Xianfeng Tang
How Far Are LLMs from Professional Poker Players? Revisiting Game-Theoretic Reasoning with Agentic Tool Use
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly applied in high-stakes domains, their ability to reason strategically under uncertainty becomes critical. Poker provides a rigorous testbed, requiring not only strong actions but also principled, game-theoretic reasoning. In this paper, we conduct a systematic study of LLMs in multiple realistic poker tasks, evaluating both gameplay outcomes and reasoning traces. Our analysis reveals LLMs fail to compete against traditional algorithms and identifies three recurring flaws: reliance on heuristics, factual misunderstandings, and a "knowing-doing" gap where actions diverge from reasoning. An initial attempt with behavior cloning and step-level reinforcement learning improves reasoning style but remains insufficient for accurate game-theoretic play. Motivated by these limitations, we propose ToolPoker, a tool-integrated reasoning framework that combines external solvers for GTO-consistent actions with more precise professional-style explanations. Experiments demonstrate that ToolPoker achieves state-of-the-art gameplay while producing reasoning traces that closely reflect game-theoretic principles.
Position: Agentic Evolution is the Path to Evolving LLMs
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) move from curated training sets into open-ended real-world environments, a fundamental limitation emerges: static training cannot keep pace with continual deployment environment change. Scaling training-time and inference-time compute improves static capability but does not close this train-deploy gap. We argue that addressing this limitation requires a new scaling axis-evolution. Existing deployment-time adaptation methods, whether parametric fine-tuning or heuristic memory accumulation, lack the strategic agency needed to diagnose failures and produce durable improvements. Our position is that agentic evolution represents the inevitable future of LLM adaptation, elevating evolution itself from a fixed pipeline to an autonomous evolver agent. We instantiate this vision in a general framework, A-Evolve, which treats deployment-time improvement as a deliberate, goal-directed optimization process over persistent system state. We further propose the evolution-scaling hypothesis: the capacity for adaptation scales with the compute allocated to evolution, positioning agentic evolution as a scalable path toward sustained, open-ended adaptation in the real world.
Trajectory2Task: Training Robust Tool-Calling Agents with Synthesized Yet Verifiable Data for Complex User Intents
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Tool-calling agents are increasingly deployed in real-world customer-facing workflows. Yet most studies on tool-calling agents focus on idealized settings with general, fixed, and well-specified tasks. In real-world applications, user requests are often (1) ambiguous, (2) changing over time, or (3) infeasible due to policy constraints, and training and evaluation data that cover these diverse, complex interaction patterns remain under-represented. To bridge the gap, we present Trajectory2Task, a verifiable data generation pipeline for studying tool use at scale under three realistic user scenarios: ambiguous intent, changing intent, and infeasible intents. The pipeline first conducts multi-turn exploration to produce valid tool-call trajectories. It then converts these trajectories into user-facing tasks with controlled intent adaptations. This process yields verifiable task that support closed-loop evaluation and training. We benchmark seven state-of-the-art LLMs on the generated complex user scenario tasks and observe frequent failures. Finally, using successful trajectories obtained from task rollouts, we fine-tune lightweight LLMs and find consistent improvements across all three conditions, along with better generalization to unseen tool-use domains, indicating stronger general tool-calling ability.
Agentic Reasoning for Large Language Models
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Reasoning is a fundamental cognitive process underlying inference, problem-solving, and decision-making. While large language models (LLMs) demonstrate strong reasoning capabilities in closed-world settings, they struggle in open-ended and dynamic environments. Agentic reasoning marks a paradigm shift by reframing LLMs as autonomous agents that plan, act, and learn through continual interaction. In this survey, we organize agentic reasoning along three complementary dimensions. First, we characterize environmental dynamics through three layers: foundational agentic reasoning, which establishes core single-agent capabilities including planning, tool use, and search in stable environments; self-evolving agentic reasoning, which studies how agents refine these capabilities through feedback, memory, and adaptation; and collective multi-agent reasoning, which extends intelligence to collaborative settings involving coordination, knowledge sharing, and shared goals. Across these layers, we distinguish in-context reasoning, which scales test-time interaction through structured orchestration, from post-training reasoning, which optimizes behaviors via reinforcement learning and supervised fine-tuning. We further review representative agentic reasoning frameworks across real-world applications and benchmarks, including science, robotics, healthcare, autonomous research, and mathematics. This survey synthesizes agentic reasoning methods into a unified roadmap bridging thought and action, and outlines open challenges and future directions, including personalization, long-horizon interaction, world modeling, scalable multi-agent training, and governance for real-world deployment.
All You Need Are Random Visual Tokens? Demystifying Token Pruning in VLLMs
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Vision Large Language Models (VLLMs) incur high computational costs due to their reliance on hundreds of visual tokens to represent images. While token pruning offers a promising solution for accelerating inference, this paper, however, identifies a key observation: in deeper layers (e.g., beyond the 20th), existing training-free pruning methods perform no better than random pruning. We hypothesize that this degradation is caused by "vanishing token information", where visual tokens progressively lose their salience with increasing network depth. To validate this hypothesis, we quantify a token's information content by measuring the change in the model output probabilities upon its removal. Using this proposed metric, our analysis of the information of visual tokens across layers reveals three key findings: (1) As layers deepen, the information of visual tokens gradually becomes uniform and eventually vanishes at an intermediate layer, which we term as "information horizon", beyond which the visual tokens become redundant; (2) The position of this horizon is not static; it extends deeper for visually intensive tasks, such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR), compared to more general tasks like Visual Question Answering (VQA); (3) This horizon is also strongly correlated with model capacity, as stronger VLLMs (e.g., Qwen2.5-VL) employ deeper visual tokens than weaker models (e.g., LLaVA-1.5). Based on our findings, we show that simple random pruning in deep layers efficiently balances performance and efficiency. Moreover, integrating random pruning consistently enhances existing methods. Using DivPrune with random pruning achieves state-of-the-art results, maintaining 96.9% of Qwen-2.5-VL-7B performance while pruning 50% of visual tokens. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/YahongWang1/Information-Horizon.
MedVLSynther: Synthesizing High-Quality Visual Question Answering from Medical Documents with Generator-Verifier LMMs
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) are increasingly capable of answering medical questions that require joint reasoning over images and text, yet training general medical VQA systems is impeded by the lack of large, openly usable, high-quality corpora. We present MedVLSynther, a rubric-guided generator-verifier framework that synthesizes high-quality multiple-choice VQA items directly from open biomedical literature by conditioning on figures, captions, and in-text references. The generator produces self-contained stems and parallel, mutually exclusive options under a machine-checkable JSON schema; a multi-stage verifier enforces essential gates (self-containment, single correct answer, clinical validity, image-text consistency), awards fine-grained positive points, and penalizes common failure modes before acceptance. Applying this pipeline to PubMed Central yields MedSynVQA: 13,087 audited questions over 14,803 images spanning 13 imaging modalities and 28 anatomical regions. Training open-weight LMMs with reinforcement learning using verifiable rewards improves accuracy across six medical VQA benchmarks, achieving averages of 55.85 (3B) and 58.15 (7B), with up to 77.57 on VQA-RAD and 67.76 on PathVQA, outperforming strong medical LMMs. A Ablations verify that both generation and verification are necessary and that more verified data consistently helps, and a targeted contamination analysis detects no leakage from evaluation suites. By operating entirely on open literature and open-weight models, MedVLSynther offers an auditable, reproducible, and privacy-preserving path to scalable medical VQA training data.
TRAJECT-Bench:A Trajectory-Aware Benchmark for Evaluating Agentic Tool Use
Oct 06, 2025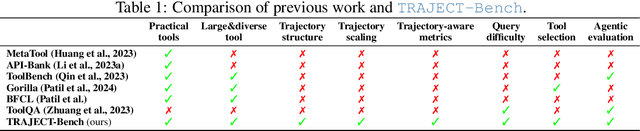

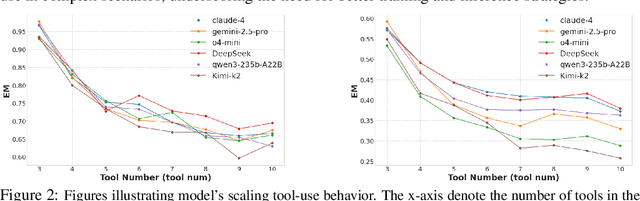
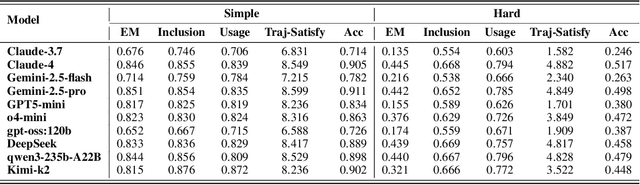
Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-based agents increasingly rely on tool use to complete real-world tasks. While existing works evaluate the LLMs' tool use capability, they largely focus on the final answers yet overlook the detailed tool usage trajectory, i.e., whether tools are selected, parameterized, and ordered correctly. We introduce TRAJECT-Bench, a trajectory-aware benchmark to comprehensively evaluate LLMs' tool use capability through diverse tasks with fine-grained evaluation metrics. TRAJECT-Bench pairs high-fidelity, executable tools across practical domains with tasks grounded in production-style APIs, and synthesizes trajectories that vary in breadth (parallel calls) and depth (interdependent chains). Besides final accuracy, TRAJECT-Bench also reports trajectory-level diagnostics, including tool selection and argument correctness, and dependency/order satisfaction. Analyses reveal failure modes such as similar tool confusion and parameter-blind selection, and scaling behavior with tool diversity and trajectory length where the bottleneck of transiting from short to mid-length trajectories is revealed, offering actionable guidance for LLMs' tool use.
Can Large Language Models Adequately Perform Symbolic Reasoning Over Time Series?
Aug 05, 2025Abstract:Uncovering hidden symbolic laws from time series data, as an aspiration dating back to Kepler's discovery of planetary motion, remains a core challenge in scientific discovery and artificial intelligence. While Large Language Models show promise in structured reasoning tasks, their ability to infer interpretable, context-aligned symbolic structures from time series data is still underexplored. To systematically evaluate this capability, we introduce SymbolBench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to assess symbolic reasoning over real-world time series across three tasks: multivariate symbolic regression, Boolean network inference, and causal discovery. Unlike prior efforts limited to simple algebraic equations, SymbolBench spans a diverse set of symbolic forms with varying complexity. We further propose a unified framework that integrates LLMs with genetic programming to form a closed-loop symbolic reasoning system, where LLMs act both as predictors and evaluators. Our empirical results reveal key strengths and limitations of current models, highlighting the importance of combining domain knowledge, context alignment, and reasoning structure to improve LLMs in automated scientific discovery.
Bradley-Terry and Multi-Objective Reward Modeling Are Complementary
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Reward models trained on human preference data have demonstrated strong effectiveness in aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with human intent under the framework of Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). However, RLHF remains vulnerable to reward hacking, where the policy exploits imperfections in the reward function rather than genuinely learning the intended behavior. Although significant efforts have been made to mitigate reward hacking, they predominantly focus on and evaluate in-distribution scenarios, where the training and testing data for the reward model share the same distribution. In this paper, we empirically show that state-of-the-art methods struggle in more challenging out-of-distribution (OOD) settings. We further demonstrate that incorporating fine-grained multi-attribute scores helps address this challenge. However, the limited availability of high-quality data often leads to weak performance of multi-objective reward functions, which can negatively impact overall performance and become the bottleneck. To address this issue, we propose a unified reward modeling framework that jointly trains Bradley--Terry (BT) single-objective and multi-objective regression-based reward functions using a shared embedding space. We theoretically establish a connection between the BT loss and the regression objective and highlight their complementary benefits. Specifically, the regression task enhances the single-objective reward function's ability to mitigate reward hacking in challenging OOD settings, while BT-based training improves the scoring capability of the multi-objective reward function, enabling a 7B model to outperform a 70B baseline. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our framework significantly improves both the robustness and the scoring performance of reward models.
RRO: LLM Agent Optimization Through Rising Reward Trajectories
May 27, 2025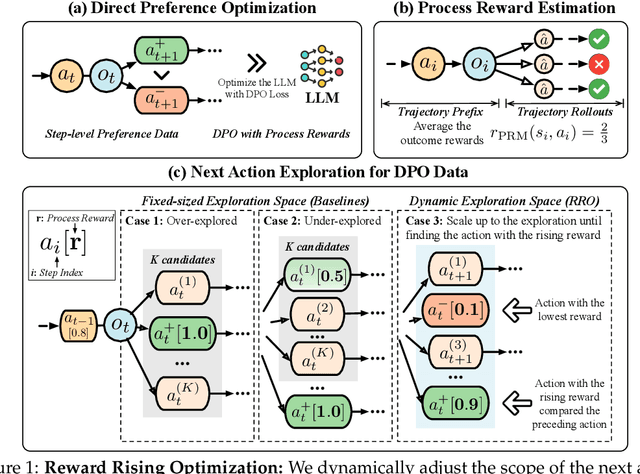
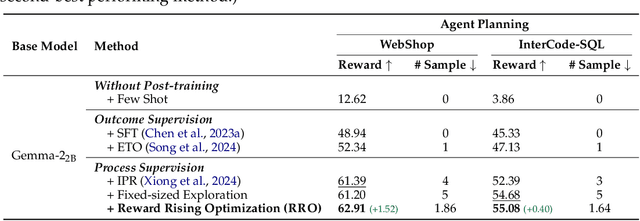
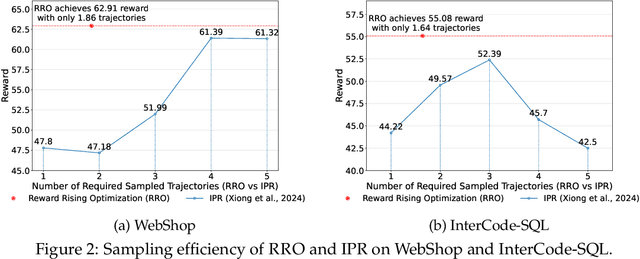
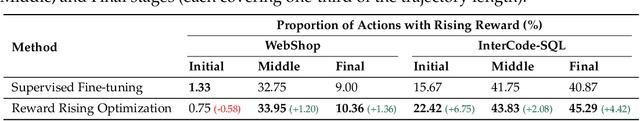
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have exhibited extraordinary performance in a variety of tasks while it remains challenging for them to solve complex multi-step tasks as agents. In practice, agents sensitive to the outcome of certain key steps which makes them likely to fail the task because of a subtle mistake in the planning trajectory. Recent approaches resort to calibrating the reasoning process through reinforcement learning. They reward or penalize every reasoning step with process supervision, as known as Process Reward Models (PRMs). However, PRMs are difficult and costly to scale up with a large number of next action candidates since they require extensive computations to acquire the training data through the per-step trajectory exploration. To mitigate this issue, we focus on the relative reward trend across successive reasoning steps and propose maintaining an increasing reward in the collected trajectories for process supervision, which we term Reward Rising Optimization (RRO). Specifically, we incrementally augment the process supervision until identifying a step exhibiting positive reward differentials, i.e. rising rewards, relative to its preceding iteration. This method dynamically expands the search space for the next action candidates, efficiently capturing high-quality data. We provide mathematical groundings and empirical results on the WebShop and InterCode-SQL benchmarks, showing that our proposed RRO achieves superior performance while requiring much less exploration cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge