Zhichen Zeng
TSAQA: Time Series Analysis Question And Answering Benchmark
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Time series data are integral to critical applications across domains such as finance, healthcare, transportation, and environmental science. While recent work has begun to explore multi-task time series question answering (QA), current benchmarks remain limited to forecasting and anomaly detection tasks. We introduce TSAQA, a novel unified benchmark designed to broaden task coverage and evaluate diverse temporal analysis capabilities. TSAQA integrates six diverse tasks under a single framework ranging from conventional analysis, including anomaly detection and classification, to advanced analysis, such as characterization, comparison, data transformation, and temporal relationship analysis. Spanning 210k samples across 13 domains, the dataset employs diverse formats, including true-or-false (TF), multiple-choice (MC), and a novel puzzling (PZ), to comprehensively assess time series analysis. Zero-shot evaluation demonstrates that these tasks are challenging for current Large Language Models (LLMs): the best-performing commercial LLM, Gemini-2.5-Flash, achieves an average score of only 65.08. Although instruction tuning boosts open-source performance: the best-performing open-source model, LLaMA-3.1-8B, shows significant room for improvement, highlighting the complexity of temporal analysis for LLMs.
Agentic Reasoning for Large Language Models
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Reasoning is a fundamental cognitive process underlying inference, problem-solving, and decision-making. While large language models (LLMs) demonstrate strong reasoning capabilities in closed-world settings, they struggle in open-ended and dynamic environments. Agentic reasoning marks a paradigm shift by reframing LLMs as autonomous agents that plan, act, and learn through continual interaction. In this survey, we organize agentic reasoning along three complementary dimensions. First, we characterize environmental dynamics through three layers: foundational agentic reasoning, which establishes core single-agent capabilities including planning, tool use, and search in stable environments; self-evolving agentic reasoning, which studies how agents refine these capabilities through feedback, memory, and adaptation; and collective multi-agent reasoning, which extends intelligence to collaborative settings involving coordination, knowledge sharing, and shared goals. Across these layers, we distinguish in-context reasoning, which scales test-time interaction through structured orchestration, from post-training reasoning, which optimizes behaviors via reinforcement learning and supervised fine-tuning. We further review representative agentic reasoning frameworks across real-world applications and benchmarks, including science, robotics, healthcare, autonomous research, and mathematics. This survey synthesizes agentic reasoning methods into a unified roadmap bridging thought and action, and outlines open challenges and future directions, including personalization, long-horizon interaction, world modeling, scalable multi-agent training, and governance for real-world deployment.
SRT: Accelerating Reinforcement Learning via Speculative Rollout with Tree-Structured Cache
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:We present Speculative Rollout with Tree-Structured Cache (SRT), a simple, model-free approach to accelerate on-policy reinforcement learning (RL) for language models without sacrificing distributional correctness. SRT exploits the empirical similarity of rollouts for the same prompt across training steps by storing previously generated continuations in a per-prompt tree-structured cache. During generation, the current policy uses this tree as the draft model for performing speculative decoding. To keep the cache fresh and improve draft model quality, SRT updates trees online from ongoing rollouts and proactively performs run-ahead generation during idle GPU bubbles. Integrated into standard RL pipelines (\textit{e.g.}, PPO, GRPO and DAPO) and multi-turn settings, SRT consistently reduces generation and step latency and lowers per-token inference cost, achieving up to 2.08x wall-clock time speedup during rollout.
Subspace Alignment for Vision-Language Model Test-time Adaptation
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs), despite their extraordinary zero-shot capabilities, are vulnerable to distribution shifts. Test-time adaptation (TTA) emerges as a predominant strategy to adapt VLMs to unlabeled test data on the fly. However, existing TTA methods heavily rely on zero-shot predictions as pseudo-labels for self-training, which can be unreliable under distribution shifts and misguide adaptation due to two fundamental limitations. First (Modality Gap), distribution shifts induce gaps between visual and textual modalities, making cross-modal relations inaccurate. Second (Visual Nuisance), visual embeddings encode rich but task-irrelevant noise that often overwhelms task-specific semantics under distribution shifts. To address these limitations, we propose SubTTA, which aligns the semantic subspaces of both modalities to enhance zero-shot predictions to better guide the TTA process. To bridge the modality gap, SubTTA extracts the principal subspaces of both modalities and aligns the visual manifold to the textual semantic anchor by minimizing their chordal distance. To eliminate visual nuisance, SubTTA projects the aligned visual features onto the task-specific textual subspace, which filters out task-irrelevant noise by constraining visual embeddings within the valid semantic span, and standard TTA is further performed on the purified space to refine the decision boundaries. Extensive experiments on various benchmarks and VLM architectures demonstrate the effectiveness of SubTTA, yielding an average improvement of 2.24% over state-of-the-art TTA methods.
AdaFuse: Adaptive Ensemble Decoding with Test-Time Scaling for LLMs
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) exhibit complementary strengths arising from differences in pretraining data, model architectures, and decoding behaviors. Inference-time ensembling provides a practical way to combine these capabilities without retraining. However, existing ensemble approaches suffer from fundamental limitations. Most rely on fixed fusion granularity, which lacks the flexibility required for mid-generation adaptation and fails to adapt to different generation characteristics across tasks. To address these challenges, we propose AdaFuse, an adaptive ensemble decoding framework that dynamically selects semantically appropriate fusion units during generation. Rather than committing to a fixed granularity, AdaFuse adjusts fusion behavior on the fly based on the decoding context, with words serving as basic building blocks for alignment. To be specific, we introduce an uncertainty-based criterion to decide whether to apply ensembling at each decoding step. Under confident decoding states, the model continues generation directly. In less certain states, AdaFuse invokes a diversity-aware scaling strategy to explore alternative candidate continuations and inform ensemble decisions. This design establishes a synergistic interaction between adaptive ensembling and test-time scaling, where ensemble decisions guide targeted exploration, and the resulting diversity in turn strengthens ensemble quality. Experiments on open-domain question answering, arithmetic reasoning, and machine translation demonstrate that AdaFuse consistently outperforms strong ensemble baselines, achieving an average relative improvement of 6.88%. The code is available at https://github.com/CCM0111/AdaFuse.
ALERT: Zero-shot LLM Jailbreak Detection via Internal Discrepancy Amplification
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Despite rich safety alignment strategies, large language models (LLMs) remain highly susceptible to jailbreak attacks, which compromise safety guardrails and pose serious security risks. Existing detection methods mainly detect jailbreak status relying on jailbreak templates present in the training data. However, few studies address the more realistic and challenging zero-shot jailbreak detection setting, where no jailbreak templates are available during training. This setting better reflects real-world scenarios where new attacks continually emerge and evolve. To address this challenge, we propose a layer-wise, module-wise, and token-wise amplification framework that progressively magnifies internal feature discrepancies between benign and jailbreak prompts. We uncover safety-relevant layers, identify specific modules that inherently encode zero-shot discriminative signals, and localize informative safety tokens. Building upon these insights, we introduce ALERT (Amplification-based Jailbreak Detector), an efficient and effective zero-shot jailbreak detector that introduces two independent yet complementary classifiers on amplified representations. Extensive experiments on three safety benchmarks demonstrate that ALERT achieves consistently strong zero-shot detection performance. Specifically, (i) across all datasets and attack strategies, ALERT reliably ranks among the top two methods, and (ii) it outperforms the second-best baseline by at least 10% in average Accuracy and F1-score, and sometimes by up to 40%.
Local Linear Attention: An Optimal Interpolation of Linear and Softmax Attention For Test-Time Regression
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Transformer architectures have achieved remarkable success in various domains. While efficient alternatives to Softmax Attention have been widely studied, the search for more expressive mechanisms grounded in theoretical insight-even at greater computational cost-has been relatively underexplored. In this work, we bridge this gap by proposing Local Linear Attention (LLA), a novel attention mechanism derived from nonparametric statistics through the lens of test-time regression. First, we show that LLA offers theoretical advantages over Linear and Softmax Attention for associative memory via a bias-variance trade-off analysis. Next, we address its computational challenges and propose two memory-efficient primitives to tackle the $\Theta(n^2 d)$ and $\Theta(n d^2)$ complexity. We then introduce FlashLLA, a hardware-efficient, blockwise algorithm that enables scalable and parallel computation on modern accelerators. In addition, we implement and profile a customized inference kernel that significantly reduces memory overheads. Finally, we empirically validate the advantages and limitations of LLA on test-time regression, in-context regression, associative recall and state tracking tasks. Experiment results demonstrate that LLA effectively adapts to non-stationarity, outperforming strong baselines in test-time training and in-context learning, and exhibiting promising evidence for its scalability and applicability in large-scale models. Code is available at https://github.com/Yifei-Zuo/Flash-LLA.
Flow Matching Meets Biology and Life Science: A Survey
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Over the past decade, advances in generative modeling, such as generative adversarial networks, masked autoencoders, and diffusion models, have significantly transformed biological research and discovery, enabling breakthroughs in molecule design, protein generation, drug discovery, and beyond. At the same time, biological applications have served as valuable testbeds for evaluating the capabilities of generative models. Recently, flow matching has emerged as a powerful and efficient alternative to diffusion-based generative modeling, with growing interest in its application to problems in biology and life sciences. This paper presents the first comprehensive survey of recent developments in flow matching and its applications in biological domains. We begin by systematically reviewing the foundations and variants of flow matching, and then categorize its applications into three major areas: biological sequence modeling, molecule generation and design, and peptide and protein generation. For each, we provide an in-depth review of recent progress. We also summarize commonly used datasets and software tools, and conclude with a discussion of potential future directions. The corresponding curated resources are available at https://github.com/Violet24K/Awesome-Flow-Matching-Meets-Biology.
PLANETALIGN: A Comprehensive Python Library for Benchmarking Network Alignment
May 27, 2025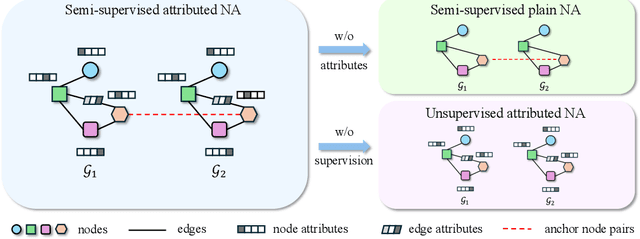
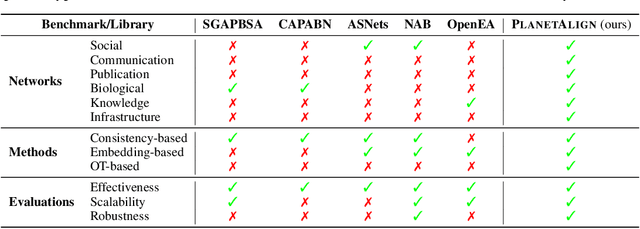
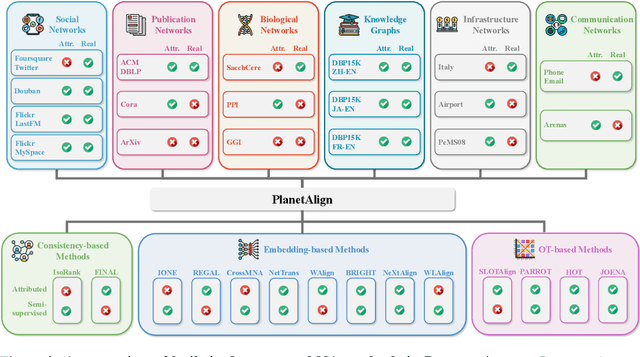
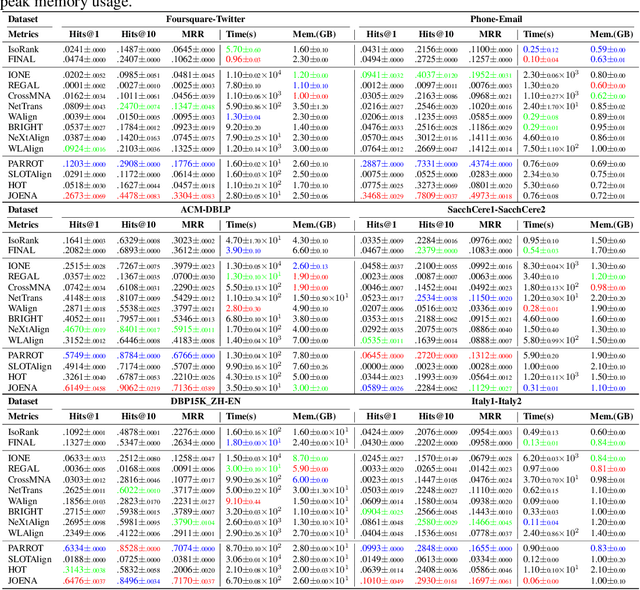
Abstract:Network alignment (NA) aims to identify node correspondence across different networks and serves as a critical cornerstone behind various downstream multi-network learning tasks. Despite growing research in NA, there lacks a comprehensive library that facilitates the systematic development and benchmarking of NA methods. In this work, we introduce PLANETALIGN, a comprehensive Python library for network alignment that features a rich collection of built-in datasets, methods, and evaluation pipelines with easy-to-use APIs. Specifically, PLANETALIGN integrates 18 datasets and 14 NA methods with extensible APIs for easy use and development of NA methods. Our standardized evaluation pipeline encompasses a wide range of metrics, enabling a systematic assessment of the effectiveness, scalability, and robustness of NA methods. Through extensive comparative studies, we reveal practical insights into the strengths and limitations of existing NA methods. We hope that PLANETALIGN can foster a deeper understanding of the NA problem and facilitate the development and benchmarking of more effective, scalable, and robust methods in the future. The source code of PLANETALIGN is available at https://github.com/yq-leo/PlanetAlign.
Pave Your Own Path: Graph Gradual Domain Adaptation on Fused Gromov-Wasserstein Geodesics
May 19, 2025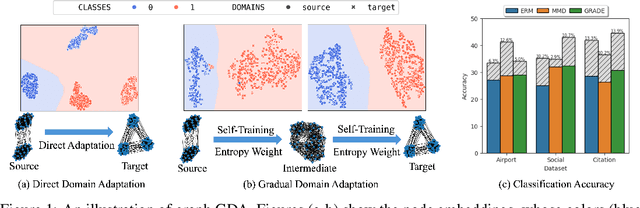
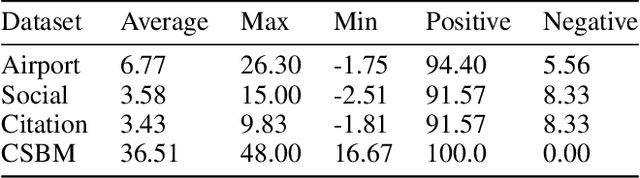
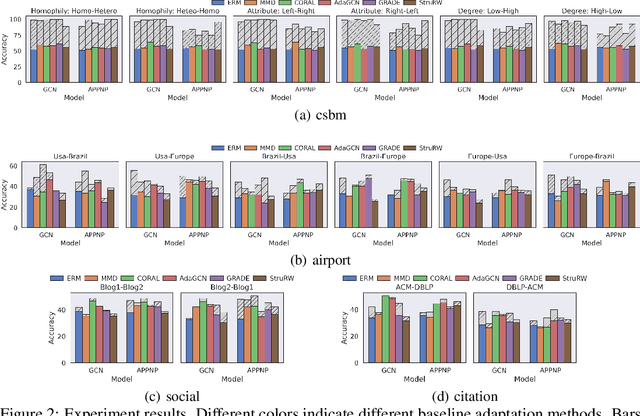
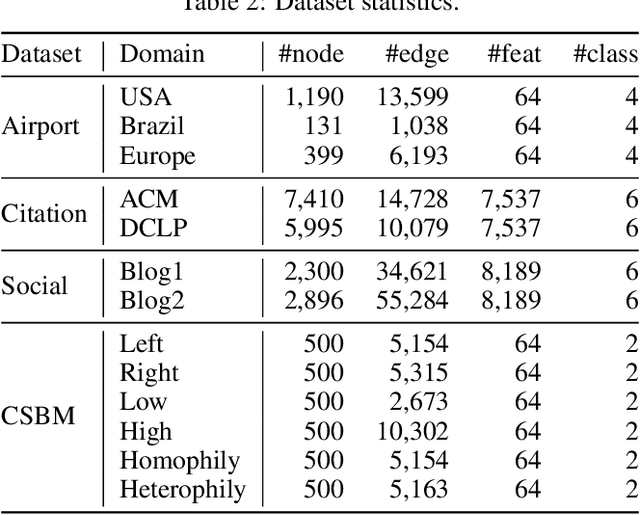
Abstract:Graph neural networks, despite their impressive performance, are highly vulnerable to distribution shifts on graphs. Existing graph domain adaptation (graph DA) methods often implicitly assume a \textit{mild} shift between source and target graphs, limiting their applicability to real-world scenarios with \textit{large} shifts. Gradual domain adaptation (GDA) has emerged as a promising approach for addressing large shifts by gradually adapting the source model to the target domain via a path of unlabeled intermediate domains. Existing GDA methods exclusively focus on independent and identically distributed (IID) data with a predefined path, leaving their extension to \textit{non-IID graphs without a given path} an open challenge. To bridge this gap, we present Gadget, the first GDA framework for non-IID graph data. First (\textit{theoretical foundation}), the Fused Gromov-Wasserstein (FGW) distance is adopted as the domain discrepancy for non-IID graphs, based on which, we derive an error bound revealing that the target domain error is proportional to the length of the path. Second (\textit{optimal path}), guided by the error bound, we identify the FGW geodesic as the optimal path, which can be efficiently generated by our proposed algorithm. The generated path can be seamlessly integrated with existing graph DA methods to handle large shifts on graphs, improving state-of-the-art graph DA methods by up to 6.8\% in node classification accuracy on real-world datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge