. Based on this design, we train a reward model named VerifyRM, which achieves higher accuracy on VerifyBench compared to other models of the same size. We conduct reinforcement learning using both VerifyRM and Cooper. Our experiments show that Cooper not only alleviates reward hacking but also improves end-to-end RL performance, for instance, achieving a 0.54% gain in average accuracy on Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct. Our findings demonstrate that dynamically updating reward model is an effective way to combat reward hacking, providing a reference for better integrating reward models into RL.
ViewSpatial-Bench: Evaluating Multi-perspective Spatial Localization in Vision-Language Models
May 27, 2025



Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in understanding and reasoning about visual content, but significant challenges persist in tasks requiring cross-viewpoint understanding and spatial reasoning. We identify a critical limitation: current VLMs excel primarily at egocentric spatial reasoning (from the camera's perspective) but fail to generalize to allocentric viewpoints when required to adopt another entity's spatial frame of reference. We introduce ViewSpatial-Bench, the first comprehensive benchmark designed specifically for multi-viewpoint spatial localization recognition evaluation across five distinct task types, supported by an automated 3D annotation pipeline that generates precise directional labels. Comprehensive evaluation of diverse VLMs on ViewSpatial-Bench reveals a significant performance disparity: models demonstrate reasonable performance on camera-perspective tasks but exhibit reduced accuracy when reasoning from a human viewpoint. By fine-tuning VLMs on our multi-perspective spatial dataset, we achieve an overall performance improvement of 46.24% across tasks, highlighting the efficacy of our approach. Our work establishes a crucial benchmark for spatial intelligence in embodied AI systems and provides empirical evidence that modeling 3D spatial relationships enhances VLMs' corresponding spatial comprehension capabilities.
PLANETALIGN: A Comprehensive Python Library for Benchmarking Network Alignment
May 27, 2025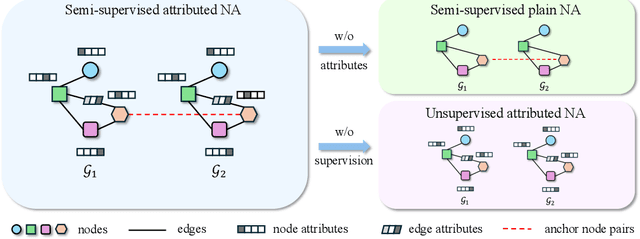
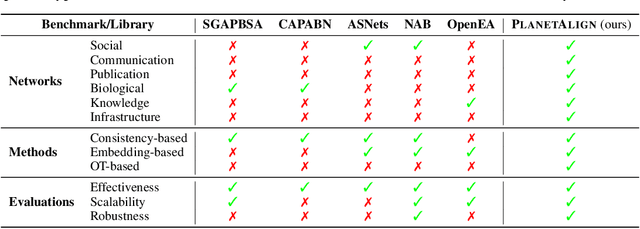
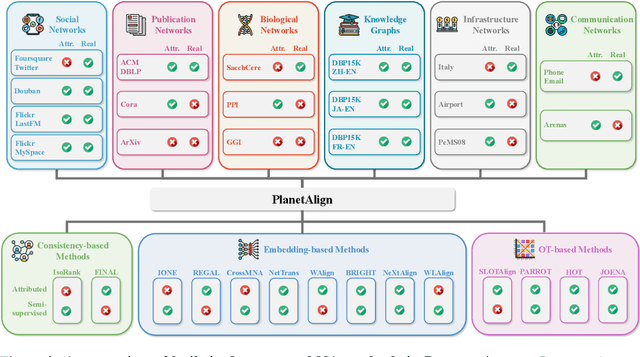
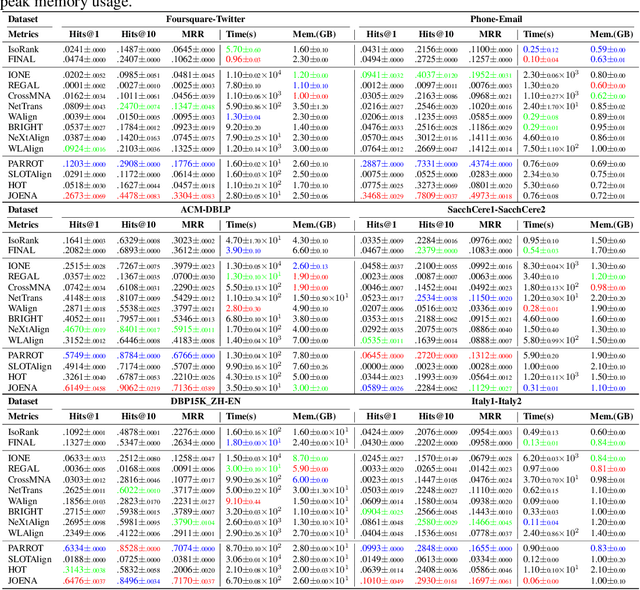
Abstract:Network alignment (NA) aims to identify node correspondence across different networks and serves as a critical cornerstone behind various downstream multi-network learning tasks. Despite growing research in NA, there lacks a comprehensive library that facilitates the systematic development and benchmarking of NA methods. In this work, we introduce PLANETALIGN, a comprehensive Python library for network alignment that features a rich collection of built-in datasets, methods, and evaluation pipelines with easy-to-use APIs. Specifically, PLANETALIGN integrates 18 datasets and 14 NA methods with extensible APIs for easy use and development of NA methods. Our standardized evaluation pipeline encompasses a wide range of metrics, enabling a systematic assessment of the effectiveness, scalability, and robustness of NA methods. Through extensive comparative studies, we reveal practical insights into the strengths and limitations of existing NA methods. We hope that PLANETALIGN can foster a deeper understanding of the NA problem and facilitate the development and benchmarking of more effective, scalable, and robust methods in the future. The source code of PLANETALIGN is available at https://github.com/yq-leo/PlanetAlign.
Do Large Language Models Excel in Complex Logical Reasoning with Formal Language?
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have been shown to achieve breakthrough performance on complex logical reasoning tasks. Nevertheless, most existing research focuses on employing formal language to guide LLMs to derive reliable reasoning paths, while systematic evaluations of these capabilities are still limited. In this paper, we aim to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of LLMs across various logical reasoning problems utilizing formal languages. From the perspective of three dimensions, i.e., spectrum of LLMs, taxonomy of tasks, and format of trajectories, our key findings are: 1) Thinking models significantly outperform Instruct models, especially when formal language is employed; 2) All LLMs exhibit limitations in inductive reasoning capability, irrespective of whether they use a formal language; 3) Data with PoT format achieves the best generalization performance across other languages. Additionally, we also curate the formal-relative training data to further enhance the small language models, and the experimental results indicate that a simple rejected fine-tuning method can better enable LLMs to generalize across formal languages and achieve the best overall performance. Our codes and reports are available at https://github.com/jiangjin1999/FormalEval.
Let LLMs Break Free from Overthinking via Self-Braking Tuning
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs), such as OpenAI o1 and DeepSeek-R1, have significantly enhanced their reasoning capabilities by generating longer chains of thought, demonstrating outstanding performance across a variety of tasks. However, this performance gain comes at the cost of a substantial increase in redundant reasoning during the generation process, leading to high computational overhead and exacerbating the issue of overthinking. Although numerous existing approaches aim to address the problem of overthinking, they often rely on external interventions. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, Self-Braking Tuning (SBT), which tackles overthinking from the perspective of allowing the model to regulate its own reasoning process, thus eliminating the reliance on external control mechanisms. We construct a set of overthinking identification metrics based on standard answers and design a systematic method to detect redundant reasoning. This method accurately identifies unnecessary steps within the reasoning trajectory and generates training signals for learning self-regulation behaviors. Building on this foundation, we develop a complete strategy for constructing data with adaptive reasoning lengths and introduce an innovative braking prompt mechanism that enables the model to naturally learn when to terminate reasoning at an appropriate point. Experiments across mathematical benchmarks (AIME, AMC, MATH500, GSM8K) demonstrate that our method reduces token consumption by up to 60% while maintaining comparable accuracy to unconstrained models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge