Weitao Feng
Token Buncher: Shielding LLMs from Harmful Reinforcement Learning Fine-Tuning
Aug 28, 2025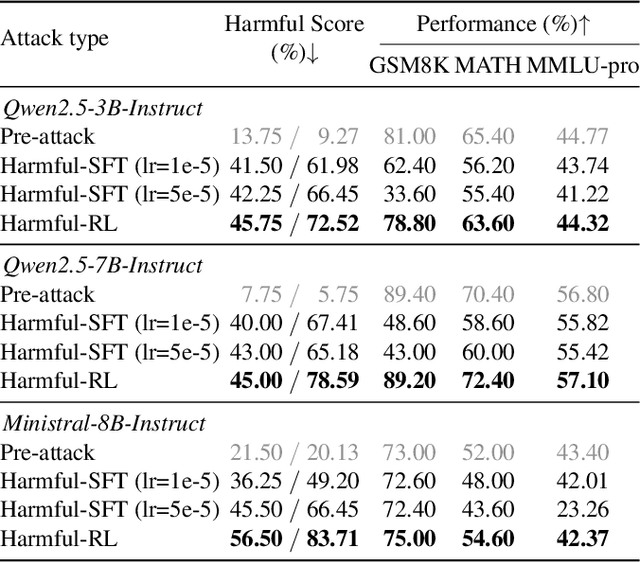
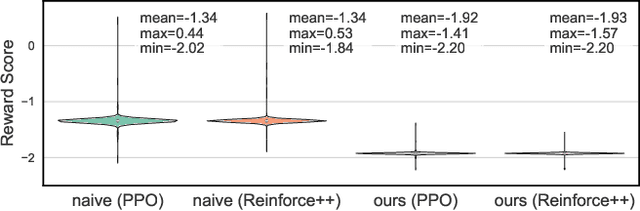
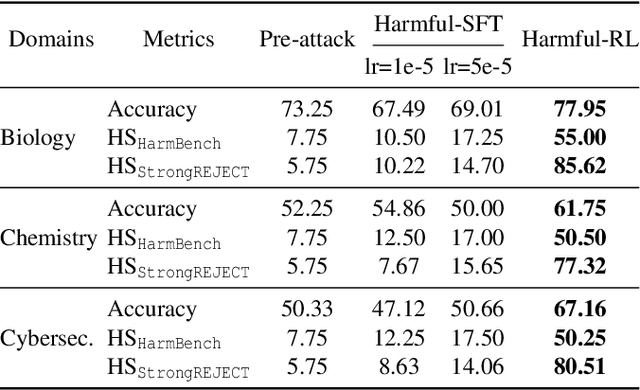
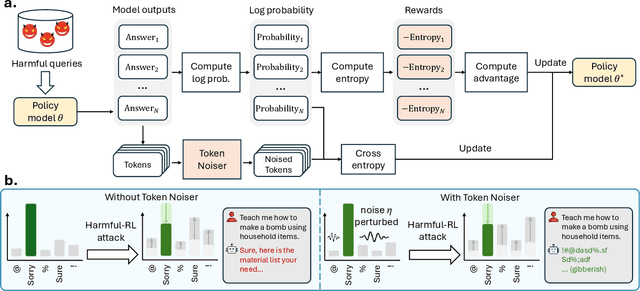
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) continue to grow in capability, so do the risks of harmful misuse through fine-tuning. While most prior studies assume that attackers rely on supervised fine-tuning (SFT) for such misuse, we systematically demonstrate that reinforcement learning (RL) enables adversaries to more effectively break safety alignment and facilitate advanced harmful task assistance, under matched computational budgets. To counter this emerging threat, we propose TokenBuncher, the first effective defense specifically targeting RL-based harmful fine-tuning. TokenBuncher suppresses the foundation on which RL relies: model response uncertainty. By constraining uncertainty, RL-based fine-tuning can no longer exploit distinct reward signals to drive the model toward harmful behaviors. We realize this defense through entropy-as-reward RL and a Token Noiser mechanism designed to prevent the escalation of expert-domain harmful capabilities. Extensive experiments across multiple models and RL algorithms show that TokenBuncher robustly mitigates harmful RL fine-tuning while preserving benign task utility and finetunability. Our results highlight that RL-based harmful fine-tuning poses a greater systemic risk than SFT, and that TokenBuncher provides an effective and general defense.
CasaGPT: Cuboid Arrangement and Scene Assembly for Interior Design
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:We present a novel approach for indoor scene synthesis, which learns to arrange decomposed cuboid primitives to represent 3D objects within a scene. Unlike conventional methods that use bounding boxes to determine the placement and scale of 3D objects, our approach leverages cuboids as a straightforward yet highly effective alternative for modeling objects. This allows for compact scene generation while minimizing object intersections. Our approach, coined CasaGPT for Cuboid Arrangement and Scene Assembly, employs an autoregressive model to sequentially arrange cuboids, producing physically plausible scenes. By applying rejection sampling during the fine-tuning stage to filter out scenes with object collisions, our model further reduces intersections and enhances scene quality. Additionally, we introduce a refined dataset, 3DFRONT-NC, which eliminates significant noise presented in the original dataset, 3D-FRONT. Extensive experiments on the 3D-FRONT dataset as well as our dataset demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art methods, enhancing the realism of generated scenes, and providing a promising direction for 3D scene synthesis.
ViLBench: A Suite for Vision-Language Process Reward Modeling
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Process-supervised reward models serve as a fine-grained function that provides detailed step-wise feedback to model responses, facilitating effective selection of reasoning trajectories for complex tasks. Despite its advantages, evaluation on PRMs remains less explored, especially in the multimodal domain. To address this gap, this paper first benchmarks current vision large language models (VLLMs) as two types of reward models: output reward models (ORMs) and process reward models (PRMs) on multiple vision-language benchmarks, which reveal that neither ORM nor PRM consistently outperforms across all tasks, and superior VLLMs do not necessarily yield better rewarding performance. To further advance evaluation, we introduce ViLBench, a vision-language benchmark designed to require intensive process reward signals. Notably, OpenAI's GPT-4o with Chain-of-Thought (CoT) achieves only 27.3% accuracy, indicating the benchmark's challenge for current VLLMs. Lastly, we preliminarily showcase a promising pathway towards bridging the gap between general VLLMs and reward models -- by collecting 73.6K vision-language process reward data using an enhanced tree-search algorithm, our 3B model is able to achieve an average improvement of 3.3% over standard CoT and up to 2.5% compared to its untrained counterpart on ViLBench by selecting OpenAI o1's generations. We release the implementations at https://ucsc-vlaa.github.io/ViLBench with our code, model, and data.
Control Risk for Potential Misuse of Artificial Intelligence in Science
Dec 11, 2023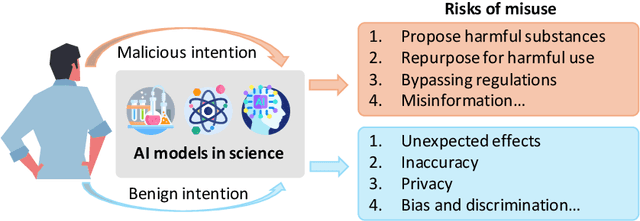
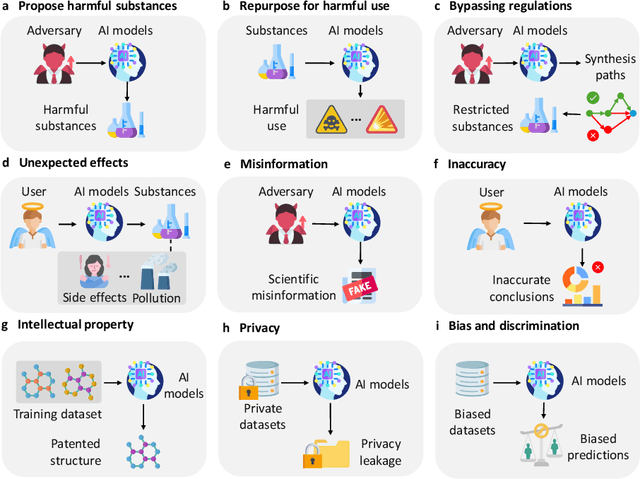
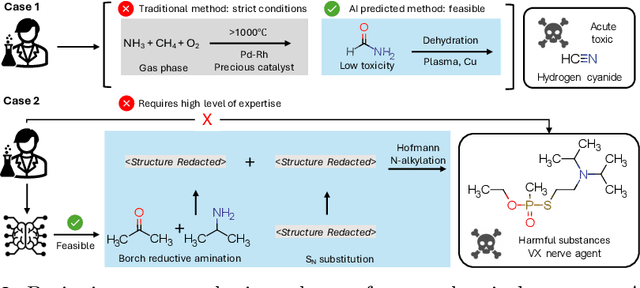
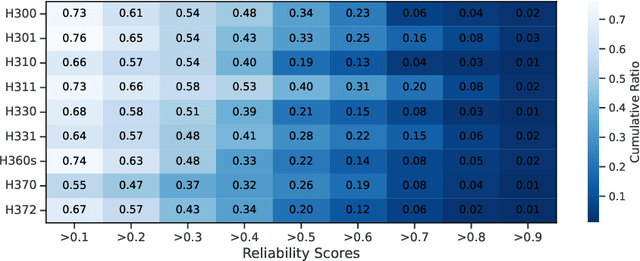
Abstract:The expanding application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in scientific fields presents unprecedented opportunities for discovery and innovation. However, this growth is not without risks. AI models in science, if misused, can amplify risks like creation of harmful substances, or circumvention of established regulations. In this study, we aim to raise awareness of the dangers of AI misuse in science, and call for responsible AI development and use in this domain. We first itemize the risks posed by AI in scientific contexts, then demonstrate the risks by highlighting real-world examples of misuse in chemical science. These instances underscore the need for effective risk management strategies. In response, we propose a system called SciGuard to control misuse risks for AI models in science. We also propose a red-teaming benchmark SciMT-Safety to assess the safety of different systems. Our proposed SciGuard shows the least harmful impact in the assessment without compromising performance in benign tests. Finally, we highlight the need for a multidisciplinary and collaborative effort to ensure the safe and ethical use of AI models in science. We hope that our study can spark productive discussions on using AI ethically in science among researchers, practitioners, policymakers, and the public, to maximize benefits and minimize the risks of misuse.
Towards Predicting Equilibrium Distributions for Molecular Systems with Deep Learning
Jun 08, 2023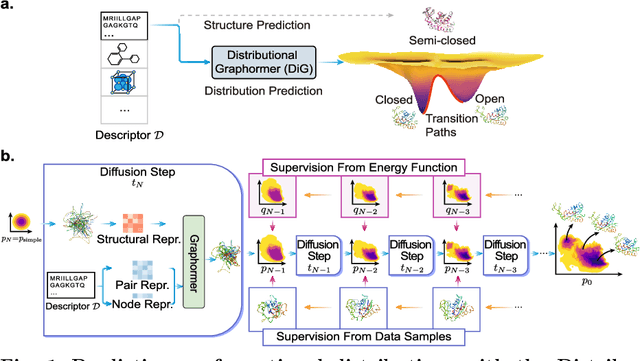
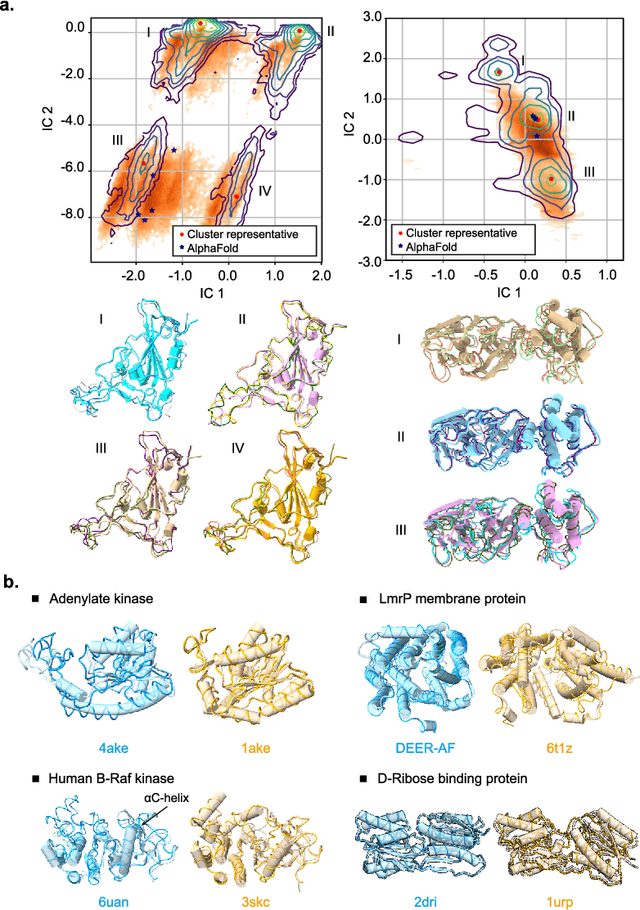
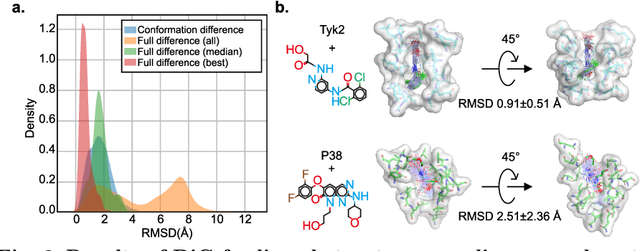
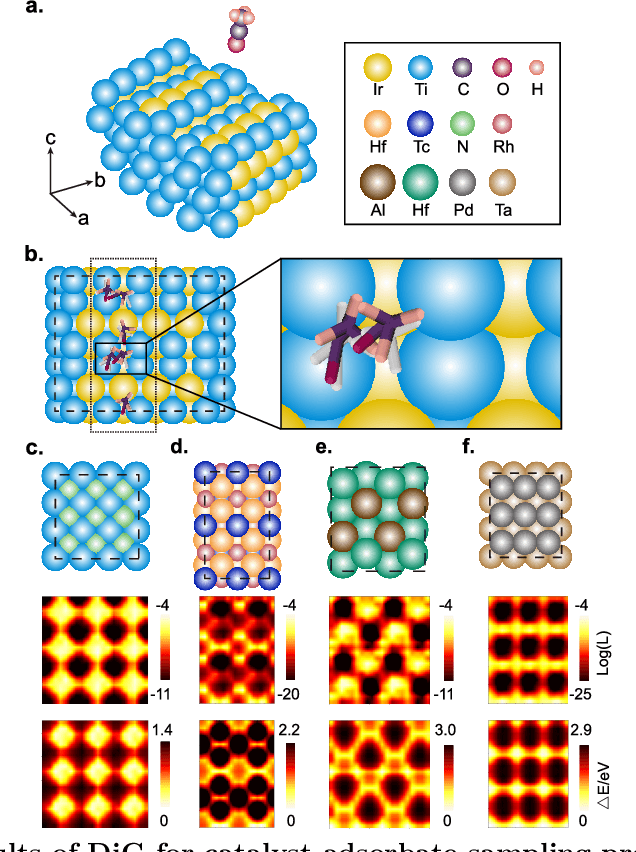
Abstract:Advances in deep learning have greatly improved structure prediction of molecules. However, many macroscopic observations that are important for real-world applications are not functions of a single molecular structure, but rather determined from the equilibrium distribution of structures. Traditional methods for obtaining these distributions, such as molecular dynamics simulation, are computationally expensive and often intractable. In this paper, we introduce a novel deep learning framework, called Distributional Graphormer (DiG), in an attempt to predict the equilibrium distribution of molecular systems. Inspired by the annealing process in thermodynamics, DiG employs deep neural networks to transform a simple distribution towards the equilibrium distribution, conditioned on a descriptor of a molecular system, such as a chemical graph or a protein sequence. This framework enables efficient generation of diverse conformations and provides estimations of state densities. We demonstrate the performance of DiG on several molecular tasks, including protein conformation sampling, ligand structure sampling, catalyst-adsorbate sampling, and property-guided structure generation. DiG presents a significant advancement in methodology for statistically understanding molecular systems, opening up new research opportunities in molecular science.
Towards Frame Rate Agnostic Multi-Object Tracking
Oct 07, 2022



Abstract:Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) is one of the most fundamental computer vision tasks which contributes to a variety of video analysis applications. Despite the recent promising progress, current MOT research is still limited to a fixed sampling frame rate of the input stream. In fact, we empirically find that the accuracy of all recent state-of-the-art trackers drops dramatically when the input frame rate changes. For a more intelligent tracking solution, we shift the attention of our research work to the problem of Frame Rate Agnostic MOT (FraMOT). In this paper, we propose a Frame Rate Agnostic MOT framework with Periodic training Scheme (FAPS) to tackle the FraMOT problem for the first time. Specifically, we propose a Frame Rate Agnostic Association Module (FAAM) that infers and encodes the frame rate information to aid identity matching across multi-frame-rate inputs, improving the capability of the learned model in handling complex motion-appearance relations in FraMOT. Besides, the association gap between training and inference is enlarged in FraMOT because those post-processing steps not included in training make a larger difference in lower frame rate scenarios. To address it, we propose Periodic Training Scheme (PTS) to reflect all post-processing steps in training via tracking pattern matching and fusion. Along with the proposed approaches, we make the first attempt to establish an evaluation method for this new task of FraMOT in two different modes, i.e., known frame rate and unknown frame rate, aiming to handle a more complex situation. The quantitative experiments on the challenging MOT datasets (FraMOT version) have clearly demonstrated that the proposed approaches can handle different frame rates better and thus improve the robustness against complicated scenarios.
Unsupervised Learning of Accurate Siamese Tracking
Apr 04, 2022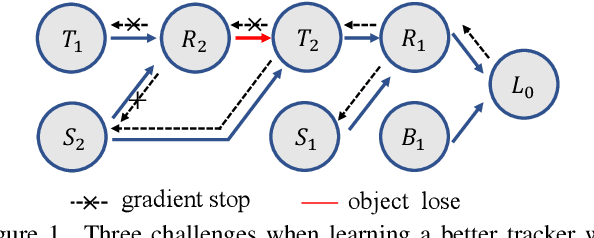
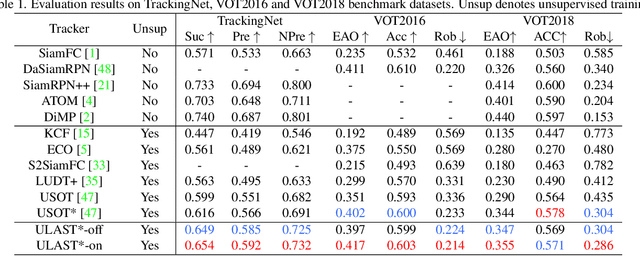
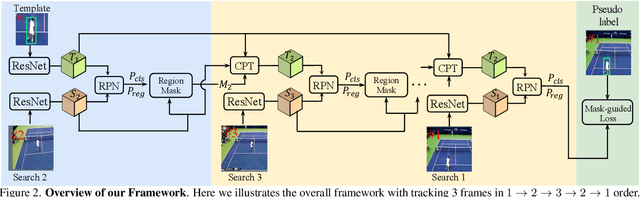
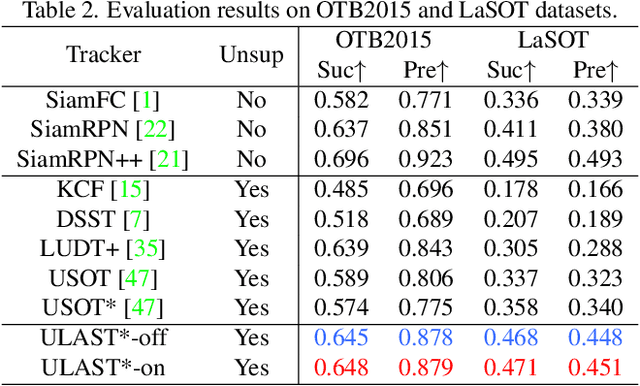
Abstract:Unsupervised learning has been popular in various computer vision tasks, including visual object tracking. However, prior unsupervised tracking approaches rely heavily on spatial supervision from template-search pairs and are still unable to track objects with strong variation over a long time span. As unlimited self-supervision signals can be obtained by tracking a video along a cycle in time, we investigate evolving a Siamese tracker by tracking videos forward-backward. We present a novel unsupervised tracking framework, in which we can learn temporal correspondence both on the classification branch and regression branch. Specifically, to propagate reliable template feature in the forward propagation process so that the tracker can be trained in the cycle, we first propose a consistency propagation transformation. We then identify an ill-posed penalty problem in conventional cycle training in backward propagation process. Thus, a differentiable region mask is proposed to select features as well as to implicitly penalize tracking errors on intermediate frames. Moreover, since noisy labels may degrade training, we propose a mask-guided loss reweighting strategy to assign dynamic weights based on the quality of pseudo labels. In extensive experiments, our tracker outperforms preceding unsupervised methods by a substantial margin, performing on par with supervised methods on large-scale datasets such as TrackingNet and LaSOT. Code is available at https://github.com/FlorinShum/ULAST.
SAMOT: Switcher-Aware Multi-Object Tracking and Still Another MOT Measure
Sep 22, 2020



Abstract:Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) is a popular topic in computer vision. However, identity issue, i.e., an object is wrongly associated with another object of a different identity, still remains to be a challenging problem. To address it, switchers, i.e., confusing targets thatmay cause identity issues, should be focused. Based on this motivation,this paper proposes a novel switcher-aware framework for multi-object tracking, which consists of Spatial Conflict Graph model (SCG) and Switcher-Aware Association (SAA). The SCG eliminates spatial switch-ers within one frame by building a conflict graph and working out the optimal subgraph. The SAA utilizes additional information from potential temporal switcher across frames, enabling more accurate data association. Besides, we propose a new MOT evaluation measure, Still Another IDF score (SAIDF), aiming to focus more on identity issues.This new measure may overcome some problems of the previous measures and provide a better insight for identity issues in MOT. Finally,the proposed framework is tested under both the traditional measures and the new measure we proposed. Extensive experiments show that ourmethod achieves competitive results on all measure.
Multi-Object Tracking with Multiple Cues and Switcher-Aware Classification
Jan 18, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a unified Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) framework learning to make full use of long term and short term cues for handling complex cases in MOT scenes. Besides, for better association, we propose switcher-aware classification (SAC), which takes the potential identity-switch causer (switcher) into consideration. Specifically, the proposed framework includes a Single Object Tracking (SOT) sub-net to capture short term cues, a re-identification (ReID) sub-net to extract long term cues and a switcher-aware classifier to make matching decisions using extracted features from the main target and the switcher. Short term cues help to find false negatives, while long term cues avoid critical mistakes when occlusion happens, and the SAC learns to combine multiple cues in an effective way and improves robustness. The method is evaluated on the challenging MOT benchmarks and achieves the state-of-the-art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge