Juan Wang
LLM-as-a-Supervisor: Mistaken Therapeutic Behaviors Trigger Targeted Supervisory Feedback
Aug 12, 2025



Abstract:Although large language models (LLMs) hold significant promise in psychotherapy, their direct application in patient-facing scenarios raises ethical and safety concerns. Therefore, this work shifts towards developing an LLM as a supervisor to train real therapists. In addition to the privacy of clinical therapist training data, a fundamental contradiction complicates the training of therapeutic behaviors: clear feedback standards are necessary to ensure a controlled training system, yet there is no absolute "gold standard" for appropriate therapeutic behaviors in practice. In contrast, many common therapeutic mistakes are universal and identifiable, making them effective triggers for targeted feedback that can serve as clearer evidence. Motivated by this, we create a novel therapist-training paradigm: (1) guidelines for mistaken behaviors and targeted correction strategies are first established as standards; (2) a human-in-the-loop dialogue-feedback dataset is then constructed, where a mistake-prone agent intentionally makes standard mistakes during interviews naturally, and a supervisor agent locates and identifies mistakes and provides targeted feedback; (3) after fine-tuning on this dataset, the final supervisor model is provided for real therapist training. The detailed experimental results of automated, human and downstream assessments demonstrate that models fine-tuned on our dataset MATE, can provide high-quality feedback according to the clinical guideline, showing significant potential for the therapist training scenario.
NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image (T2I) generation model quality assessment, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2025. The aim of this challenge is to address the fine-grained quality assessment of text-to-image generation models. This challenge evaluates text-to-image models from two aspects: image-text alignment and image structural distortion detection, and is divided into the alignment track and the structural track. The alignment track uses the EvalMuse-40K, which contains around 40K AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 20 popular generative models. The alignment track has a total of 371 registered participants. A total of 1,883 submissions are received in the development phase, and 507 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The structure track uses the EvalMuse-Structure, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) with corresponding structural distortion mask. A total of 211 participants have registered in the structure track. A total of 1155 submissions are received in the development phase, and 487 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 8 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on T2I model quality assessment.
SoftHGNN: Soft Hypergraph Neural Networks for General Visual Recognition
May 21, 2025Abstract:Visual recognition relies on understanding both the semantics of image tokens and the complex interactions among them. Mainstream self-attention methods, while effective at modeling global pair-wise relations, fail to capture high-order associations inherent in real-world scenes and often suffer from redundant computation. Hypergraphs extend conventional graphs by modeling high-order interactions and offer a promising framework for addressing these limitations. However, existing hypergraph neural networks typically rely on static and hard hyperedge assignments, leading to excessive and redundant hyperedges with hard binary vertex memberships that overlook the continuity of visual semantics. To overcome these issues, we present Soft Hypergraph Neural Networks (SoftHGNNs), which extend the methodology of hypergraph computation, to make it truly efficient and versatile in visual recognition tasks. Our framework introduces the concept of soft hyperedges, where each vertex is associated with hyperedges via continuous participation weights rather than hard binary assignments. This dynamic and differentiable association is achieved by using the learnable hyperedge prototype. Through similarity measurements between token features and the prototype, the model generates semantically rich soft hyperedges. SoftHGNN then aggregates messages over soft hyperedges to capture high-order semantics. To further enhance efficiency when scaling up the number of soft hyperedges, we incorporate a sparse hyperedge selection mechanism that activates only the top-k important hyperedges, along with a load-balancing regularizer to ensure balanced hyperedge utilization. Experimental results across three tasks on five datasets demonstrate that SoftHGNN efficiently captures high-order associations in visual scenes, achieving significant performance improvements.
SEAGULL: No-reference Image Quality Assessment for Regions of Interest via Vision-Language Instruction Tuning
Nov 15, 2024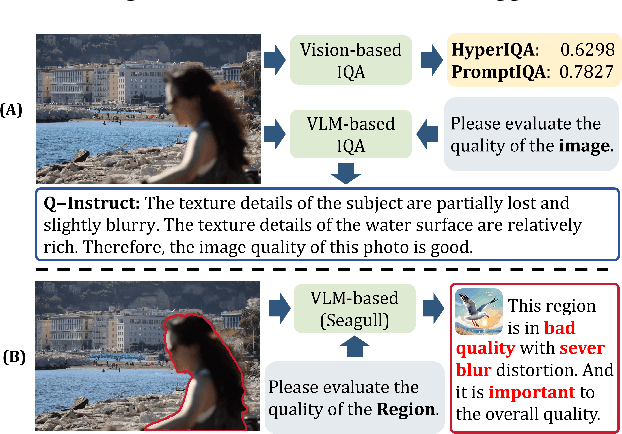



Abstract:Existing Image Quality Assessment (IQA) methods achieve remarkable success in analyzing quality for overall image, but few works explore quality analysis for Regions of Interest (ROIs). The quality analysis of ROIs can provide fine-grained guidance for image quality improvement and is crucial for scenarios focusing on region-level quality. This paper proposes a novel network, SEAGULL, which can SEe and Assess ROIs quality with GUidance from a Large vision-Language model. SEAGULL incorporates a vision-language model (VLM), masks generated by Segment Anything Model (SAM) to specify ROIs, and a meticulously designed Mask-based Feature Extractor (MFE) to extract global and local tokens for specified ROIs, enabling accurate fine-grained IQA for ROIs. Moreover, this paper constructs two ROI-based IQA datasets, SEAGULL-100w and SEAGULL-3k, for training and evaluating ROI-based IQA. SEAGULL-100w comprises about 100w synthetic distortion images with 33 million ROIs for pre-training to improve the model's ability of regional quality perception, and SEAGULL-3k contains about 3k authentic distortion ROIs to enhance the model's ability to perceive real world distortions. After pre-training on SEAGULL-100w and fine-tuning on SEAGULL-3k, SEAGULL shows remarkable performance on fine-grained ROI quality assessment. Code and datasets are publicly available at the https://github.com/chencn2020/Seagull.
Autonomous Driving in Unstructured Environments: How Far Have We Come?
Oct 10, 2024

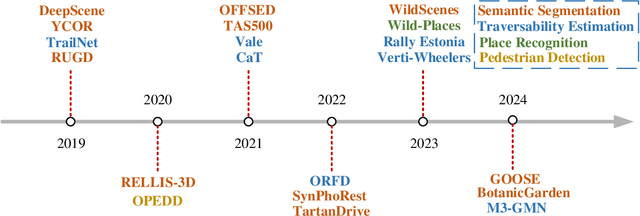
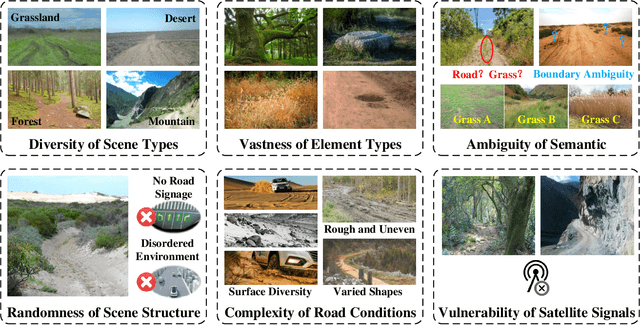
Abstract:Research on autonomous driving in unstructured outdoor environments is less advanced than in structured urban settings due to challenges like environmental diversities and scene complexity. These environments-such as rural areas and rugged terrains-pose unique obstacles that are not common in structured urban areas. Despite these difficulties, autonomous driving in unstructured outdoor environments is crucial for applications in agriculture, mining, and military operations. Our survey reviews over 250 papers for autonomous driving in unstructured outdoor environments, covering offline mapping, pose estimation, environmental perception, path planning, end-to-end autonomous driving, datasets, and relevant challenges. We also discuss emerging trends and future research directions. This review aims to consolidate knowledge and encourage further research for autonomous driving in unstructured environments. To support ongoing work, we maintain an active repository with up-to-date literature and open-source projects at: https://github.com/chaytonmin/Survey-Autonomous-Driving-in-Unstructured-Environments.
Structure-Centric Robust Monocular Depth Estimation via Knowledge Distillation
Oct 09, 2024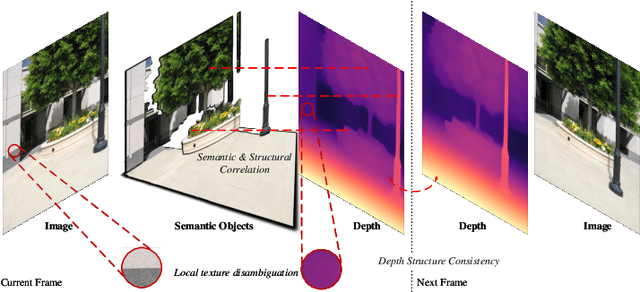
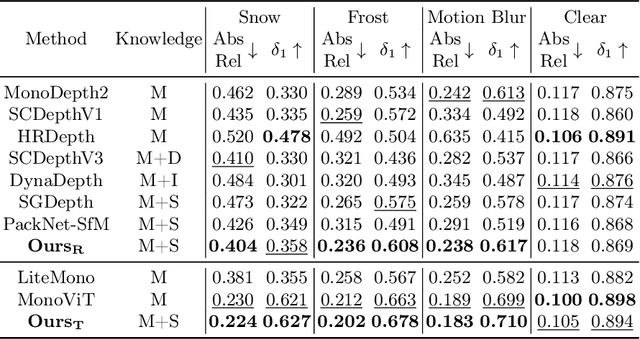
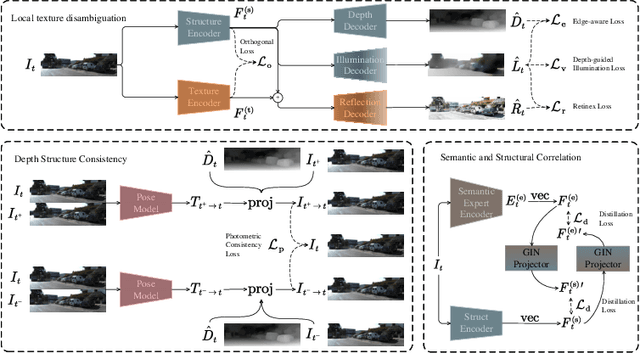
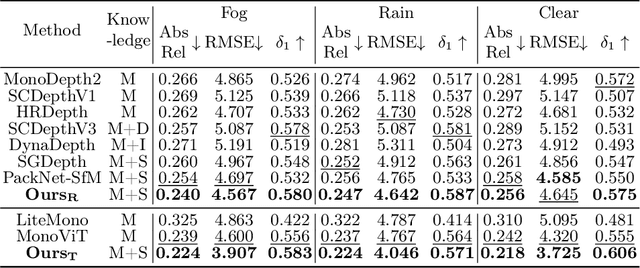
Abstract:Monocular depth estimation, enabled by self-supervised learning, is a key technique for 3D perception in computer vision. However, it faces significant challenges in real-world scenarios, which encompass adverse weather variations, motion blur, as well as scenes with poor lighting conditions at night. Our research reveals that we can divide monocular depth estimation into three sub-problems: depth structure consistency, local texture disambiguation, and semantic-structural correlation. Our approach tackles the non-robustness of existing self-supervised monocular depth estimation models to interference textures by adopting a structure-centered perspective and utilizing the scene structure characteristics demonstrated by semantics and illumination. We devise a novel approach to reduce over-reliance on local textures, enhancing robustness against missing or interfering patterns. Additionally, we incorporate a semantic expert model as the teacher and construct inter-model feature dependencies via learnable isomorphic graphs to enable aggregation of semantic structural knowledge. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art out-of-distribution monocular depth estimation performance across a range of public adverse scenario datasets. It demonstrates notable scalability and compatibility, without necessitating extensive model engineering. This showcases the potential for customizing models for diverse industrial applications.
MobileIQA: Exploiting Mobile-level Diverse Opinion Network For No-Reference Image Quality Assessment Using Knowledge Distillation
Sep 02, 2024Abstract:With the rising demand for high-resolution (HR) images, No-Reference Image Quality Assessment (NR-IQA) gains more attention, as it can ecaluate image quality in real-time on mobile devices and enhance user experience. However, existing NR-IQA methods often resize or crop the HR images into small resolution, which leads to a loss of important details. And most of them are of high computational complexity, which hinders their application on mobile devices due to limited computational resources. To address these challenges, we propose MobileIQA, a novel approach that utilizes lightweight backbones to efficiently assess image quality while preserving image details through high-resolution input. MobileIQA employs the proposed multi-view attention learning (MAL) module to capture diverse opinions, simulating subjective opinions provided by different annotators during the dataset annotation process. The model uses a teacher model to guide the learning of a student model through knowledge distillation. This method significantly reduces computational complexity while maintaining high performance. Experiments demonstrate that MobileIQA outperforms novel IQA methods on evaluation metrics and computational efficiency. The code is available at https://github.com/chencn2020/MobileIQA.
Map-Free Visual Relocalization Enhanced by Instance Knowledge and Depth Knowledge
Aug 23, 2024
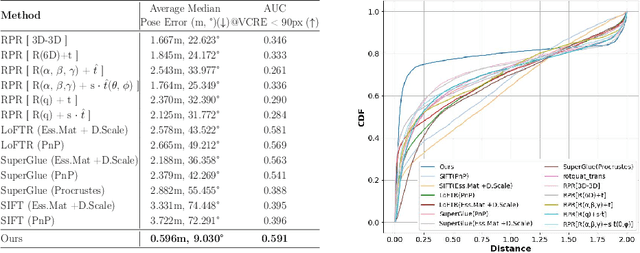
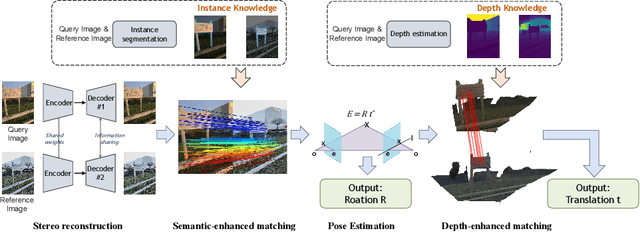

Abstract:Map-free relocalization technology is crucial for applications in autonomous navigation and augmented reality, but relying on pre-built maps is often impractical. It faces significant challenges due to limitations in matching methods and the inherent lack of scale in monocular images. These issues lead to substantial rotational and metric errors and even localization failures in real-world scenarios. Large matching errors significantly impact the overall relocalization process, affecting both rotational and translational accuracy. Due to the inherent limitations of the camera itself, recovering the metric scale from a single image is crucial, as this significantly impacts the translation error. To address these challenges, we propose a map-free relocalization method enhanced by instance knowledge and depth knowledge. By leveraging instance-based matching information to improve global matching results, our method significantly reduces the possibility of mismatching across different objects. The robustness of instance knowledge across the scene helps the feature point matching model focus on relevant regions and enhance matching accuracy. Additionally, we use estimated metric depth from a single image to reduce metric errors and improve scale recovery accuracy. By integrating methods dedicated to mitigating large translational and rotational errors, our approach demonstrates superior performance in map-free relocalization techniques.
LCE: A Framework for Explainability of DNNs for Ultrasound Image Based on Concept Discovery
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:Explaining the decisions of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) for medical images has become increasingly important. Existing attribution methods have difficulty explaining the meaning of pixels while existing concept-based methods are limited by additional annotations or specific model structures that are difficult to apply to ultrasound images. In this paper, we propose the Lesion Concept Explainer (LCE) framework, which combines attribution methods with concept-based methods. We introduce the Segment Anything Model (SAM), fine-tuned on a large number of medical images, for concept discovery to enable a meaningful explanation of ultrasound image DNNs. The proposed framework is evaluated in terms of both faithfulness and understandability. We point out deficiencies in the popular faithfulness evaluation metrics and propose a new evaluation metric. Our evaluation of public and private breast ultrasound datasets (BUSI and FG-US-B) shows that LCE performs well compared to commonly-used explainability methods. Finally, we also validate that LCE can consistently provide reliable explanations for more meaningful fine-grained diagnostic tasks in breast ultrasound.
LncRNA-disease association prediction method based on heterogeneous information completion and convolutional neural network
Jun 02, 2024



Abstract:The emerging research shows that lncRNA has crucial research value in a series of complex human diseases. Therefore, the accurate identification of lncRNA-disease associations (LDAs) is very important for the warning and treatment of diseases. However, most of the existing methods have limitations in identifying nonlinear LDAs, and it remains a huge challenge to predict new LDAs. In this paper, a deep learning model based on a heterogeneous network and convolutional neural network (CNN) is proposed for lncRNA-disease association prediction, named HCNNLDA. The heterogeneous network containing the lncRNA, disease, and miRNA nodes, is constructed firstly. The embedding matrix of a lncRNA-disease node pair is constructed according to various biological premises about lncRNAs, diseases, and miRNAs. Then, the low-dimensional feature representation is fully learned by the convolutional neural network. In the end, the XGBoot classifier model is trained to predict the potential LDAs. HCNNLDA obtains a high AUC value of 0.9752 and AUPR of 0.9740 under the 5-fold cross-validation. The experimental results show that the proposed model has better performance than that of several latest prediction models. Meanwhile, the effectiveness of HCNNLDA in identifying novel LDAs is further demonstrated by case studies of three diseases. To sum up, HCNNLDA is a feasible calculation model to predict LDAs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge