Dimitrios Hatzinakos
CDFL: Efficient Federated Human Activity Recognition using Contrastive Learning and Deep Clustering
Jul 17, 2024Abstract:In the realm of ubiquitous computing, Human Activity Recognition (HAR) is vital for the automation and intelligent identification of human actions through data from diverse sensors. However, traditional machine learning approaches by aggregating data on a central server and centralized processing are memory-intensive and raise privacy concerns. Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a solution by training a global model collaboratively across multiple devices by exchanging their local model parameters instead of local data. However, in realistic settings, sensor data on devices is non-independently and identically distributed (Non-IID). This means that data activity recorded by most devices is sparse, and sensor data distribution for each client may be inconsistent. As a result, typical FL frameworks in heterogeneous environments suffer from slow convergence and poor performance due to deviation of the global model's objective from the global objective. Most FL methods applied to HAR are either designed for overly ideal scenarios without considering the Non-IID problem or present privacy and scalability concerns. This work addresses these challenges, proposing CDFL, an efficient federated learning framework for image-based HAR. CDFL efficiently selects a representative set of privacy-preserved images using contrastive learning and deep clustering, reduces communication overhead by selecting effective clients for global model updates, and improves global model quality by training on privacy-preserved data. Our comprehensive experiments carried out on three public datasets, namely Stanford40, PPMI, and VOC2012, demonstrate the superiority of CDFL in terms of performance, convergence rate, and bandwidth usage compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
AV-DiT: Efficient Audio-Visual Diffusion Transformer for Joint Audio and Video Generation
Jun 11, 2024


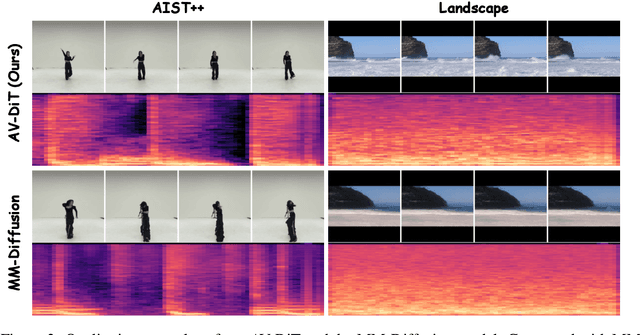
Abstract:Recent Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have shown impressive capabilities in generating high-quality single-modality content, including images, videos, and audio. However, it is still under-explored whether the transformer-based diffuser can efficiently denoise the Gaussian noises towards superb multimodal content creation. To bridge this gap, we introduce AV-DiT, a novel and efficient audio-visual diffusion transformer designed to generate high-quality, realistic videos with both visual and audio tracks. To minimize model complexity and computational costs, AV-DiT utilizes a shared DiT backbone pre-trained on image-only data, with only lightweight, newly inserted adapters being trainable. This shared backbone facilitates both audio and video generation. Specifically, the video branch incorporates a trainable temporal attention layer into a frozen pre-trained DiT block for temporal consistency. Additionally, a small number of trainable parameters adapt the image-based DiT block for audio generation. An extra shared DiT block, equipped with lightweight parameters, facilitates feature interaction between audio and visual modalities, ensuring alignment. Extensive experiments on the AIST++ and Landscape datasets demonstrate that AV-DiT achieves state-of-the-art performance in joint audio-visual generation with significantly fewer tunable parameters. Furthermore, our results highlight that a single shared image generative backbone with modality-specific adaptations is sufficient for constructing a joint audio-video generator. Our source code and pre-trained models will be released.
Evaluation of PPG Biometrics for Authentication in different states
Dec 22, 2017



Abstract:Amongst all medical biometric traits, Photoplethysmograph (PPG) is the easiest to acquire. PPG records the blood volume change with just combination of Light Emitting Diode and Photodiode from any part of the body. With IoT and smart homes' penetration, PPG recording can easily be integrated with other vital wearable devices. PPG represents peculiarity of hemodynamics and cardiovascular system for each individual. This paper presents non-fiducial method for PPG based biometric authentication. Being a physiological signal, PPG signal alters with physical/mental stress and time. For robustness, these variations cannot be ignored. While, most of the previous works focused only on single session, this paper demonstrates extensive performance evaluation of PPG biometrics against single session data, different emotions, physical exercise and time-lapse using Continuous Wavelet Transform (CWT) and Direct Linear Discriminant Analysis (DLDA). When evaluated on different states and datasets, equal error rate (EER) of $0.5\%$-$6\%$ was achieved for $45$-$60$s average training time. Our CWT/DLDA based technique outperformed all other dimensionality reduction techniques and previous work.
CNN-Based Prediction of Frame-Level Shot Importance for Video Summarization
Aug 23, 2017
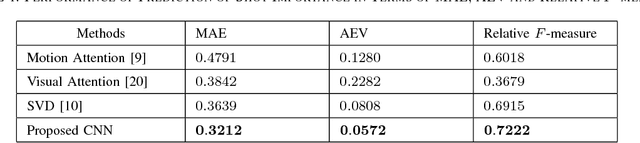
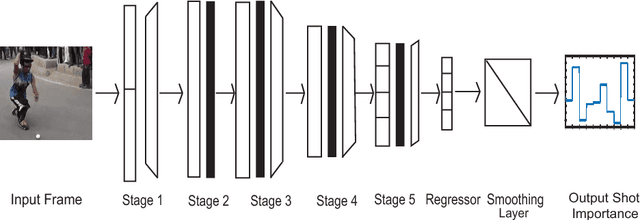
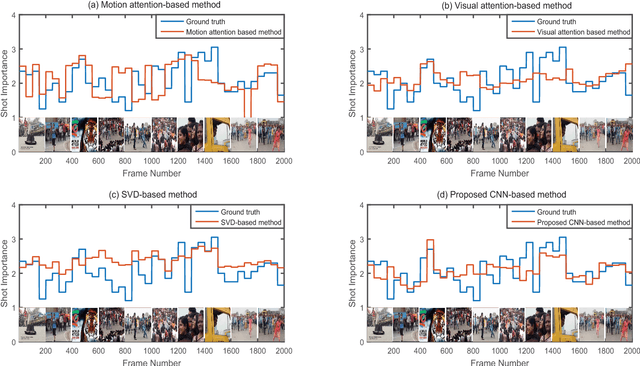
Abstract:In the Internet, ubiquitous presence of redundant, unedited, raw videos has made video summarization an important problem. Traditional methods of video summarization employ a heuristic set of hand-crafted features, which in many cases fail to capture subtle abstraction of a scene. This paper presents a deep learning method that maps the context of a video to the importance of a scene similar to that is perceived by humans. In particular, a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based architecture is proposed to mimic the frame-level shot importance for user-oriented video summarization. The weights and biases of the CNN are trained extensively through off-line processing, so that it can provide the importance of a frame of an unseen video almost instantaneously. Experiments on estimating the shot importance is carried out using the publicly available database TVSum50. It is shown that the performance of the proposed network is substantially better than that of commonly referred feature-based methods for estimating the shot importance in terms of mean absolute error, absolute error variance, and relative F-measure.
Statistical Selection of CNN-Based Audiovisual Features for Instantaneous Estimation of Human Emotional States
Aug 23, 2017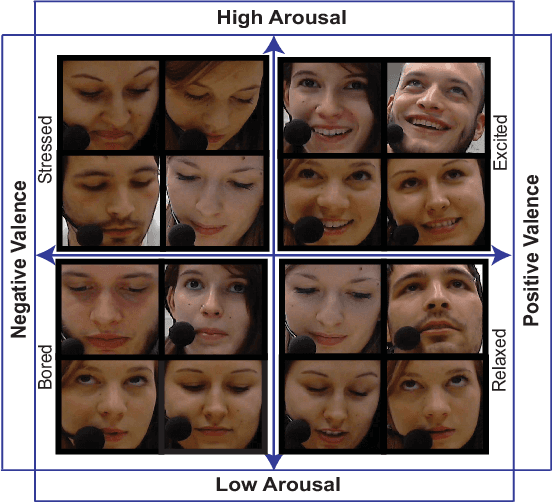
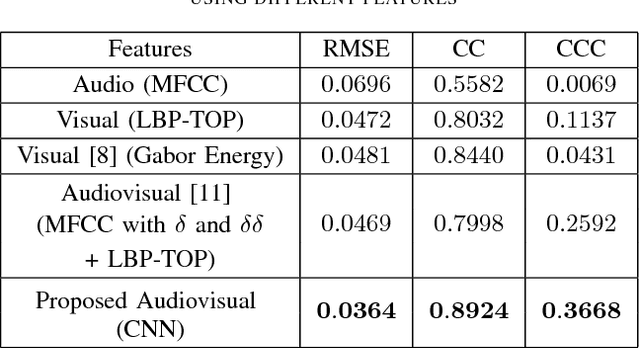
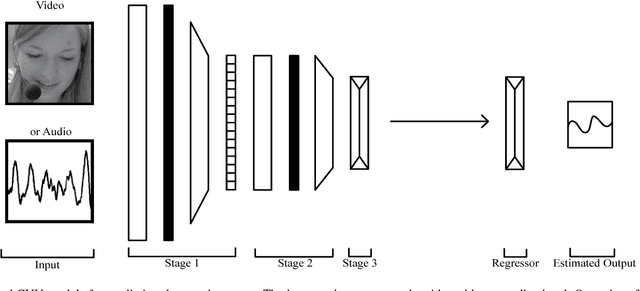
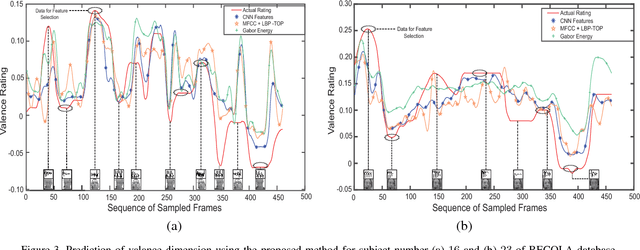
Abstract:Automatic prediction of continuous-level emotional state requires selection of suitable affective features to develop a regression system based on supervised machine learning. This paper investigates the performance of features statistically learned using convolutional neural networks for instantaneously predicting the continuous dimensions of emotional states. Features with minimum redundancy and maximum relevancy are chosen by using the mutual information-based selection process. The performance of frame-by-frame prediction of emotional state using the moderate length features as proposed in this paper is evaluated on spontaneous and naturalistic human-human conversation of RECOLA database. Experimental results show that the proposed model can be used for instantaneous prediction of emotional state with an accuracy higher than traditional audio or video features that are used for affective computation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge