Xinjie Wang
DreamLifting: A Plug-in Module Lifting MV Diffusion Models for 3D Asset Generation
Sep 09, 2025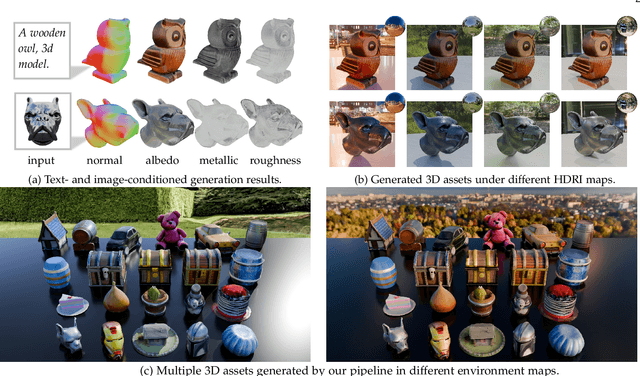

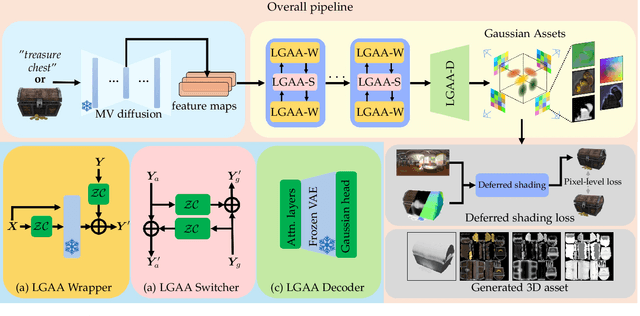
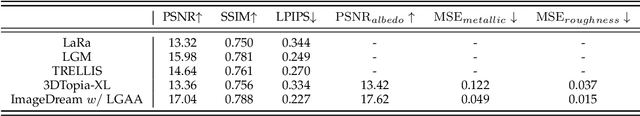
Abstract:The labor- and experience-intensive creation of 3D assets with physically based rendering (PBR) materials demands an autonomous 3D asset creation pipeline. However, most existing 3D generation methods focus on geometry modeling, either baking textures into simple vertex colors or leaving texture synthesis to post-processing with image diffusion models. To achieve end-to-end PBR-ready 3D asset generation, we present Lightweight Gaussian Asset Adapter (LGAA), a novel framework that unifies the modeling of geometry and PBR materials by exploiting multi-view (MV) diffusion priors from a novel perspective. The LGAA features a modular design with three components. Specifically, the LGAA Wrapper reuses and adapts network layers from MV diffusion models, which encapsulate knowledge acquired from billions of images, enabling better convergence in a data-efficient manner. To incorporate multiple diffusion priors for geometry and PBR synthesis, the LGAA Switcher aligns multiple LGAA Wrapper layers encapsulating different knowledge. Then, a tamed variational autoencoder (VAE), termed LGAA Decoder, is designed to predict 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS) with PBR channels. Finally, we introduce a dedicated post-processing procedure to effectively extract high-quality, relightable mesh assets from the resulting 2DGS. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate the superior performance of LGAA with both text-and image-conditioned MV diffusion models. Additionally, the modular design enables flexible incorporation of multiple diffusion priors, and the knowledge-preserving scheme leads to efficient convergence trained on merely 69k multi-view instances. Our code, pre-trained weights, and the dataset used will be publicly available via our project page: https://zx-yin.github.io/dreamlifting/.
DIPO: Dual-State Images Controlled Articulated Object Generation Powered by Diverse Data
May 28, 2025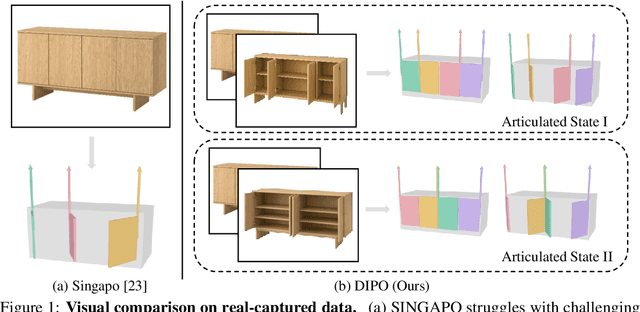
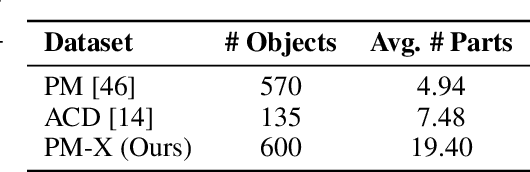
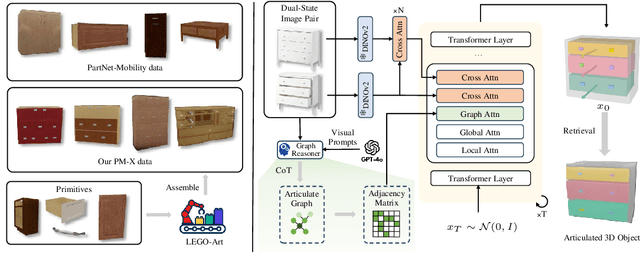
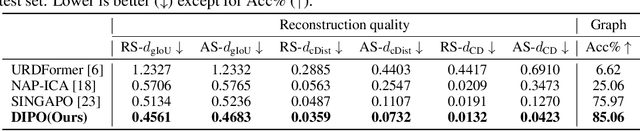
Abstract:We present DIPO, a novel framework for the controllable generation of articulated 3D objects from a pair of images: one depicting the object in a resting state and the other in an articulated state. Compared to the single-image approach, our dual-image input imposes only a modest overhead for data collection, but at the same time provides important motion information, which is a reliable guide for predicting kinematic relationships between parts. Specifically, we propose a dual-image diffusion model that captures relationships between the image pair to generate part layouts and joint parameters. In addition, we introduce a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) based graph reasoner that explicitly infers part connectivity relationships. To further improve robustness and generalization on complex articulated objects, we develop a fully automated dataset expansion pipeline, name LEGO-Art, that enriches the diversity and complexity of PartNet-Mobility dataset. We propose PM-X, a large-scale dataset of complex articulated 3D objects, accompanied by rendered images, URDF annotations, and textual descriptions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DIPO significantly outperforms existing baselines in both the resting state and the articulated state, while the proposed PM-X dataset further enhances generalization to diverse and structurally complex articulated objects. Our code and dataset will be released to the community upon publication.
GeoFlow-SLAM: A Robust Tightly-Coupled RGBD-Inertial Fusion SLAM for Dynamic Legged Robotics
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:This paper presents GeoFlow-SLAM, a robust and effective Tightly-Coupled RGBD-inertial SLAM for legged robots operating in highly dynamic environments.By integrating geometric consistency, legged odometry constraints, and dual-stream optical flow (GeoFlow), our method addresses three critical challenges:feature matching and pose initialization failures during fast locomotion and visual feature scarcity in texture-less scenes.Specifically, in rapid motion scenarios, feature matching is notably enhanced by leveraging dual-stream optical flow, which combines prior map points and poses. Additionally, we propose a robust pose initialization method for fast locomotion and IMU error in legged robots, integrating IMU/Legged odometry, inter-frame Perspective-n-Point (PnP), and Generalized Iterative Closest Point (GICP). Furthermore, a novel optimization framework that tightly couples depth-to-map and GICP geometric constraints is first introduced to improve the robustness and accuracy in long-duration, visually texture-less environments. The proposed algorithms achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) on collected legged robots and open-source datasets. To further promote research and development, the open-source datasets and code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/NSN-Hello/GeoFlow-SLAM
GaussTR: Foundation Model-Aligned Gaussian Transformer for Self-Supervised 3D Spatial Understanding
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:3D Semantic Occupancy Prediction is fundamental for spatial understanding as it provides a comprehensive semantic cognition of surrounding environments. However, prevalent approaches primarily rely on extensive labeled data and computationally intensive voxel-based modeling, restricting the scalability and generalizability of 3D representation learning. In this paper, we introduce GaussTR, a novel Gaussian Transformer that leverages alignment with foundation models to advance self-supervised 3D spatial understanding. GaussTR adopts a Transformer architecture to predict sparse sets of 3D Gaussians that represent scenes in a feed-forward manner. Through aligning rendered Gaussian features with diverse knowledge from pre-trained foundation models, GaussTR facilitates the learning of versatile 3D representations and enables open-vocabulary occupancy prediction without explicit annotations. Empirical evaluations on the Occ3D-nuScenes dataset showcase GaussTR's state-of-the-art zero-shot performance, achieving 11.70 mIoU while reducing training duration by approximately 50%. These experimental results highlight the significant potential of GaussTR for scalable and holistic 3D spatial understanding, with promising implications for autonomous driving and embodied agents. Code is available at https://github.com/hustvl/GaussTR.
Gaussian Object Carver: Object-Compositional Gaussian Splatting with surfaces completion
Dec 03, 2024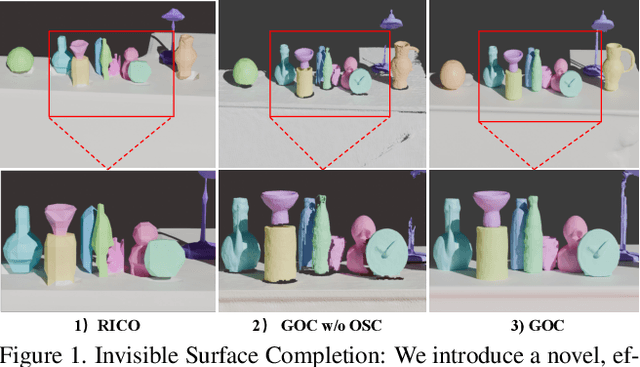
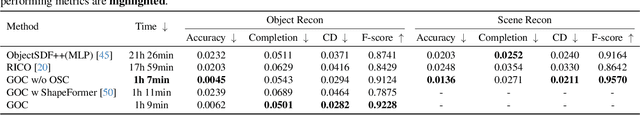
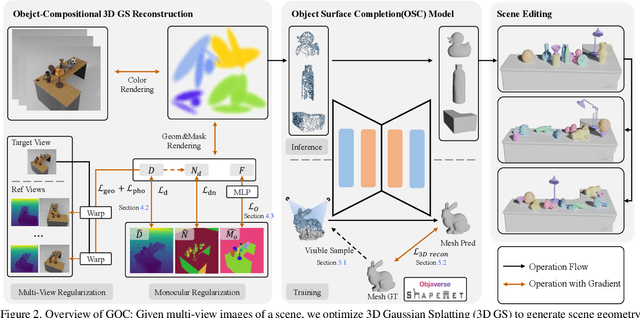
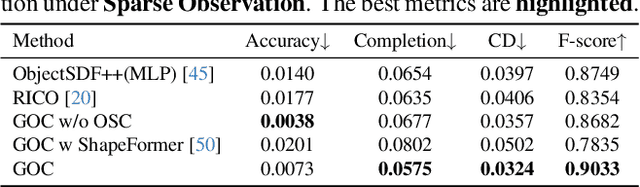
Abstract:3D scene reconstruction is a foundational problem in computer vision. Despite recent advancements in Neural Implicit Representations (NIR), existing methods often lack editability and compositional flexibility, limiting their use in scenarios requiring high interactivity and object-level manipulation. In this paper, we introduce the Gaussian Object Carver (GOC), a novel, efficient, and scalable framework for object-compositional 3D scene reconstruction. GOC leverages 3D Gaussian Splatting (GS), enriched with monocular geometry priors and multi-view geometry regularization, to achieve high-quality and flexible reconstruction. Furthermore, we propose a zero-shot Object Surface Completion (OSC) model, which uses 3D priors from 3d object data to reconstruct unobserved surfaces, ensuring object completeness even in occluded areas. Experimental results demonstrate that GOC improves reconstruction efficiency and geometric fidelity. It holds promise for advancing the practical application of digital twins in embodied AI, AR/VR, and interactive simulation environments.
Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Mobile Edge Computing for Intelligent Internet of Things
Aug 01, 2020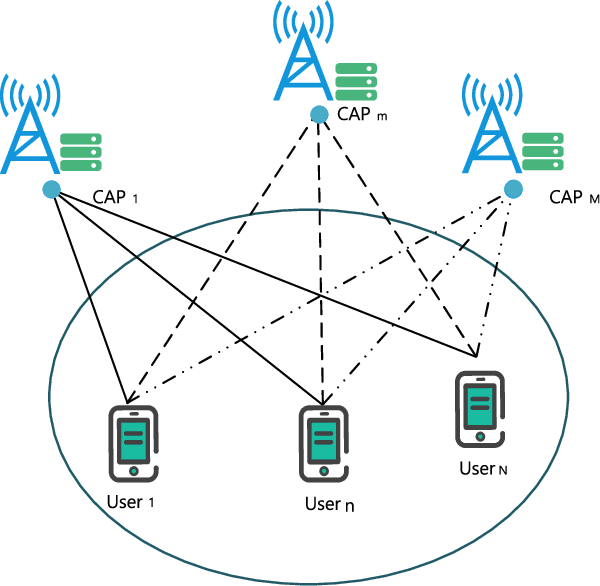



Abstract:In this paper, we investigate mobile edge computing (MEC) networks for intelligent internet of things (IoT), where multiple users have some computational tasks assisted by multiple computational access points (CAPs). By offloading some tasks to the CAPs, the system performance can be improved through reducing the latency and energy consumption, which are the two important metrics of interest in the MEC networks. We devise the system by proposing the offloading strategy intelligently through the deep reinforcement learning algorithm. In this algorithm, Deep Q-Network is used to automatically learn the offloading decision in order to optimize the system performance, and a neural network (NN) is trained to predict the offloading action, where the training data is generated from the environmental system. Moreover, we employ the bandwidth allocation in order to optimize the wireless spectrum for the links between the users and CAPs, where several bandwidth allocation schemes are proposed. In further, we use the CAP selection in order to choose one best CAP to assist the computational tasks from the users. Simulation results are finally presented to show the effectiveness of the proposed reinforcement learning offloading strategy. In particular, the system cost of latency and energy consumption can be reduced significantly by the proposed deep reinforcement learning based algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge