Wanting Li
Orchestrating Intelligence: Confidence-Aware Routing for Efficient Multi-Agent Collaboration across Multi-Scale Models
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:While multi-agent systems (MAS) have demonstrated superior performance over single-agent approaches in complex reasoning tasks, they often suffer from significant computational inefficiencies. Existing frameworks typically deploy large language models (LLMs) uniformly across all agent roles, failing to account for the varying cognitive demands of different reasoning stages. We address this inefficiency by proposing OI-MAS framework, a novel multi-agent framework that implements an adaptive model-selection policy across a heterogeneous pool of multi-scale LLMs. Specifically, OI-MAS introduces a state-dependent routing mechanism that dynamically selects agent roles and model scales throughout the reasoning process. In addition, we introduce a confidence-aware mechanism that selects appropriate model scales conditioned on task complexity, thus reducing unnecessary reliance on large-scale models. Experimental results show that OI-MAS consistently outperforms baseline multi-agent systems, improving accuracy by up to 12.88\% while reducing cost by up to 79.78\%.
Mem4D: Decoupling Static and Dynamic Memory for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing dense geometry for dynamic scenes from a monocular video is a critical yet challenging task. Recent memory-based methods enable efficient online reconstruction, but they fundamentally suffer from a Memory Demand Dilemma: The memory representation faces an inherent conflict between the long-term stability required for static structures and the rapid, high-fidelity detail retention needed for dynamic motion. This conflict forces existing methods into a compromise, leading to either geometric drift in static structures or blurred, inaccurate reconstructions of dynamic objects. To address this dilemma, we propose Mem4D, a novel framework that decouples the modeling of static geometry and dynamic motion. Guided by this insight, we design a dual-memory architecture: 1) The Transient Dynamics Memory (TDM) focuses on capturing high-frequency motion details from recent frames, enabling accurate and fine-grained modeling of dynamic content; 2) The Persistent Structure Memory (PSM) compresses and preserves long-term spatial information, ensuring global consistency and drift-free reconstruction for static elements. By alternating queries to these specialized memories, Mem4D simultaneously maintains static geometry with global consistency and reconstructs dynamic elements with high fidelity. Experiments on challenging benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art or competitive performance while maintaining high efficiency. Codes will be publicly available.
Aux-Think: Exploring Reasoning Strategies for Data-Efficient Vision-Language Navigation
May 17, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Navigation (VLN) is a critical task for developing embodied agents that can follow natural language instructions to navigate in complex real-world environments. Recent advances in VLN by large pretrained models have significantly improved generalization and instruction grounding compared to traditional approaches. However, the role of reasoning strategies in navigation-an action-centric, long-horizon task-remains underexplored, despite Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning's demonstrated success in static tasks like visual question answering. To address this gap, we conduct the first systematic evaluation of reasoning strategies for VLN, including No-Think (direct action prediction), Pre-Think (reason before action), and Post-Think (reason after action). Surprisingly, our findings reveal the Inference-time Reasoning Collapse issue, where inference-time reasoning degrades navigation accuracy, highlighting the challenges of integrating reasoning into VLN. Based on this insight, we propose Aux-Think, a framework that trains models to internalize structured reasoning patterns through CoT supervision, while inferring action directly without reasoning in online prediction. To support this framework, we release R2R-CoT-320k, the first Chain-of-Thought annotated dataset for VLN. Extensive experiments show that Aux-Think reduces training effort greatly and achieves the best performance under the same data scale.
AlayaDB: The Data Foundation for Efficient and Effective Long-context LLM Inference
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:AlayaDB is a cutting-edge vector database system natively architected for efficient and effective long-context inference for Large Language Models (LLMs) at AlayaDB AI. Specifically, it decouples the KV cache and attention computation from the LLM inference systems, and encapsulates them into a novel vector database system. For the Model as a Service providers (MaaS), AlayaDB consumes fewer hardware resources and offers higher generation quality for various workloads with different kinds of Service Level Objectives (SLOs), when comparing with the existing alternative solutions (e.g., KV cache disaggregation, retrieval-based sparse attention). The crux of AlayaDB is that it abstracts the attention computation and cache management for LLM inference into a query processing procedure, and optimizes the performance via a native query optimizer. In this work, we demonstrate the effectiveness of AlayaDB via (i) three use cases from our industry partners, and (ii) extensive experimental results on LLM inference benchmarks.
OminiAdapt: Learning Cross-Task Invariance for Robust and Environment-Aware Robotic Manipulation
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid development of embodied intelligence, leveraging large-scale human data for high-level imitation learning on humanoid robots has become a focal point of interest in both academia and industry. However, applying humanoid robots to precision operation domains remains challenging due to the complexities they face in perception and control processes, the long-standing physical differences in morphology and actuation mechanisms between humanoid robots and humans, and the lack of task-relevant features obtained from egocentric vision. To address the issue of covariate shift in imitation learning, this paper proposes an imitation learning algorithm tailored for humanoid robots. By focusing on the primary task objectives, filtering out background information, and incorporating channel feature fusion with spatial attention mechanisms, the proposed algorithm suppresses environmental disturbances and utilizes a dynamic weight update strategy to significantly improve the success rate of humanoid robots in accomplishing target tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method exhibits robustness and scalability across various typical task scenarios, providing new ideas and approaches for autonomous learning and control in humanoid robots. The project will be open-sourced on GitHub.
MambaVO: Deep Visual Odometry Based on Sequential Matching Refinement and Training Smoothing
Dec 28, 2024Abstract:Deep visual odometry has demonstrated great advancements by learning-to-optimize technology. This approach heavily relies on the visual matching across frames. However, ambiguous matching in challenging scenarios leads to significant errors in geometric modeling and bundle adjustment optimization, which undermines the accuracy and robustness of pose estimation. To address this challenge, this paper proposes MambaVO, which conducts robust initialization, Mamba-based sequential matching refinement, and smoothed training to enhance the matching quality and improve the pose estimation in deep visual odometry. Specifically, when a new frame is received, it is matched with the closest keyframe in the maintained Point-Frame Graph (PFG) via the semi-dense based Geometric Initialization Module (GIM). Then the initialized PFG is processed by a proposed Geometric Mamba Module (GMM), which exploits the matching features to refine the overall inter-frame pixel-to-pixel matching. The refined PFG is finally processed by deep BA to optimize the poses and the map. To deal with the gradient variance, a Trending-Aware Penalty (TAP) is proposed to smooth training by balancing the pose loss and the matching loss to enhance convergence and stability. A loop closure module is finally applied to enable MambaVO++. On public benchmarks, MambaVO and MambaVO++ demonstrate SOTA accuracy performance, while ensuring real-time running performance with low GPU memory requirement. Codes will be publicly available.
Dust to Tower: Coarse-to-Fine Photo-Realistic Scene Reconstruction from Sparse Uncalibrated Images
Dec 27, 2024



Abstract:Photo-realistic scene reconstruction from sparse-view, uncalibrated images is highly required in practice. Although some successes have been made, existing methods are either Sparse-View but require accurate camera parameters (i.e., intrinsic and extrinsic), or SfM-free but need densely captured images. To combine the advantages of both methods while addressing their respective weaknesses, we propose Dust to Tower (D2T), an accurate and efficient coarse-to-fine framework to optimize 3DGS and image poses simultaneously from sparse and uncalibrated images. Our key idea is to first construct a coarse model efficiently and subsequently refine it using warped and inpainted images at novel viewpoints. To do this, we first introduce a Coarse Construction Module (CCM) which exploits a fast Multi-View Stereo model to initialize a 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) and recover initial camera poses. To refine the 3D model at novel viewpoints, we propose a Confidence Aware Depth Alignment (CADA) module to refine the coarse depth maps by aligning their confident parts with estimated depths by a Mono-depth model. Then, a Warped Image-Guided Inpainting (WIGI) module is proposed to warp the training images to novel viewpoints by the refined depth maps, and inpainting is applied to fulfill the ``holes" in the warped images caused by view-direction changes, providing high-quality supervision to further optimize the 3D model and the camera poses. Extensive experiments and ablation studies demonstrate the validity of D2T and its design choices, achieving state-of-the-art performance in both tasks of novel view synthesis and pose estimation while keeping high efficiency. Codes will be publicly available.
GSLAMOT: A Tracklet and Query Graph-based Simultaneous Locating, Mapping, and Multiple Object Tracking System
Aug 17, 2024Abstract:For interacting with mobile objects in unfamiliar environments, simultaneously locating, mapping, and tracking the 3D poses of multiple objects are crucially required. This paper proposes a Tracklet Graph and Query Graph-based framework, i.e., GSLAMOT, to address this challenge. GSLAMOT utilizes camera and LiDAR multimodal information as inputs and divides the representation of the dynamic scene into a semantic map for representing the static environment, a trajectory of the ego-agent, and an online maintained Tracklet Graph (TG) for tracking and predicting the 3D poses of the detected mobile objects. A Query Graph (QG) is constructed in each frame by object detection to query and update TG. For accurate object association, a Multi-criteria Star Graph Association (MSGA) method is proposed to find matched objects between the detections in QG and the predicted tracklets in TG. Then, an Object-centric Graph Optimization (OGO) method is proposed to simultaneously optimize the TG, the semantic map, and the agent trajectory. It triangulates the detected objects into the map to enrich the map's semantic information. We address the efficiency issues to handle the three tightly coupled tasks in parallel. Experiments are conducted on KITTI, Waymo, and an emulated Traffic Congestion dataset that highlights challenging scenarios. Experiments show that GSLAMOT enables accurate crowded object tracking while conducting SLAM accurately in challenging scenarios, demonstrating more excellent performances than the state-of-the-art methods. The code and dataset are at https://gslamot.github.io.
RoCo:Robust Collaborative Perception By Iterative Object Matching and Pose Adjustment
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:Collaborative autonomous driving with multiple vehicles usually requires the data fusion from multiple modalities. To ensure effective fusion, the data from each individual modality shall maintain a reasonably high quality. However, in collaborative perception, the quality of object detection based on a modality is highly sensitive to the relative pose errors among the agents. It leads to feature misalignment and significantly reduces collaborative performance. To address this issue, we propose RoCo, a novel unsupervised framework to conduct iterative object matching and agent pose adjustment. To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first to model the pose correction problem in collaborative perception as an object matching task, which reliably associates common objects detected by different agents. On top of this, we propose a graph optimization process to adjust the agent poses by minimizing the alignment errors of the associated objects, and the object matching is re-done based on the adjusted agent poses. This process is carried out iteratively until convergence. Experimental study on both simulated and real-world datasets demonstrates that the proposed framework RoCo consistently outperforms existing relevant methods in terms of the collaborative object detection performance, and exhibits highly desired robustness when the pose information of agents is with high-level noise. Ablation studies are also provided to show the impact of its key parameters and components. The code is released at https://github.com/HuangZhe885/RoCo.
* ACM MM2024
IDLL: Inverse Depth Line based Visual Localization in Challenging Environments
Apr 23, 2023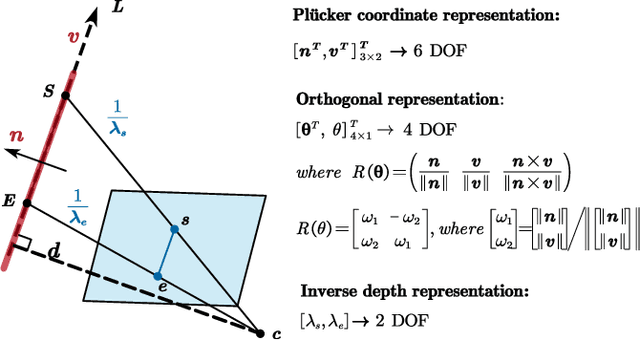

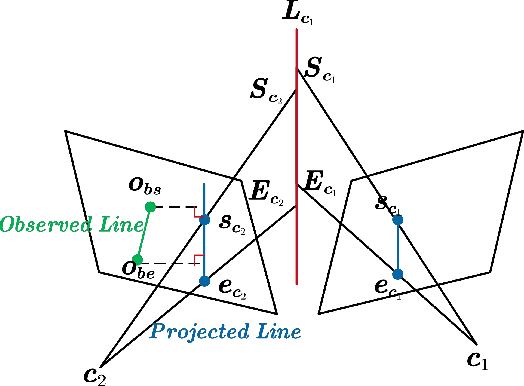
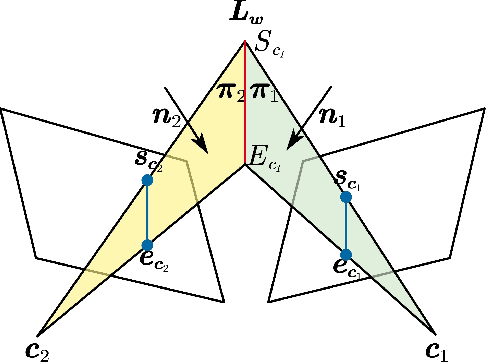
Abstract:Precise and real-time localization of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or robots in GNSS denied indoor environments are critically important for various logistics and surveillance applications. Vision-based simultaneously locating and mapping (VSLAM) are key solutions but suffer location drifts in texture-less, man-made indoor environments. Line features are rich in man-made environments which can be exploited to improve the localization robustness, but existing point-line based VSLAM methods still lack accuracy and efficiency for the representation of lines introducing unnecessary degrees of freedoms. In this paper, we propose Inverse Depth Line Localization(IDLL), which models each extracted line feature using two inverse depth variables exploiting the fact that the projected pixel coordinates on the image plane are rather accurate, which partially restrict the lines. This freedom-reduced representation of lines enables easier line determination and faster convergence of bundle adjustment in each step, therefore achieves more accurate and more efficient frame-to-frame registration and frame-to-map registration using both point and line visual features. We redesign the whole front-end and back-end modules of VSLAM using this line model. IDLL is extensively evaluated in multiple perceptually-challenging datasets. The results show it is more accurate, robust, and needs lower computational overhead than the current state-of-the-art of feature-based VSLAM methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge