Liu Liu
UniGeo: A Unified 3D Indoor Object Detection Framework Integrating Geometry-Aware Learning and Dynamic Channel Gating
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The growing adoption of robotics and augmented reality in real-world applications has driven considerable research interest in 3D object detection based on point clouds. While previous methods address unified training across multiple datasets, they fail to model geometric relationships in sparse point cloud scenes and ignore the feature distribution in significant areas, which ultimately restricts their performance. To deal with this issue, a unified 3D indoor detection framework, called UniGeo, is proposed. To model geometric relations in scenes, we first propose a geometry-aware learning module that establishes a learnable mapping from spatial relationships to feature weights, which enabes explicit geometric feature enhancement. Then, to further enhance point cloud feature representation, we propose a dynamic channel gating mechanism that leverages learnable channel-wise weighting. This mechanism adaptively optimizes features generated by the sparse 3D U-Net network, significantly enhancing key geometric information. Extensive experiments on six different indoor scene datasets clearly validate the superior performance of our method.
YOLO-DS: Fine-Grained Feature Decoupling via Dual-Statistic Synergy Operator for Object Detection
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:One-stage object detection, particularly the YOLO series, strikes a favorable balance between accuracy and efficiency. However, existing YOLO detectors lack explicit modeling of heterogeneous object responses within shared feature channels, which limits further performance gains. To address this, we propose YOLO-DS, a framework built around a novel Dual-Statistic Synergy Operator (DSO). The DSO decouples object features by jointly modeling the channel-wise mean and the peak-to-mean difference. Building upon the DSO, we design two lightweight gating modules: the Dual-Statistic Synergy Gating (DSG) module for adaptive channel-wise feature selection, and the Multi-Path Segmented Gating (MSG) module for depth-wise feature weighting. On the MS-COCO benchmark, YOLO-DS consistently outperforms YOLOv8 across five model scales (N, S, M, L, X), achieving AP gains of 1.1% to 1.7% with only a minimal increase in inference latency. Extensive visualization, ablation, and comparative studies validate the effectiveness of our approach, demonstrating its superior capability in discriminating heterogeneous objects with high efficiency.
Tears or Cheers? Benchmarking LLMs via Culturally Elicited Distinct Affective Responses
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Culture serves as a fundamental determinant of human affective processing and profoundly shapes how individuals perceive and interpret emotional stimuli. Despite this intrinsic link extant evaluations regarding cultural alignment within Large Language Models primarily prioritize declarative knowledge such as geographical facts or established societal customs. These benchmarks remain insufficient to capture the subjective interpretative variance inherent to diverse sociocultural lenses. To address this limitation, we introduce CEDAR, a multimodal benchmark constructed entirely from scenarios capturing Culturally \underline{\textsc{E}}licited \underline{\textsc{D}}istinct \underline{\textsc{A}}ffective \underline{\textsc{R}}esponses. To construct CEDAR, we implement a novel pipeline that leverages LLM-generated provisional labels to isolate instances yielding cross-cultural emotional distinctions, and subsequently derives reliable ground-truth annotations through rigorous human evaluation. The resulting benchmark comprises 10,962 instances across seven languages and 14 fine-grained emotion categories, with each language including 400 multimodal and 1,166 text-only samples. Comprehensive evaluations of 17 representative multilingual models reveal a dissociation between language consistency and cultural alignment, demonstrating that culturally grounded affective understanding remains a significant challenge for current models.
A Novel Deep Learning-Based Coarse-to-Fine Frame Synchronization Method for OTFS Systems
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation is a robust candidate waveform for future wireless systems, particularly in high-mobility scenarios, as it effectively mitigates the impact of rapidly time-varying channels by mapping symbols in the delay-Doppler (DD) domain. However, accurate frame synchronization in OTFS systems remains a challenge due to the performance limitations of conventional algorithms. To address this, we propose a low-complexity synchronization method based on a coarse-to-fine deep residual network (ResNet) architecture. Unlike traditional approaches relying on high-overhead preamble structures, our method exploits the intrinsic periodic features of OTFS pilots in the delay-time (DT) domain to formulate synchronization as a hierarchical classification problem. Specifically, the proposed architecture employs a two-stage strategy to first narrow the search space and then pinpoint the precise symbol timing offset (STO), thereby significantly reducing computational complexity while maintaining high estimation accuracy. We construct a comprehensive simulation dataset incorporating diverse channel models and randomized STO to validate the method. Extensive simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves robust signal start detection and superior accuracy compared to conventional benchmarks, particularly in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regimes and high-mobility scenarios.
RecurGS: Interactive Scene Modeling via Discrete-State Recurrent Gaussian Fusion
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in 3D scene representations have enabled high-fidelity novel view synthesis, yet adapting to discrete scene changes and constructing interactive 3D environments remain open challenges in vision and robotics. Existing approaches focus solely on updating a single scene without supporting novel-state synthesis. Others rely on diffusion-based object-background decoupling that works on one state at a time and cannot fuse information across multiple observations. To address these limitations, we introduce RecurGS, a recurrent fusion framework that incrementally integrates discrete Gaussian scene states into a single evolving representation capable of interaction. RecurGS detects object-level changes across consecutive states, aligns their geometric motion using semantic correspondence and Lie-algebra based SE(3) refinement, and performs recurrent updates that preserve historical structures through replay supervision. A voxelized, visibility-aware fusion module selectively incorporates newly observed regions while keeping stable areas fixed, mitigating catastrophic forgetting and enabling efficient long-horizon updates. RecurGS supports object-level manipulation, synthesizes novel scene states without requiring additional scans, and maintains photorealistic fidelity across evolving environments. Extensive experiments across synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our framework delivers high-quality reconstructions with substantially improved update efficiency, providing a scalable step toward continuously interactive Gaussian worlds.
Bandwidth-Efficient Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts via Low-Rank Compensation
Dec 18, 2025



Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models scale capacity via sparse activation but stress memory and bandwidth. Offloading alleviates GPU memory by fetching experts on demand, yet token-level routing causes irregular transfers that make inference I/O-bound. Static uniform quantization reduces traffic but degrades accuracy under aggressive compression by ignoring expert heterogeneity. We present Bandwidth-Efficient Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts via Low-Rank Compensation, which performs router-guided precision restoration using precomputed low-rank compensators. At inference time, our method transfers compact low-rank factors with Top-n (n<k) experts per token and applies compensation to them, keeping others low-bit. Integrated with offloading on GPU and GPU-NDP systems, our method delivers a superior bandwidth-accuracy trade-off and improved throughput.
SparseST: Exploiting Data Sparsity in Spatiotemporal Modeling and Prediction
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Spatiotemporal data mining (STDM) has a wide range of applications in various complex physical systems (CPS), i.e., transportation, manufacturing, healthcare, etc. Among all the proposed methods, the Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory (ConvLSTM) has proved to be generalizable and extendable in different applications and has multiple variants achieving state-of-the-art performance in various STDM applications. However, ConvLSTM and its variants are computationally expensive, which makes them inapplicable in edge devices with limited computational resources. With the emerging need for edge computing in CPS, efficient AI is essential to reduce the computational cost while preserving the model performance. Common methods of efficient AI are developed to reduce redundancy in model capacity (i.e., model pruning, compression, etc.). However, spatiotemporal data mining naturally requires extensive model capacity, as the embedded dependencies in spatiotemporal data are complex and hard to capture, which limits the model redundancy. Instead, there is a fairly high level of data and feature redundancy that introduces an unnecessary computational burden, which has been largely overlooked in existing research. Therefore, we developed a novel framework SparseST, that pioneered in exploiting data sparsity to develop an efficient spatiotemporal model. In addition, we explore and approximate the Pareto front between model performance and computational efficiency by designing a multi-objective composite loss function, which provides a practical guide for practitioners to adjust the model according to computational resource constraints and the performance requirements of downstream tasks.
SciAgent: A Unified Multi-Agent System for Generalistic Scientific Reasoning
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have enabled AI systems to achieve expert-level performance on domain-specific scientific tasks, yet these systems remain narrow and handcrafted. We introduce SciAgent, a unified multi-agent system designed for generalistic scientific reasoning-the ability to adapt reasoning strategies across disciplines and difficulty levels. SciAgent organizes problem solving as a hierarchical process: a Coordinator Agent interprets each problem's domain and complexity, dynamically orchestrating specialized Worker Systems, each composed of interacting reasoning Sub-agents for symbolic deduction, conceptual modeling, numerical computation, and verification. These agents collaboratively assemble and refine reasoning pipelines tailored to each task. Across mathematics and physics Olympiads (IMO, IMC, IPhO, CPhO), SciAgent consistently attains or surpasses human gold-medalist performance, demonstrating both domain generality and reasoning adaptability. Additionally, SciAgent has been tested on the International Chemistry Olympiad (IChO) and selected problems from the Humanity's Last Exam (HLE) benchmark, further confirming the system's ability to generalize across diverse scientific domains. This work establishes SciAgent as a concrete step toward generalistic scientific intelligence-AI systems capable of coherent, cross-disciplinary reasoning at expert levels.
Remodeling Semantic Relationships in Vision-Language Fine-Tuning
Nov 13, 2025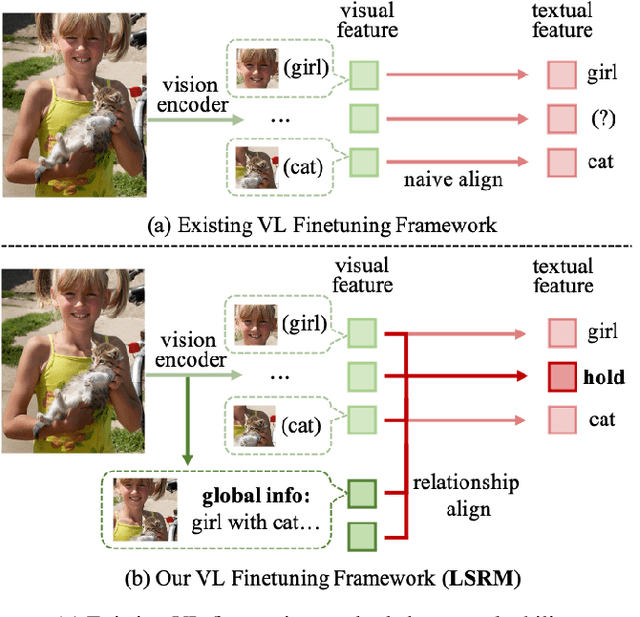

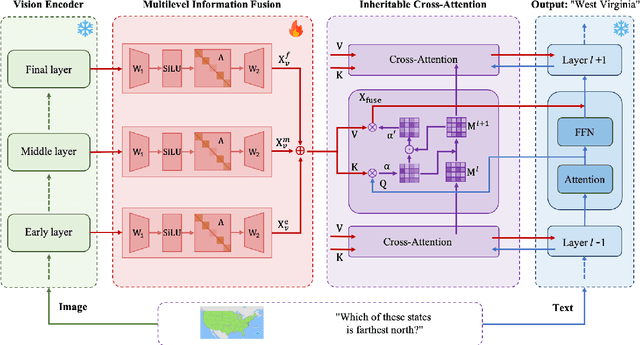

Abstract:Vision-language fine-tuning has emerged as an efficient paradigm for constructing multimodal foundation models. While textual context often highlights semantic relationships within an image, existing fine-tuning methods typically overlook this information when aligning vision and language, thus leading to suboptimal performance. Toward solving this problem, we propose a method that can improve multimodal alignment and fusion based on both semantics and relationships.Specifically, we first extract multilevel semantic features from different vision encoder to capture more visual cues of the relationships. Then, we learn to project the vision features to group related semantics, among which are more likely to have relationships. Finally, we fuse the visual features with the textual by using inheritable cross-attention, where we globally remove the redundant visual relationships by discarding visual-language feature pairs with low correlation. We evaluate our proposed method on eight foundation models and two downstream tasks, visual question answering and image captioning, and show that it outperforms all existing methods.
Exploring Category-level Articulated Object Pose Tracking on SE(3) Manifolds
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Articulated objects are prevalent in daily life and robotic manipulation tasks. However, compared to rigid objects, pose tracking for articulated objects remains an underexplored problem due to their inherent kinematic constraints. To address these challenges, this work proposes a novel point-pair-based pose tracking framework, termed \textbf{PPF-Tracker}. The proposed framework first performs quasi-canonicalization of point clouds in the SE(3) Lie group space, and then models articulated objects using Point Pair Features (PPF) to predict pose voting parameters by leveraging the invariance properties of SE(3). Finally, semantic information of joint axes is incorporated to impose unified kinematic constraints across all parts of the articulated object. PPF-Tracker is systematically evaluated on both synthetic datasets and real-world scenarios, demonstrating strong generalization across diverse and challenging environments. Experimental results highlight the effectiveness and robustness of PPF-Tracker in multi-frame pose tracking of articulated objects. We believe this work can foster advances in robotics, embodied intelligence, and augmented reality. Codes are available at https://github.com/mengxh20/PPFTracker.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge