Zhiyuan Li
SAIL: Self-Amplified Iterative Learning for Diffusion Model Alignment with Minimal Human Feedback
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Aligning diffusion models with human preferences remains challenging, particularly when reward models are unavailable or impractical to obtain, and collecting large-scale preference datasets is prohibitively expensive. \textit{This raises a fundamental question: can we achieve effective alignment using only minimal human feedback, without auxiliary reward models, by unlocking the latent capabilities within diffusion models themselves?} In this paper, we propose \textbf{SAIL} (\textbf{S}elf-\textbf{A}mplified \textbf{I}terative \textbf{L}earning), a novel framework that enables diffusion models to act as their own teachers through iterative self-improvement. Starting from a minimal seed set of human-annotated preference pairs, SAIL operates in a closed-loop manner where the model progressively generates diverse samples, self-annotates preferences based on its evolving understanding, and refines itself using this self-augmented dataset. To ensure robust learning and prevent catastrophic forgetting, we introduce a ranked preference mixup strategy that carefully balances exploration with adherence to initial human priors. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SAIL consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across multiple benchmarks while using merely 6\% of the preference data required by existing approaches, revealing that diffusion models possess remarkable self-improvement capabilities that, when properly harnessed, can effectively replace both large-scale human annotation and external reward models.
Information-Theoretic Multi-Model Fusion for Target-Oriented Adaptive Sampling in Materials Design
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Target-oriented discovery under limited evaluation budgets requires making reliable progress in high-dimensional, heterogeneous design spaces where each new measurement is costly, whether experimental or high-fidelity simulation. We present an information-theoretic framework for target-oriented adaptive sampling that reframes optimization as trajectory discovery: instead of approximating the full response surface, the method maintains and refines a low-entropy information state that concentrates search on target-relevant directions. The approach couples data, model beliefs, and physics/structure priors through dimension-aware information budgeting, adaptive bootstrapped distillation over a heterogeneous surrogate reservoir, and structure-aware candidate manifold analysis with Kalman-inspired multi-model fusion to balance consensus-driven exploitation and disagreement-driven exploration. Evaluated under a single unified protocol without dataset-specific tuning, the framework improves sample efficiency and reliability across 14 single- and multi-objective materials design tasks spanning candidate pools from $600$ to $4 \times 10^6$ and feature dimensions from $10$ to $10^3$, typically reaching top-performing regions within 100 evaluations. Complementary 20-dimensional synthetic benchmarks (Ackley, Rastrigin, Schwefel) further demonstrate robustness to rugged and multimodal landscapes.
Sparsely Supervised Diffusion
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Diffusion models have shown remarkable success across a wide range of generative tasks. However, they often suffer from spatially inconsistent generation, arguably due to the inherent locality of their denoising mechanisms. This can yield samples that are locally plausible but globally inconsistent. To mitigate this issue, we propose sparsely supervised learning for diffusion models, a simple yet effective masking strategy that can be implemented with only a few lines of code. Interestingly, the experiments show that it is safe to mask up to 98\% of pixels during diffusion model training. Our method delivers competitive FID scores across experiments and, most importantly, avoids training instability on small datasets. Moreover, the masking strategy reduces memorization and promotes the use of essential contextual information during generation.
AGGC: Adaptive Group Gradient Clipping for Stabilizing Large Language Model Training
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:To stabilize the training of Large Language Models (LLMs), gradient clipping is a nearly ubiquitous heuristic used to alleviate exploding gradients. However, traditional global norm clipping erroneously presupposes gradient homogeneity across different functional modules, leading to an adverse "spill-over" effect where volatile parameters force unnecessary scaling on stable ones. To overcome this, we propose Adaptive Group-wise Gradient Clipping (AGGC). AGGC partitions parameters into groups based on functional types and regulates each according to its historical behavior using an Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Specifically, it constructs an adaptive interval to simultaneously mitigate gradient explosion and vanishing, while employing a time-dependent scheduling mechanism to balance exploration and convergence. Experiments on LLaMA 2-7B, Mistral-7B, and Gemma-7B models show that AGGC consistently outperforms LoRA and frequently surpasses Full Fine-Tuning. On the GSM8K benchmark, Mistral-7B fine-tuned with AGGC achieves an accuracy of 72.93%, exceeding LoRA's 69.5%. AGGC also effectively stabilizes Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), enhancing the logic deduction of Qwen 2.5 and Llama 3.2 models. Experimental results demonstrate that AGGC effectively addresses the limitations of traditional gradient clipping methods, particularly in overcoming gradient heterogeneity, by utilizing a modular, adaptive clipping strategy to stabilize the training process. Due to its lightweight design, AGGC can be seamlessly integrated into existing post-training pipelines with negligible overhead.
LADY: Linear Attention for Autonomous Driving Efficiency without Transformers
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:End-to-end paradigms have demonstrated great potential for autonomous driving. Additionally, most existing methods are built upon Transformer architectures. However, transformers incur a quadratic attention cost, limiting their ability to model long spatial and temporal sequences-particularly on resource-constrained edge platforms. As autonomous driving inherently demands efficient temporal modeling, this challenge severely limits their deployment and real-time performance. Recently, linear attention mechanisms have gained increasing attention due to their superior spatiotemporal complexity. However, existing linear attention architectures are limited to self-attention, lacking support for cross-modal and cross-temporal interactions-both crucial for autonomous driving. In this work, we propose LADY, the first fully linear attention-based generative model for end-to-end autonomous driving. LADY enables fusion of long-range temporal context at inference with constant computational and memory costs, regardless of the history length of camera and LiDAR features. Additionally, we introduce a lightweight linear cross-attention mechanism that enables effective cross-modal information exchange. Experiments on the NAVSIM and Bench2Drive benchmarks demonstrate that LADY achieves state-of-the-art performance with constant-time and memory complexity, offering improved planning performance and significantly reduced computational cost. Additionally, the model has been deployed and validated on edge devices, demonstrating its practicality in resource-limited scenarios.
PersonaLive! Expressive Portrait Image Animation for Live Streaming
Dec 12, 2025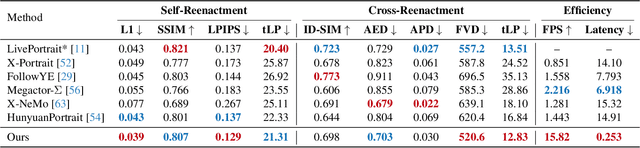
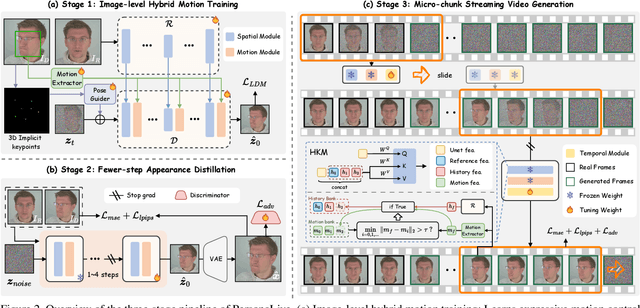

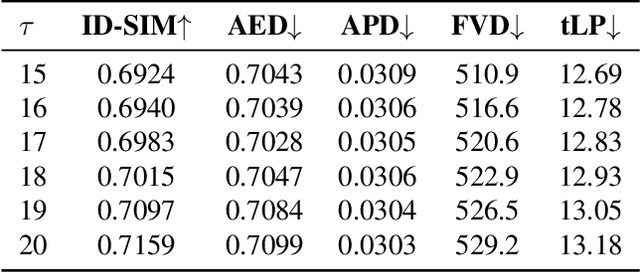
Abstract:Current diffusion-based portrait animation models predominantly focus on enhancing visual quality and expression realism, while overlooking generation latency and real-time performance, which restricts their application range in the live streaming scenario. We propose PersonaLive, a novel diffusion-based framework towards streaming real-time portrait animation with multi-stage training recipes. Specifically, we first adopt hybrid implicit signals, namely implicit facial representations and 3D implicit keypoints, to achieve expressive image-level motion control. Then, a fewer-step appearance distillation strategy is proposed to eliminate appearance redundancy in the denoising process, greatly improving inference efficiency. Finally, we introduce an autoregressive micro-chunk streaming generation paradigm equipped with a sliding training strategy and a historical keyframe mechanism to enable low-latency and stable long-term video generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PersonaLive achieves state-of-the-art performance with up to 7-22x speedup over prior diffusion-based portrait animation models.
Honesty over Accuracy: Trustworthy Language Models through Reinforced Hesitation
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Modern language models fail a fundamental requirement of trustworthy intelligence: knowing when not to answer. Despite achieving impressive accuracy on benchmarks, these models produce confident hallucinations, even when wrong answers carry catastrophic consequences. Our evaluations on GSM8K, MedQA and GPQA show frontier models almost never abstain despite explicit warnings of severe penalties, suggesting that prompts cannot override training that rewards any answer over no answer. As a remedy, we propose Reinforced Hesitation (RH): a modification to Reinforcement Learning from Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) to use ternary rewards (+1 correct, 0 abstention, -$λ$ error) instead of binary. Controlled experiments on logic puzzles reveal that varying $λ$ produces distinct models along a Pareto frontier, where each training penalty yields the optimal model for its corresponding risk regime: low penalties produce aggressive answerers, high penalties conservative abstainers. We then introduce two inference strategies that exploit trained abstention as a coordination signal: cascading routes queries through models with decreasing risk tolerance, while self-cascading re-queries the same model on abstention. Both outperform majority voting with lower computational cost. These results establish abstention as a first-class training objective that transforms ``I don't know'' from failure into a coordination signal, enabling models to earn trust through calibrated honesty about their limits.
Kimi Linear: An Expressive, Efficient Attention Architecture
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce Kimi Linear, a hybrid linear attention architecture that, for the first time, outperforms full attention under fair comparisons across various scenarios -- including short-context, long-context, and reinforcement learning (RL) scaling regimes. At its core lies Kimi Delta Attention (KDA), an expressive linear attention module that extends Gated DeltaNet with a finer-grained gating mechanism, enabling more effective use of limited finite-state RNN memory. Our bespoke chunkwise algorithm achieves high hardware efficiency through a specialized variant of the Diagonal-Plus-Low-Rank (DPLR) transition matrices, which substantially reduces computation compared to the general DPLR formulation while remaining more consistent with the classical delta rule. We pretrain a Kimi Linear model with 3B activated parameters and 48B total parameters, based on a layerwise hybrid of KDA and Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA). Our experiments show that with an identical training recipe, Kimi Linear outperforms full MLA with a sizeable margin across all evaluated tasks, while reducing KV cache usage by up to 75% and achieving up to 6 times decoding throughput for a 1M context. These results demonstrate that Kimi Linear can be a drop-in replacement for full attention architectures with superior performance and efficiency, including tasks with longer input and output lengths. To support further research, we open-source the KDA kernel and vLLM implementations, and release the pre-trained and instruction-tuned model checkpoints.
DP-FedLoRA: Privacy-Enhanced Federated Fine-Tuning for On-Device Large Language Models
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:As on-device large language model (LLM) systems become increasingly prevalent, federated fine-tuning enables advanced language understanding and generation directly on edge devices; however, it also involves processing sensitive, user-specific data, raising significant privacy concerns within the federated learning framework. To address these challenges, we propose DP-FedLoRA, a privacy-enhanced federated fine-tuning framework that integrates LoRA-based adaptation with differential privacy in a communication-efficient setting. Each client locally clips and perturbs its LoRA matrices using Gaussian noise to satisfy ($\epsilon$, $\delta$)-differential privacy. We further provide a theoretical analysis demonstrating the unbiased nature of the updates and deriving bounds on the variance introduced by noise, offering practical guidance for privacy-budget calibration. Experimental results across mainstream benchmarks show that DP-FedLoRA delivers competitive performance while offering strong privacy guarantees, paving the way for scalable and privacy-preserving LLM deployment in on-device environments.
Megrez2 Technical Report
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:We present Megrez2, a novel lightweight and high-performance language model architecture optimized for device native deployment. Megrez2 introduces a novel cross-layer expert sharing mechanism, which significantly reduces total parameter count by reusing expert modules across adjacent transformer layers while maintaining most of the model's capacity. It also incorporates pre-gated routing, enabling memory-efficient expert loading and faster inference. As the first instantiation of the Megrez2 architecture, we introduce the Megrez2-Preview model, which is pre-trained on a 5-trillion-token corpus and further enhanced through supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards. With only 3B activated and 7.5B stored parameters, Megrez2-Preview demonstrates competitive or superior performance compared to larger models on a wide range of tasks, including language understanding, instruction following, mathematical reasoning, and code generation. These results highlight the effectiveness of the Megrez2 architecture to achieve a balance between accuracy, efficiency, and deployability, making it a strong candidate for real-world, resource-constrained applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge