Chang Zong
Test-Time Reinforcement Learning for GUI Grounding via Region Consistency
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Graphical User Interface (GUI) grounding, the task of mapping natural language instructions to precise screen coordinates, is fundamental to autonomous GUI agents. While existing methods achieve strong performance through extensive supervised training or reinforcement learning with labeled rewards, they remain constrained by the cost and availability of pixel-level annotations. We observe that when models generate multiple predictions for the same GUI element, the spatial overlap patterns reveal implicit confidence signals that can guide more accurate localization. Leveraging this insight, we propose GUI-RC (Region Consistency), a test-time scaling method that constructs spatial voting grids from multiple sampled predictions to identify consensus regions where models show highest agreement. Without any training, GUI-RC improves accuracy by 2-3% across various architectures on ScreenSpot benchmarks. We further introduce GUI-RCPO (Region Consistency Policy Optimization), which transforms these consistency patterns into rewards for test-time reinforcement learning. By computing how well each prediction aligns with the collective consensus, GUI-RCPO enables models to iteratively refine their outputs on unlabeled data during inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate the generality of our approach: GUI-RC boosts Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct from 80.11% to 83.57% on ScreenSpot-v2, while GUI-RCPO further improves it to 85.14% through self-supervised optimization. Our approach reveals the untapped potential of test-time scaling and test-time reinforcement learning for GUI grounding, offering a promising path toward more robust and data-efficient GUI agents.
Structural-Temporal Coupling Anomaly Detection with Dynamic Graph Transformer
May 13, 2025Abstract:Detecting anomalous edges in dynamic graphs is an important task in many applications over evolving triple-based data, such as social networks, transaction management, and epidemiology. A major challenge with this task is the absence of structural-temporal coupling information, which decreases the ability of the representation to distinguish anomalies from normal instances. Existing methods focus on handling independent structural and temporal features with embedding models, which ignore the deep interaction between these two types of information. In this paper, we propose a structural-temporal coupling anomaly detection architecture with a dynamic graph transformer model. Specifically, we introduce structural and temporal features from two integration levels to provide anomaly-aware graph evolutionary patterns. Then, a dynamic graph transformer enhanced by two-dimensional positional encoding is implemented to capture both discrimination and contextual consistency signals. Extensive experiments on six datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms current state-of-the-art models. Finally, a case study illustrates the strength of our method when applied to a real-world task.
Ask2Loc: Learning to Locate Instructional Visual Answers by Asking Questions
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Locating specific segments within an instructional video is an efficient way to acquire guiding knowledge. Generally, the task of obtaining video segments for both verbal explanations and visual demonstrations is known as visual answer localization (VAL). However, users often need multiple interactions to obtain answers that align with their expectations when using the system. During these interactions, humans deepen their understanding of the video content by asking themselves questions, thereby accurately identifying the location. Therefore, we propose a new task, named In-VAL, to simulate the multiple interactions between humans and videos in the procedure of obtaining visual answers. The In-VAL task requires interactively addressing several semantic gap issues, including 1) the ambiguity of user intent in the input questions, 2) the incompleteness of language in video subtitles, and 3) the fragmentation of content in video segments. To address these issues, we propose Ask2Loc, a framework for resolving In-VAL by asking questions. It includes three key modules: 1) a chatting module to refine initial questions and uncover clear intentions, 2) a rewriting module to generate fluent language and create complete descriptions, and 3) a searching module to broaden local context and provide integrated content. We conduct extensive experiments on three reconstructed In-VAL datasets. Compared to traditional end-to-end and two-stage methods, our proposed Ask2Loc can improve performance by up to 14.91 (mIoU) on the In-VAL task. Our code and datasets can be accessed at https://github.com/changzong/Ask2Loc.
Stock Movement Prediction with Multimodal Stable Fusion via Gated Cross-Attention Mechanism
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:The accurate prediction of stock movements is crucial for investment strategies. Stock prices are subject to the influence of various forms of information, including financial indicators, sentiment analysis, news documents, and relational structures. Predominant analytical approaches, however, tend to address only unimodal or bimodal sources, neglecting the complexity of multimodal data. Further complicating the landscape are the issues of data sparsity and semantic conflicts between these modalities, which are frequently overlooked by current models, leading to unstable performance and limiting practical applicability. To address these shortcomings, this study introduces a novel architecture, named Multimodal Stable Fusion with Gated Cross-Attention (MSGCA), designed to robustly integrate multimodal input for stock movement prediction. The MSGCA framework consists of three integral components: (1) a trimodal encoding module, responsible for processing indicator sequences, dynamic documents, and a relational graph, and standardizing their feature representations; (2) a cross-feature fusion module, where primary and consistent features guide the multimodal fusion of the three modalities via a pair of gated cross-attention networks; and (3) a prediction module, which refines the fused features through temporal and dimensional reduction to execute precise movement forecasting. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that the MSGCA framework exceeds current leading methods, achieving performance gains of 8.1%, 6.1%, 21.7% and 31.6% on four multimodal datasets, respectively, attributed to its enhanced multimodal fusion stability.
ProSwitch: Knowledge-Guided Language Model Fine-Tuning to Generate Professional and Non-Professional Styled Text
Mar 27, 2024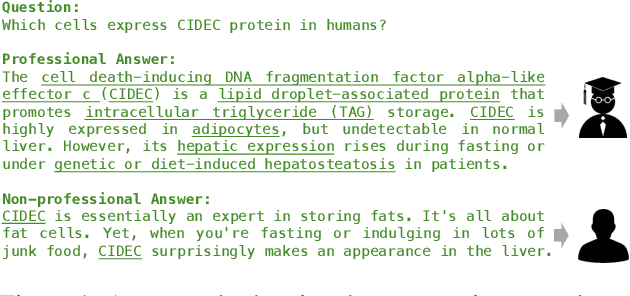



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated efficacy in various linguistic applications, including text summarization and controlled text generation. However, studies into their capacity of switching between styles via fine-tuning remain underexplored. This study concentrates on textual professionalism and introduces a novel methodology, named ProSwitch, which equips a language model with the ability to produce both professional and non-professional responses through knowledge-guided instruction tuning. ProSwitch unfolds across three phases: data preparation for gathering domain knowledge and training corpus; instruction tuning for optimizing language models with multiple levels of instruction formats; and comprehensive evaluation for assessing the professionalism discrimination and reference-based quality of generated text. Comparative analysis of ProSwitch against both general and specialized language models reveals that our approach outperforms baselines in switching between professional and non-professional text generation.
Triad: A Framework Leveraging a Multi-Role LLM-based Agent to Solve Knowledge Base Question Answering
Feb 22, 2024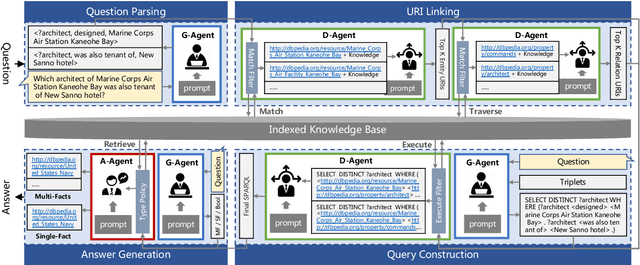
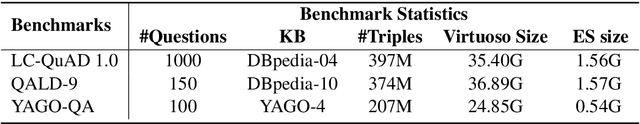
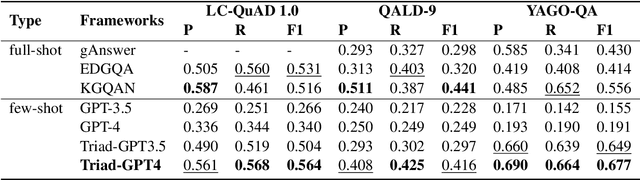
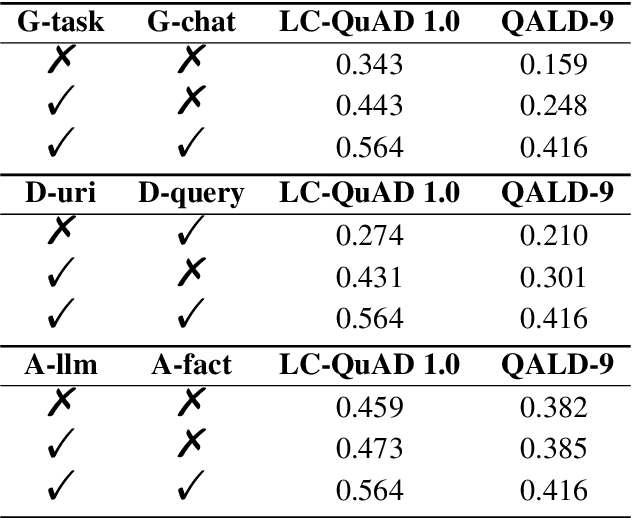
Abstract:Recent progress with LLM-based agents has shown promising results across various tasks. However, their use in answering questions from knowledge bases remains largely unexplored. Implementing a KBQA system using traditional methods is challenging due to the shortage of task-specific training data and the complexity of creating task-focused model structures. In this paper, we present Triad, a unified framework that utilizes an LLM-based agent with three roles for KBQA tasks. The agent is assigned three roles to tackle different KBQA subtasks: agent as a generalist for mastering various subtasks, as a decision maker for the selection of candidates, and as an advisor for answering questions with knowledge. Our KBQA framework is executed in four phases, involving the collaboration of the agent's multiple roles. We evaluated the performance of our framework using three benchmark datasets, and the results show that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art systems on the LC-QuAD and YAGO-QA benchmarks, yielding F1 scores of 11.8% and 20.7%, respectively.
Citation Trajectory Prediction via Publication Influence Representation Using Temporal Knowledge Graph
Oct 02, 2022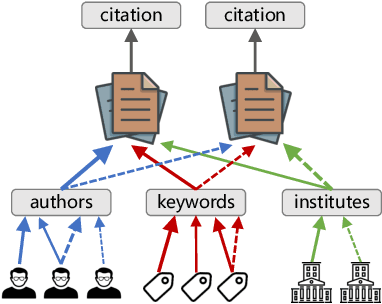

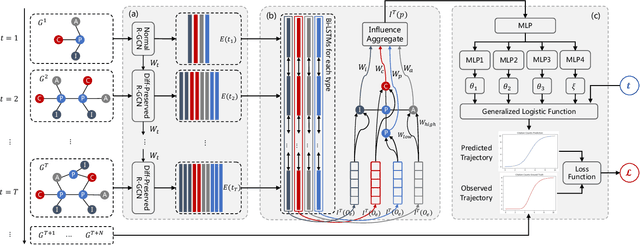

Abstract:Predicting the impact of publications in science and technology has become an important research area, which is useful in various real world scenarios such as technology investment, research direction selection, and technology policymaking. Citation trajectory prediction is one of the most popular tasks in this area. Existing approaches mainly rely on mining temporal and graph data from academic articles. Some recent methods are capable of handling cold-start prediction by aggregating metadata features of new publications. However, the implicit factors causing citations and the richer information from handling temporal and attribute features still need to be explored. In this paper, we propose CTPIR, a new citation trajectory prediction framework that is able to represent the influence (the momentum of citation) of either new or existing publications using the history information of all their attributes. Our framework is composed of three modules: difference-preserved graph embedding, fine-grained influence representation, and learning-based trajectory calculation. To test the effectiveness of our framework in more situations, we collect and construct a new temporal knowledge graph dataset from the real world, named AIPatent, which stems from global patents in the field of artificial intelligence. Experiments are conducted on both the APS academic dataset and our contributed AIPatent dataset. The results demonstrate the strengths of our approach in the citation trajectory prediction task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge