Zhizhong Su
MapDream: Task-Driven Map Learning for Vision-Language Navigation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Navigation (VLN) requires agents to follow natural language instructions in partially observed 3D environments, motivating map representations that aggregate spatial context beyond local perception. However, most existing approaches rely on hand-crafted maps constructed independently of the navigation policy. We argue that maps should instead be learned representations shaped directly by navigation objectives rather than exhaustive reconstructions. Based on this insight, we propose MapDream, a map-in-the-loop framework that formulates map construction as autoregressive bird's-eye-view (BEV) image synthesis. The framework jointly learns map generation and action prediction, distilling environmental context into a compact three-channel BEV map that preserves only navigation-critical affordances. Supervised pre-training bootstraps a reliable mapping-to-control interface, while the autoregressive design enables end-to-end joint optimization through reinforcement fine-tuning. Experiments on R2R-CE and RxR-CE achieve state-of-the-art monocular performance, validating task-driven generative map learning.
RecurGS: Interactive Scene Modeling via Discrete-State Recurrent Gaussian Fusion
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in 3D scene representations have enabled high-fidelity novel view synthesis, yet adapting to discrete scene changes and constructing interactive 3D environments remain open challenges in vision and robotics. Existing approaches focus solely on updating a single scene without supporting novel-state synthesis. Others rely on diffusion-based object-background decoupling that works on one state at a time and cannot fuse information across multiple observations. To address these limitations, we introduce RecurGS, a recurrent fusion framework that incrementally integrates discrete Gaussian scene states into a single evolving representation capable of interaction. RecurGS detects object-level changes across consecutive states, aligns their geometric motion using semantic correspondence and Lie-algebra based SE(3) refinement, and performs recurrent updates that preserve historical structures through replay supervision. A voxelized, visibility-aware fusion module selectively incorporates newly observed regions while keeping stable areas fixed, mitigating catastrophic forgetting and enabling efficient long-horizon updates. RecurGS supports object-level manipulation, synthesizes novel scene states without requiring additional scans, and maintains photorealistic fidelity across evolving environments. Extensive experiments across synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our framework delivers high-quality reconstructions with substantially improved update efficiency, providing a scalable step toward continuously interactive Gaussian worlds.
Motus: A Unified Latent Action World Model
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:While a general embodied agent must function as a unified system, current methods are built on isolated models for understanding, world modeling, and control. This fragmentation prevents unifying multimodal generative capabilities and hinders learning from large-scale, heterogeneous data. In this paper, we propose Motus, a unified latent action world model that leverages existing general pretrained models and rich, sharable motion information. Motus introduces a Mixture-of-Transformer (MoT) architecture to integrate three experts (i.e., understanding, video generation, and action) and adopts a UniDiffuser-style scheduler to enable flexible switching between different modeling modes (i.e., world models, vision-language-action models, inverse dynamics models, video generation models, and video-action joint prediction models). Motus further leverages the optical flow to learn latent actions and adopts a recipe with three-phase training pipeline and six-layer data pyramid, thereby extracting pixel-level "delta action" and enabling large-scale action pretraining. Experiments show that Motus achieves superior performance against state-of-the-art methods in both simulation (a +15% improvement over X-VLA and a +45% improvement over Pi0.5) and real-world scenarios(improved by +11~48%), demonstrating unified modeling of all functionalities and priors significantly benefits downstream robotic tasks.
DreamLifting: A Plug-in Module Lifting MV Diffusion Models for 3D Asset Generation
Sep 09, 2025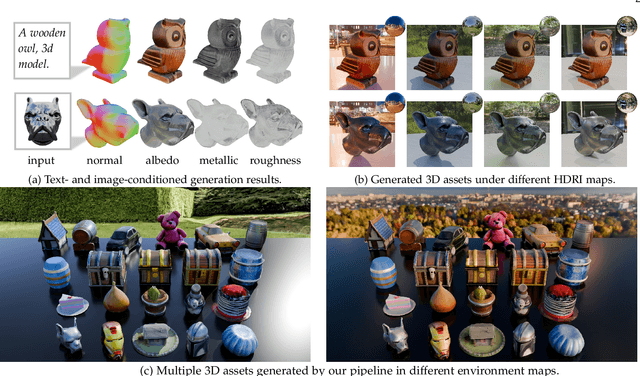

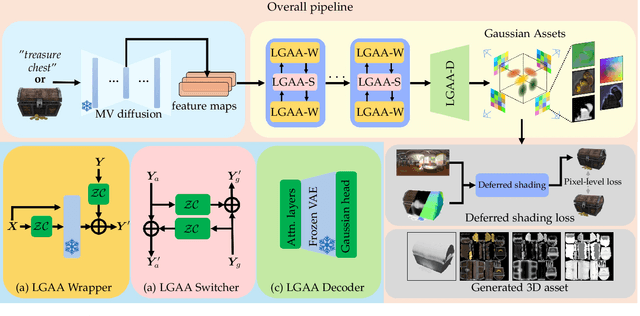
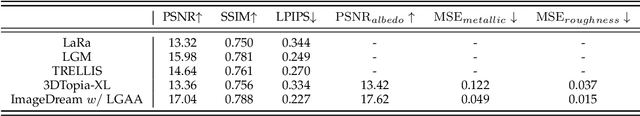
Abstract:The labor- and experience-intensive creation of 3D assets with physically based rendering (PBR) materials demands an autonomous 3D asset creation pipeline. However, most existing 3D generation methods focus on geometry modeling, either baking textures into simple vertex colors or leaving texture synthesis to post-processing with image diffusion models. To achieve end-to-end PBR-ready 3D asset generation, we present Lightweight Gaussian Asset Adapter (LGAA), a novel framework that unifies the modeling of geometry and PBR materials by exploiting multi-view (MV) diffusion priors from a novel perspective. The LGAA features a modular design with three components. Specifically, the LGAA Wrapper reuses and adapts network layers from MV diffusion models, which encapsulate knowledge acquired from billions of images, enabling better convergence in a data-efficient manner. To incorporate multiple diffusion priors for geometry and PBR synthesis, the LGAA Switcher aligns multiple LGAA Wrapper layers encapsulating different knowledge. Then, a tamed variational autoencoder (VAE), termed LGAA Decoder, is designed to predict 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) with PBR channels. Finally, we introduce a dedicated post-processing procedure to effectively extract high-quality, relightable mesh assets from the resulting 2DGS. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate the superior performance of LGAA with both text-and image-conditioned MV diffusion models. Additionally, the modular design enables flexible incorporation of multiple diffusion priors, and the knowledge-preserving scheme leads to efficient convergence trained on merely 69k multi-view instances. Our code, pre-trained weights, and the dataset used will be publicly available via our project page: https://zx-yin.github.io/dreamlifting/.
IGFuse: Interactive 3D Gaussian Scene Reconstruction via Multi-Scans Fusion
Aug 18, 2025



Abstract:Reconstructing complete and interactive 3D scenes remains a fundamental challenge in computer vision and robotics, particularly due to persistent object occlusions and limited sensor coverage. Multiview observations from a single scene scan often fail to capture the full structural details. Existing approaches typically rely on multi stage pipelines, such as segmentation, background completion, and inpainting or require per-object dense scanning, both of which are error-prone, and not easily scalable. We propose IGFuse, a novel framework that reconstructs interactive Gaussian scene by fusing observations from multiple scans, where natural object rearrangement between captures reveal previously occluded regions. Our method constructs segmentation aware Gaussian fields and enforces bi-directional photometric and semantic consistency across scans. To handle spatial misalignments, we introduce a pseudo-intermediate scene state for unified alignment, alongside collaborative co-pruning strategies to refine geometry. IGFuse enables high fidelity rendering and object level scene manipulation without dense observations or complex pipelines. Extensive experiments validate the framework's strong generalization to novel scene configurations, demonstrating its effectiveness for real world 3D reconstruction and real-to-simulation transfer. Our project page is available online.
Theoretical Analysis of Relative Errors in Gradient Computations for Adversarial Attacks with CE Loss
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Gradient-based adversarial attacks using the Cross-Entropy (CE) loss often suffer from overestimation due to relative errors in gradient computation induced by floating-point arithmetic. This paper provides a rigorous theoretical analysis of these errors, conducting the first comprehensive study of floating-point computation errors in gradient-based attacks across four distinct scenarios: (i) unsuccessful untargeted attacks, (ii) successful untargeted attacks, (iii) unsuccessful targeted attacks, and (iv) successful targeted attacks. We establish theoretical foundations characterizing the behavior of relative numerical errors under different attack conditions, revealing previously unknown patterns in gradient computation instability, and identify floating-point underflow and rounding as key contributors. Building on this insight, we propose the Theoretical MIFPE (T-MIFPE) loss function, which incorporates an optimal scaling factor $T = t^*$ to minimize the impact of floating-point errors, thereby enhancing the accuracy of gradient computation in adversarial attacks. Extensive experiments on the MNIST, CIFAR-10, and CIFAR-100 datasets demonstrate that T-MIFPE outperforms existing loss functions, including CE, C\&W, DLR, and MIFPE, in terms of attack potency and robustness evaluation accuracy.
RoboTransfer: Geometry-Consistent Video Diffusion for Robotic Visual Policy Transfer
May 29, 2025Abstract:Imitation Learning has become a fundamental approach in robotic manipulation. However, collecting large-scale real-world robot demonstrations is prohibitively expensive. Simulators offer a cost-effective alternative, but the sim-to-real gap make it extremely challenging to scale. Therefore, we introduce RoboTransfer, a diffusion-based video generation framework for robotic data synthesis. Unlike previous methods, RoboTransfer integrates multi-view geometry with explicit control over scene components, such as background and object attributes. By incorporating cross-view feature interactions and global depth/normal conditions, RoboTransfer ensures geometry consistency across views. This framework allows fine-grained control, including background edits and object swaps. Experiments demonstrate that RoboTransfer is capable of generating multi-view videos with enhanced geometric consistency and visual fidelity. In addition, policies trained on the data generated by RoboTransfer achieve a 33.3% relative improvement in the success rate in the DIFF-OBJ setting and a substantial 251% relative improvement in the more challenging DIFF-ALL scenario. Explore more demos on our project page: https://horizonrobotics.github.io/robot_lab/robotransfer
DIPO: Dual-State Images Controlled Articulated Object Generation Powered by Diverse Data
May 28, 2025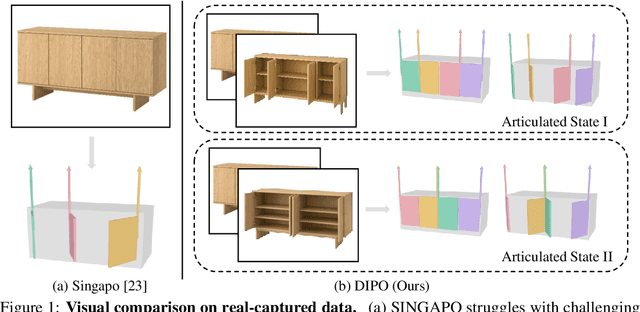
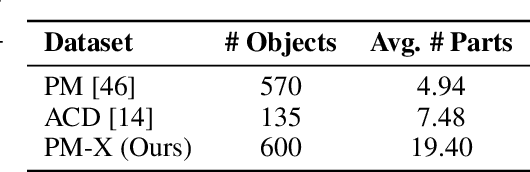
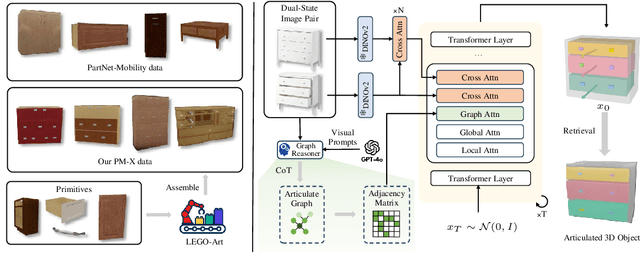
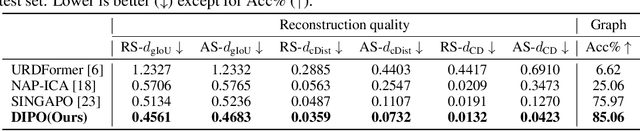
Abstract:We present DIPO, a novel framework for the controllable generation of articulated 3D objects from a pair of images: one depicting the object in a resting state and the other in an articulated state. Compared to the single-image approach, our dual-image input imposes only a modest overhead for data collection, but at the same time provides important motion information, which is a reliable guide for predicting kinematic relationships between parts. Specifically, we propose a dual-image diffusion model that captures relationships between the image pair to generate part layouts and joint parameters. In addition, we introduce a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) based graph reasoner that explicitly infers part connectivity relationships. To further improve robustness and generalization on complex articulated objects, we develop a fully automated dataset expansion pipeline, name LEGO-Art, that enriches the diversity and complexity of PartNet-Mobility dataset. We propose PM-X, a large-scale dataset of complex articulated 3D objects, accompanied by rendered images, URDF annotations, and textual descriptions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DIPO significantly outperforms existing baselines in both the resting state and the articulated state, while the proposed PM-X dataset further enhances generalization to diverse and structurally complex articulated objects. Our code and dataset will be released to the community upon publication.
SEM: Enhancing Spatial Understanding for Robust Robot Manipulation
May 22, 2025Abstract:A key challenge in robot manipulation lies in developing policy models with strong spatial understanding, the ability to reason about 3D geometry, object relations, and robot embodiment. Existing methods often fall short: 3D point cloud models lack semantic abstraction, while 2D image encoders struggle with spatial reasoning. To address this, we propose SEM (Spatial Enhanced Manipulation model), a novel diffusion-based policy framework that explicitly enhances spatial understanding from two complementary perspectives. A spatial enhancer augments visual representations with 3D geometric context, while a robot state encoder captures embodiment-aware structure through graphbased modeling of joint dependencies. By integrating these modules, SEM significantly improves spatial understanding, leading to robust and generalizable manipulation across diverse tasks that outperform existing baselines.
Aux-Think: Exploring Reasoning Strategies for Data-Efficient Vision-Language Navigation
May 17, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Navigation (VLN) is a critical task for developing embodied agents that can follow natural language instructions to navigate in complex real-world environments. Recent advances in VLN by large pretrained models have significantly improved generalization and instruction grounding compared to traditional approaches. However, the role of reasoning strategies in navigation-an action-centric, long-horizon task-remains underexplored, despite Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning's demonstrated success in static tasks like visual question answering. To address this gap, we conduct the first systematic evaluation of reasoning strategies for VLN, including No-Think (direct action prediction), Pre-Think (reason before action), and Post-Think (reason after action). Surprisingly, our findings reveal the Inference-time Reasoning Collapse issue, where inference-time reasoning degrades navigation accuracy, highlighting the challenges of integrating reasoning into VLN. Based on this insight, we propose Aux-Think, a framework that trains models to internalize structured reasoning patterns through CoT supervision, while inferring action directly without reasoning in online prediction. To support this framework, we release R2R-CoT-320k, the first Chain-of-Thought annotated dataset for VLN. Extensive experiments show that Aux-Think reduces training effort greatly and achieves the best performance under the same data scale.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge