Xu Ling
Dive into the Resolution Augmentations and Metrics in Low Resolution Face Recognition: A Plain yet Effective New Baseline
Feb 11, 2023



Abstract:Although deep learning has significantly improved Face Recognition (FR), dramatic performance deterioration may occur when processing Low Resolution (LR) faces. To alleviate this, approaches based on unified feature space are proposed with the sacrifice under High Resolution (HR) circumstances. To deal with the huge domain gap between HR and LR domains and achieve the best on both domains, we first took a closer look at the impacts of several resolution augmentations and then analyzed the difficulty of LR samples from the perspective of the model gradient produced by different resolution samples. Besides, we also find that the introduction of some resolutions could help the learning of lower resolutions. Based on these, we divide the LR samples into three difficulties according to the resolution and propose a more effective Multi-Resolution Augmentation. Then, due to the rapidly increasing domain gap as the resolution decreases, we carefully design a novel and effective metric loss based on a LogExp distance function that provides decent gradients to prevent oscillation near the convergence point or tolerance to small distance errors; it could also dynamically adjust the penalty for errors in different dimensions, allowing for more optimization of dimensions with large errors. Combining these two insights, our model could learn more general knowledge in a wide resolution range of images and balanced results can be achieved by our extremely simple framework. Moreover, the augmentations and metrics are the cornerstones of LRFR, so our method could be considered a new baseline for the LRFR task. Experiments on the LRFR datasets: SCface, XQLFW, and large-scale LRFR dataset: TinyFace demonstrate the effectiveness of our methods, while the degradation on HRFR datasets is significantly reduced.
Learn From All: Erasing Attention Consistency for Noisy Label Facial Expression Recognition
Jul 21, 2022
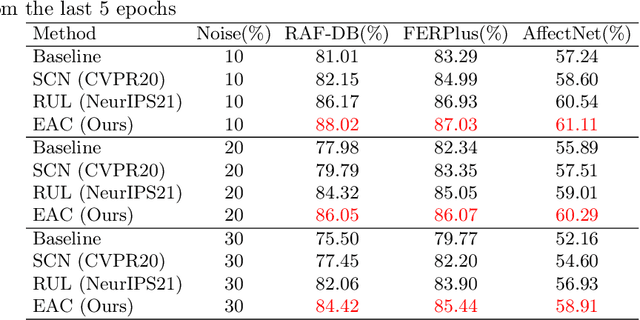
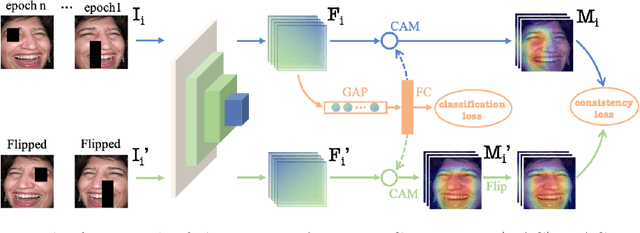
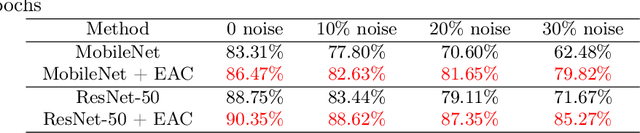
Abstract:Noisy label Facial Expression Recognition (FER) is more challenging than traditional noisy label classification tasks due to the inter-class similarity and the annotation ambiguity. Recent works mainly tackle this problem by filtering out large-loss samples. In this paper, we explore dealing with noisy labels from a new feature-learning perspective. We find that FER models remember noisy samples by focusing on a part of the features that can be considered related to the noisy labels instead of learning from the whole features that lead to the latent truth. Inspired by that, we propose a novel Erasing Attention Consistency (EAC) method to suppress the noisy samples during the training process automatically. Specifically, we first utilize the flip semantic consistency of facial images to design an imbalanced framework. We then randomly erase input images and use flip attention consistency to prevent the model from focusing on a part of the features. EAC significantly outperforms state-of-the-art noisy label FER methods and generalizes well to other tasks with a large number of classes like CIFAR100 and Tiny-ImageNet. The code is available at https://github.com/zyh-uaiaaaa/Erasing-Attention-Consistency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge