Xudong Cai
Mem4D: Decoupling Static and Dynamic Memory for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing dense geometry for dynamic scenes from a monocular video is a critical yet challenging task. Recent memory-based methods enable efficient online reconstruction, but they fundamentally suffer from a Memory Demand Dilemma: The memory representation faces an inherent conflict between the long-term stability required for static structures and the rapid, high-fidelity detail retention needed for dynamic motion. This conflict forces existing methods into a compromise, leading to either geometric drift in static structures or blurred, inaccurate reconstructions of dynamic objects. To address this dilemma, we propose Mem4D, a novel framework that decouples the modeling of static geometry and dynamic motion. Guided by this insight, we design a dual-memory architecture: 1) The Transient Dynamics Memory (TDM) focuses on capturing high-frequency motion details from recent frames, enabling accurate and fine-grained modeling of dynamic content; 2) The Persistent Structure Memory (PSM) compresses and preserves long-term spatial information, ensuring global consistency and drift-free reconstruction for static elements. By alternating queries to these specialized memories, Mem4D simultaneously maintains static geometry with global consistency and reconstructs dynamic elements with high fidelity. Experiments on challenging benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art or competitive performance while maintaining high efficiency. Codes will be publicly available.
VerifyBench: Benchmarking Reference-based Reward Systems for Large Language Models
May 21, 2025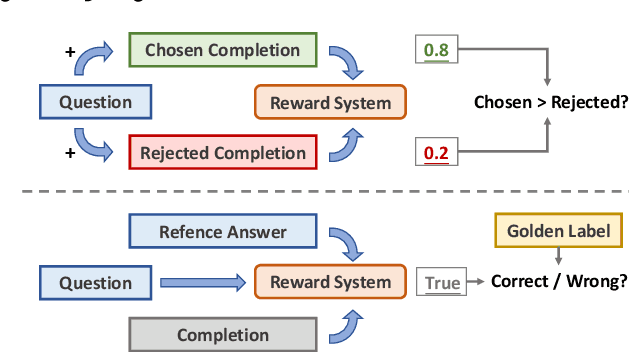
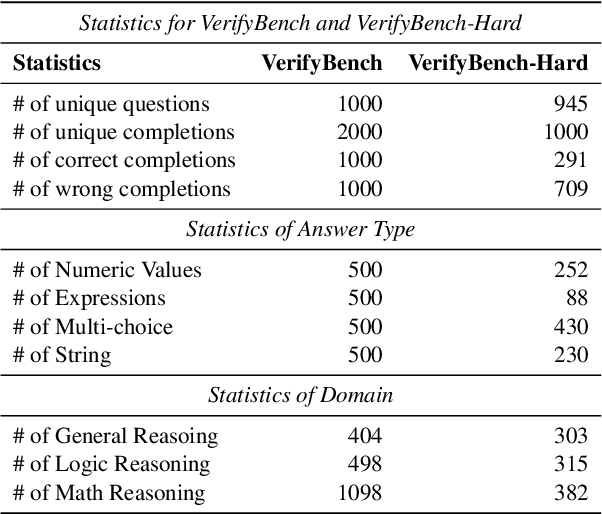
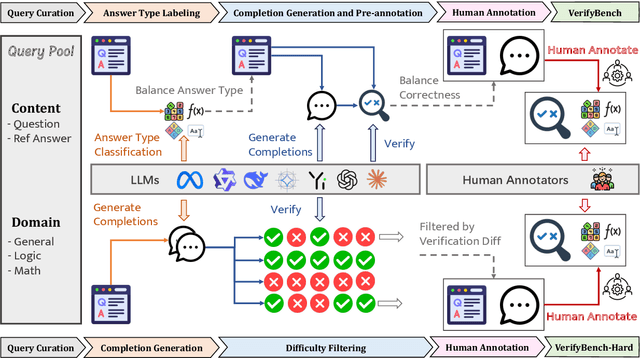
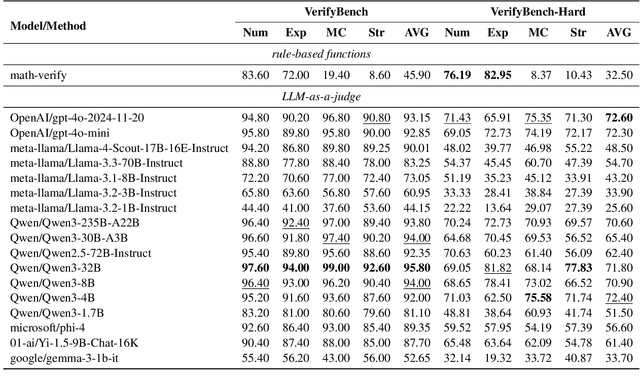
Abstract:Large reasoning models such as OpenAI o1 and DeepSeek-R1 have achieved remarkable performance in the domain of reasoning. A key component of their training is the incorporation of verifiable rewards within reinforcement learning (RL). However, existing reward benchmarks do not evaluate reference-based reward systems, leaving researchers with limited understanding of the accuracy of verifiers used in RL. In this paper, we introduce two benchmarks, VerifyBench and VerifyBench-Hard, designed to assess the performance of reference-based reward systems. These benchmarks are constructed through meticulous data collection and curation, followed by careful human annotation to ensure high quality. Current models still show considerable room for improvement on both VerifyBench and VerifyBench-Hard, especially smaller-scale models. Furthermore, we conduct a thorough and comprehensive analysis of evaluation results, offering insights for understanding and developing reference-based reward systems. Our proposed benchmarks serve as effective tools for guiding the development of verifier accuracy and the reasoning capabilities of models trained via RL in reasoning tasks.
Aux-Think: Exploring Reasoning Strategies for Data-Efficient Vision-Language Navigation
May 17, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Navigation (VLN) is a critical task for developing embodied agents that can follow natural language instructions to navigate in complex real-world environments. Recent advances in VLN by large pretrained models have significantly improved generalization and instruction grounding compared to traditional approaches. However, the role of reasoning strategies in navigation-an action-centric, long-horizon task-remains underexplored, despite Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning's demonstrated success in static tasks like visual question answering. To address this gap, we conduct the first systematic evaluation of reasoning strategies for VLN, including No-Think (direct action prediction), Pre-Think (reason before action), and Post-Think (reason after action). Surprisingly, our findings reveal the Inference-time Reasoning Collapse issue, where inference-time reasoning degrades navigation accuracy, highlighting the challenges of integrating reasoning into VLN. Based on this insight, we propose Aux-Think, a framework that trains models to internalize structured reasoning patterns through CoT supervision, while inferring action directly without reasoning in online prediction. To support this framework, we release R2R-CoT-320k, the first Chain-of-Thought annotated dataset for VLN. Extensive experiments show that Aux-Think reduces training effort greatly and achieves the best performance under the same data scale.
MambaVO: Deep Visual Odometry Based on Sequential Matching Refinement and Training Smoothing
Dec 28, 2024Abstract:Deep visual odometry has demonstrated great advancements by learning-to-optimize technology. This approach heavily relies on the visual matching across frames. However, ambiguous matching in challenging scenarios leads to significant errors in geometric modeling and bundle adjustment optimization, which undermines the accuracy and robustness of pose estimation. To address this challenge, this paper proposes MambaVO, which conducts robust initialization, Mamba-based sequential matching refinement, and smoothed training to enhance the matching quality and improve the pose estimation in deep visual odometry. Specifically, when a new frame is received, it is matched with the closest keyframe in the maintained Point-Frame Graph (PFG) via the semi-dense based Geometric Initialization Module (GIM). Then the initialized PFG is processed by a proposed Geometric Mamba Module (GMM), which exploits the matching features to refine the overall inter-frame pixel-to-pixel matching. The refined PFG is finally processed by deep BA to optimize the poses and the map. To deal with the gradient variance, a Trending-Aware Penalty (TAP) is proposed to smooth training by balancing the pose loss and the matching loss to enhance convergence and stability. A loop closure module is finally applied to enable MambaVO++. On public benchmarks, MambaVO and MambaVO++ demonstrate SOTA accuracy performance, while ensuring real-time running performance with low GPU memory requirement. Codes will be publicly available.
Dust to Tower: Coarse-to-Fine Photo-Realistic Scene Reconstruction from Sparse Uncalibrated Images
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:Photo-realistic scene reconstruction from sparse-view, uncalibrated images is highly required in practice. Although some successes have been made, existing methods are either Sparse-View but require accurate camera parameters (i.e., intrinsic and extrinsic), or SfM-free but need densely captured images. To combine the advantages of both methods while addressing their respective weaknesses, we propose Dust to Tower (D2T), an accurate and efficient coarse-to-fine framework to optimize 3DGS and image poses simultaneously from sparse and uncalibrated images. Our key idea is to first construct a coarse model efficiently and subsequently refine it using warped and inpainted images at novel viewpoints. To do this, we first introduce a Coarse Construction Module (CCM) which exploits a fast Multi-View Stereo model to initialize a 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) and recover initial camera poses. To refine the 3D model at novel viewpoints, we propose a Confidence Aware Depth Alignment (CADA) module to refine the coarse depth maps by aligning their confident parts with estimated depths by a Mono-depth model. Then, a Warped Image-Guided Inpainting (WIGI) module is proposed to warp the training images to novel viewpoints by the refined depth maps, and inpainting is applied to fulfill the ``holes" in the warped images caused by view-direction changes, providing high-quality supervision to further optimize the 3D model and the camera poses. Extensive experiments and ablation studies demonstrate the validity of D2T and its design choices, achieving state-of-the-art performance in both tasks of novel view synthesis and pose estimation while keeping high efficiency. Codes will be publicly available.
Autonomous Driving in Unstructured Environments: How Far Have We Come?
Oct 10, 2024

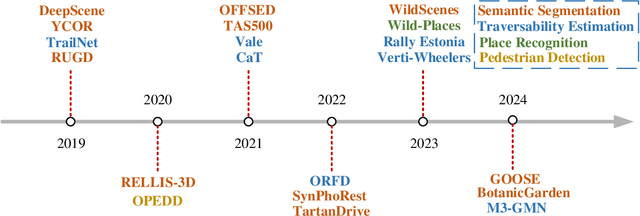
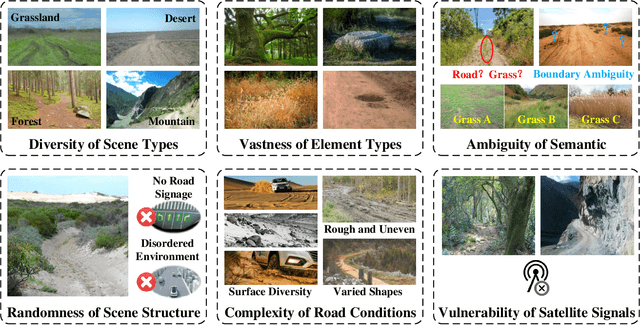
Abstract:Research on autonomous driving in unstructured outdoor environments is less advanced than in structured urban settings due to challenges like environmental diversities and scene complexity. These environments-such as rural areas and rugged terrains-pose unique obstacles that are not common in structured urban areas. Despite these difficulties, autonomous driving in unstructured outdoor environments is crucial for applications in agriculture, mining, and military operations. Our survey reviews over 250 papers for autonomous driving in unstructured outdoor environments, covering offline mapping, pose estimation, environmental perception, path planning, end-to-end autonomous driving, datasets, and relevant challenges. We also discuss emerging trends and future research directions. This review aims to consolidate knowledge and encourage further research for autonomous driving in unstructured environments. To support ongoing work, we maintain an active repository with up-to-date literature and open-source projects at: https://github.com/chaytonmin/Survey-Autonomous-Driving-in-Unstructured-Environments.
VSFormer: Mining Correlations in Flexible View Set for Multi-view 3D Shape Understanding
Sep 14, 2024



Abstract:View-based methods have demonstrated promising performance in 3D shape understanding. However, they tend to make strong assumptions about the relations between views or learn the multi-view correlations indirectly, which limits the flexibility of exploring inter-view correlations and the effectiveness of target tasks. To overcome the above problems, this paper investigates flexible organization and explicit correlation learning for multiple views. In particular, we propose to incorporate different views of a 3D shape into a permutation-invariant set, referred to as \emph{View Set}, which removes rigid relation assumptions and facilitates adequate information exchange and fusion among views. Based on that, we devise a nimble Transformer model, named \emph{VSFormer}, to explicitly capture pairwise and higher-order correlations of all elements in the set. Meanwhile, we theoretically reveal a natural correspondence between the Cartesian product of a view set and the correlation matrix in the attention mechanism, which supports our model design. Comprehensive experiments suggest that VSFormer has better flexibility, efficient inference efficiency and superior performance. Notably, VSFormer reaches state-of-the-art results on various 3d recognition datasets, including ModelNet40, ScanObjectNN and RGBD. It also establishes new records on the SHREC'17 retrieval benchmark. The code and datasets are available at \url{https://github.com/auniquesun/VSFormer}.
PRISM: PRogressive dependency maxImization for Scale-invariant image Matching
Aug 07, 2024

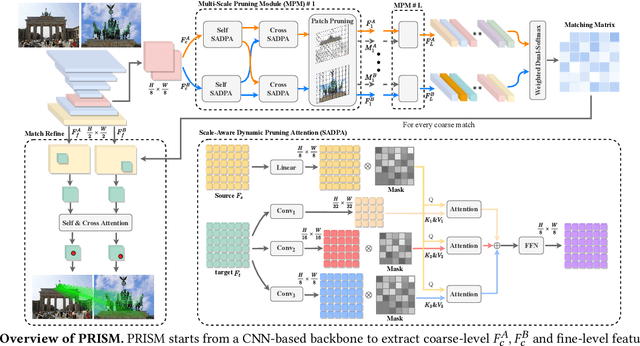

Abstract:Image matching aims at identifying corresponding points between a pair of images. Currently, detector-free methods have shown impressive performance in challenging scenarios, thanks to their capability of generating dense matches and global receptive field. However, performing feature interaction and proposing matches across the entire image is unnecessary, because not all image regions contribute to the matching process. Interacting and matching in unmatchable areas can introduce errors, reducing matching accuracy and efficiency. Meanwhile, the scale discrepancy issue still troubles existing methods. To address above issues, we propose PRogressive dependency maxImization for Scale-invariant image Matching (PRISM), which jointly prunes irrelevant patch features and tackles the scale discrepancy. To do this, we firstly present a Multi-scale Pruning Module (MPM) to adaptively prune irrelevant features by maximizing the dependency between the two feature sets. Moreover, we design the Scale-Aware Dynamic Pruning Attention (SADPA) to aggregate information from different scales via a hierarchical design. Our method's superior matching performance and generalization capability are confirmed by leading accuracy across various evaluation benchmarks and downstream tasks. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/Master-cai/PRISM.
VOLoc: Visual Place Recognition by Querying Compressed Lidar Map
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:The availability of city-scale Lidar maps enables the potential of city-scale place recognition using mobile cameras. However, the city-scale Lidar maps generally need to be compressed for storage efficiency, which increases the difficulty of direct visual place recognition in compressed Lidar maps. This paper proposes VOLoc, an accurate and efficient visual place recognition method that exploits geometric similarity to directly query the compressed Lidar map via the real-time captured image sequence. In the offline phase, VOLoc compresses the Lidar maps using a \emph{Geometry-Preserving Compressor} (GPC), in which the compression is reversible, a crucial requirement for the downstream 6DoF pose estimation. In the online phase, VOLoc proposes an online Geometric Recovery Module (GRM), which is composed of online Visual Odometry (VO) and a point cloud optimization module, such that the local scene structure around the camera is online recovered to build the \emph{Querying Point Cloud} (QPC). Then the QPC is compressed by the same GPC, and is aggregated into a global descriptor by an attention-based aggregation module, to query the compressed Lidar map in the vector space. A transfer learning mechanism is also proposed to improve the accuracy and the generality of the aggregation network. Extensive evaluations show that VOLoc provides localization accuracy even better than the Lidar-to-Lidar place recognition, setting up a new record for utilizing the compressed Lidar map by low-end mobile cameras. The code are publicly available at https://github.com/Master-cai/VOLoc.
ViewFormer: View Set Attention for Multi-view 3D Shape Understanding
Apr 29, 2023Abstract:This paper presents ViewFormer, a simple yet effective model for multi-view 3d shape recognition and retrieval. We systematically investigate the existing methods for aggregating multi-view information and propose a novel ``view set" perspective, which minimizes the relation assumption about the views and releases the representation flexibility. We devise an adaptive attention model to capture pairwise and higher-order correlations of the elements in the view set. The learned multi-view correlations are aggregated into an expressive view set descriptor for recognition and retrieval. Experiments show the proposed method unleashes surprising capabilities across different tasks and datasets. For instance, with only 2 attention blocks and 4.8M learnable parameters, ViewFormer reaches 98.8% recognition accuracy on ModelNet40 for the first time, exceeding previous best method by 1.1% . On the challenging RGBD dataset, our method achieves 98.4% recognition accuracy, which is a 4.1% absolute improvement over the strongest baseline. ViewFormer also sets new records in several evaluation dimensions of 3D shape retrieval defined on the SHREC'17 benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge