Jing Shi
More Than the Final Answer: Improving Visual Extraction and Logical Consistency in Vision-Language Models
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (RLVR) has recently been extended from text-only LLMs to vision-language models (VLMs) to elicit long-chain multimodal reasoning. However, RLVR-trained VLMs still exhibit two persistent failure modes: inaccurate visual extraction (missing or hallucinating details) and logically inconsistent chains-of-thought, largely because verifiable signals supervise only the final answer. We propose PeRL-VL (Perception and Reasoning Learning for Vision-Language Models), a decoupled framework that separately improves visual perception and textual reasoning on top of RLVR. For perception, PeRL-VL introduces a VLM-based description reward that scores the model's self-generated image descriptions for faithfulness and sufficiency. For reasoning, PeRL-VL adds a text-only Reasoning SFT stage on logic-rich chain-of-thought data, enhancing coherence and logical consistency independently of vision. Across diverse multimodal benchmarks, PeRL-VL improves average Pass@1 accuracy from 63.3% (base Qwen2.5-VL-7B) to 68.8%, outperforming standard RLVR, text-only reasoning SFT, and naive multimodal distillation from GPT-4o.
Relational Visual Similarity
Dec 08, 2025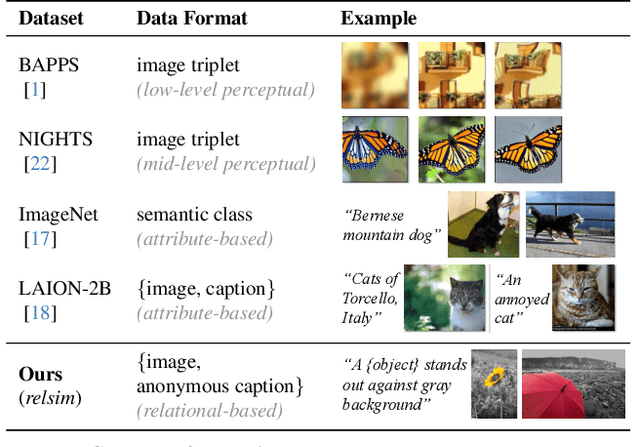
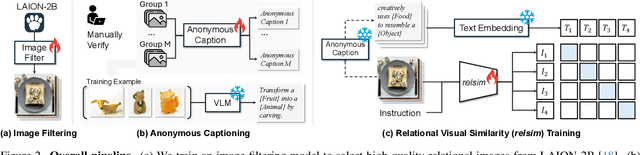
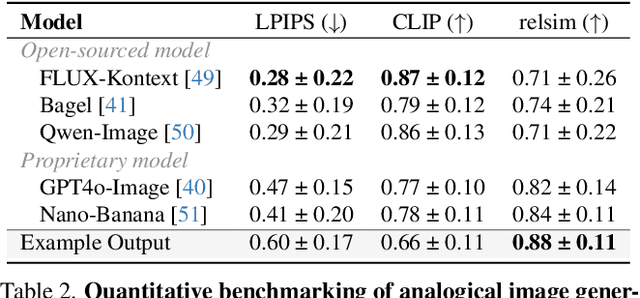

Abstract:Humans do not just see attribute similarity -- we also see relational similarity. An apple is like a peach because both are reddish fruit, but the Earth is also like a peach: its crust, mantle, and core correspond to the peach's skin, flesh, and pit. This ability to perceive and recognize relational similarity, is arguable by cognitive scientist to be what distinguishes humans from other species. Yet, all widely used visual similarity metrics today (e.g., LPIPS, CLIP, DINO) focus solely on perceptual attribute similarity and fail to capture the rich, often surprising relational similarities that humans perceive. How can we go beyond the visible content of an image to capture its relational properties? How can we bring images with the same relational logic closer together in representation space? To answer these questions, we first formulate relational image similarity as a measurable problem: two images are relationally similar when their internal relations or functions among visual elements correspond, even if their visual attributes differ. We then curate 114k image-caption dataset in which the captions are anonymized -- describing the underlying relational logic of the scene rather than its surface content. Using this dataset, we finetune a Vision-Language model to measure the relational similarity between images. This model serves as the first step toward connecting images by their underlying relational structure rather than their visible appearance. Our study shows that while relational similarity has a lot of real-world applications, existing image similarity models fail to capture it -- revealing a critical gap in visual computing.
Plot'n Polish: Zero-shot Story Visualization and Disentangled Editing with Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated significant capabilities to generate diverse and detailed visuals in various domains, and story visualization is emerging as a particularly promising application. However, as their use in real-world creative domains increases, the need for providing enhanced control, refinement, and the ability to modify images post-generation in a consistent manner becomes an important challenge. Existing methods often lack the flexibility to apply fine or coarse edits while maintaining visual and narrative consistency across multiple frames, preventing creators from seamlessly crafting and refining their visual stories. To address these challenges, we introduce Plot'n Polish, a zero-shot framework that enables consistent story generation and provides fine-grained control over story visualizations at various levels of detail.
Trust-MARL: Trust-Based Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Framework for Cooperative On-Ramp Merging Control in Heterogeneous Traffic Flow
Jun 14, 2025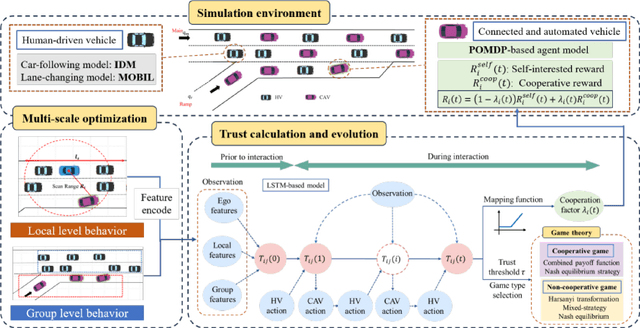

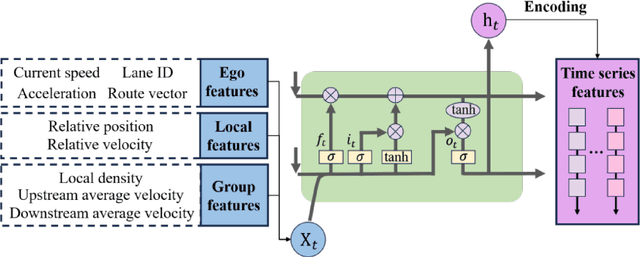
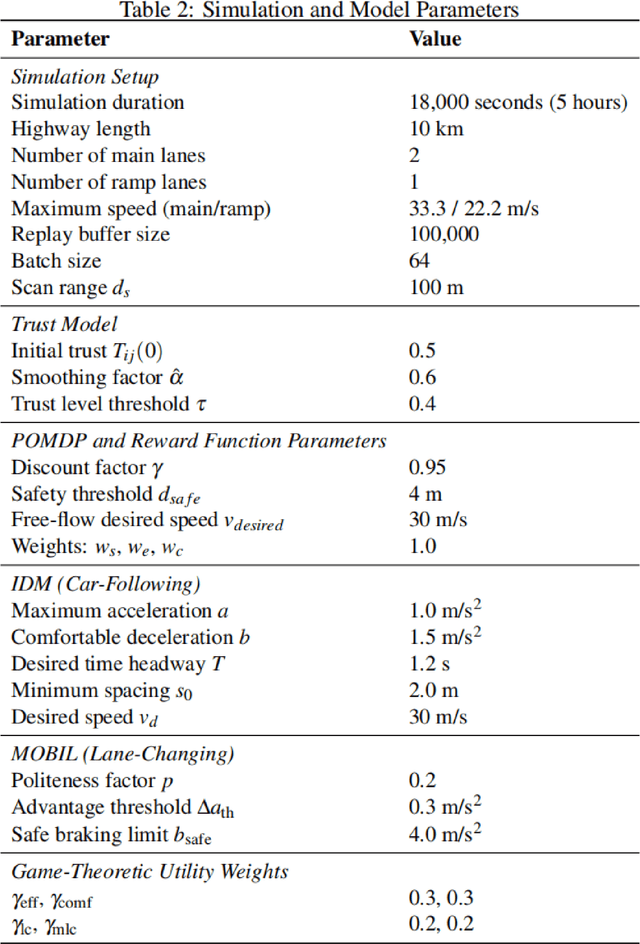
Abstract:Intelligent transportation systems require connected and automated vehicles (CAVs) to conduct safe and efficient cooperation with human-driven vehicles (HVs) in complex real-world traffic environments. However, the inherent unpredictability of human behaviour, especially at bottlenecks such as highway on-ramp merging areas, often disrupts traffic flow and compromises system performance. To address the challenge of cooperative on-ramp merging in heterogeneous traffic environments, this study proposes a trust-based multi-agent reinforcement learning (Trust-MARL) framework. At the macro level, Trust-MARL enhances global traffic efficiency by leveraging inter-agent trust to improve bottleneck throughput and mitigate traffic shockwave through emergent group-level coordination. At the micro level, a dynamic trust mechanism is designed to enable CAVs to adjust their cooperative strategies in response to real-time behaviors and historical interactions with both HVs and other CAVs. Furthermore, a trust-triggered game-theoretic decision-making module is integrated to guide each CAV in adapting its cooperation factor and executing context-aware lane-changing decisions under safety, comfort, and efficiency constraints. An extensive set of ablation studies and comparative experiments validates the effectiveness of the proposed Trust-MARL approach, demonstrating significant improvements in safety, efficiency, comfort, and adaptability across varying CAV penetration rates and traffic densities.
Give Me FP32 or Give Me Death? Challenges and Solutions for Reproducible Reasoning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are now integral across various domains and have demonstrated impressive performance. Progress, however, rests on the premise that benchmark scores are both accurate and reproducible. We demonstrate that the reproducibility of LLM performance is fragile: changing system configuration such as evaluation batch size, GPU count, and GPU version can introduce significant difference in the generated responses. This issue is especially pronounced in reasoning models, where minor rounding differences in early tokens can cascade into divergent chains of thought, ultimately affecting accuracy. For instance, under bfloat16 precision with greedy decoding, a reasoning model like DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B can exhibit up to 9% variation in accuracy and 9,000 tokens difference in response length due to differences in GPU count, type, and evaluation batch size. We trace the root cause of this variability to the non-associative nature of floating-point arithmetic under limited numerical precision. This work presents the first systematic investigation into how numerical precision affects reproducibility in LLM inference. Through carefully controlled experiments across various hardware, software, and precision settings, we quantify when and how model outputs diverge. Our analysis reveals that floating-point precision -- while critical for reproducibility -- is often neglected in evaluation practices. Inspired by this, we develop a lightweight inference pipeline, dubbed LayerCast, that stores weights in 16-bit precision but performs all computations in FP32, balancing memory efficiency with numerical stability. Code is available at https://github.com/nanomaoli/llm_reproducibility.
YoChameleon: Personalized Vision and Language Generation
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (e.g., GPT-4, Gemini, Chameleon) have evolved into powerful tools with millions of users. However, they remain generic models and lack personalized knowledge of specific user concepts. Previous work has explored personalization for text generation, yet it remains unclear how these methods can be adapted to new modalities, such as image generation. In this paper, we introduce Yo'Chameleon, the first attempt to study personalization for large multimodal models. Given 3-5 images of a particular concept, Yo'Chameleon leverages soft-prompt tuning to embed subject-specific information to (i) answer questions about the subject and (ii) recreate pixel-level details to produce images of the subject in new contexts. Yo'Chameleon is trained with (i) a self-prompting optimization mechanism to balance performance across multiple modalities, and (ii) a ``soft-positive" image generation approach to enhance image quality in a few-shot setting.
Accelerating Multi-Objective Collaborative Optimization of Doped Thermoelectric Materials via Artificial Intelligence
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:The thermoelectric performance of materials exhibits complex nonlinear dependencies on both elemental types and their proportions, rendering traditional trial-and-error approaches inefficient and time-consuming for material discovery. In this work, we present a deep learning model capable of accurately predicting thermoelectric properties of doped materials directly from their chemical formulas, achieving state-of-the-art performance. To enhance interpretability, we further incorporate sensitivity analysis techniques to elucidate how physical descriptors affect the thermoelectric figure of merit (zT). Moreover, we establish a coupled framework that integrates a surrogate model with a multi-objective genetic algorithm to efficiently explore the vast compositional space for high-performance candidates. Experimental validation confirms the discovery of a novel thermoelectric material with superior $zT$ values in the medium-temperature regime.
Visual Persona: Foundation Model for Full-Body Human Customization
Mar 19, 2025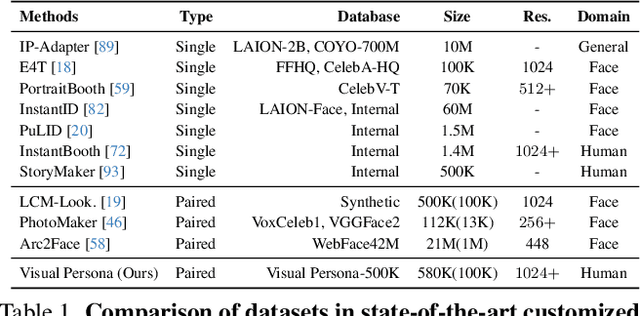

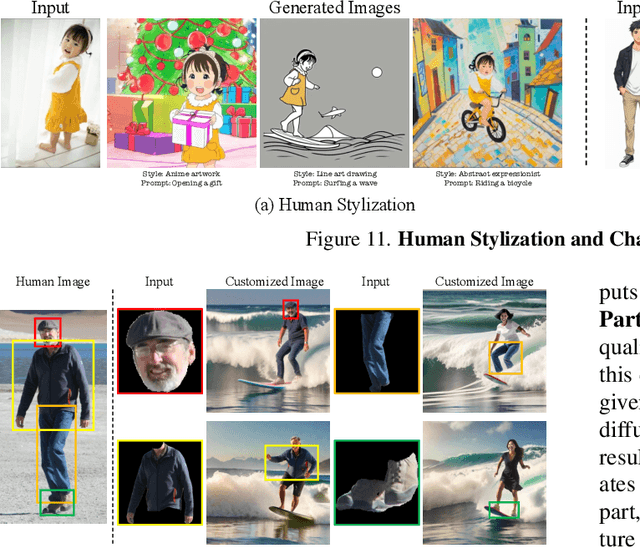
Abstract:We introduce Visual Persona, a foundation model for text-to-image full-body human customization that, given a single in-the-wild human image, generates diverse images of the individual guided by text descriptions. Unlike prior methods that focus solely on preserving facial identity, our approach captures detailed full-body appearance, aligning with text descriptions for body structure and scene variations. Training this model requires large-scale paired human data, consisting of multiple images per individual with consistent full-body identities, which is notoriously difficult to obtain. To address this, we propose a data curation pipeline leveraging vision-language models to evaluate full-body appearance consistency, resulting in Visual Persona-500K, a dataset of 580k paired human images across 100k unique identities. For precise appearance transfer, we introduce a transformer encoder-decoder architecture adapted to a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model, which augments the input image into distinct body regions, encodes these regions as local appearance features, and projects them into dense identity embeddings independently to condition the diffusion model for synthesizing customized images. Visual Persona consistently surpasses existing approaches, generating high-quality, customized images from in-the-wild inputs. Extensive ablation studies validate design choices, and we demonstrate the versatility of Visual Persona across various downstream tasks.
MAGNET: Augmenting Generative Decoders with Representation Learning and Infilling Capabilities
Jan 15, 2025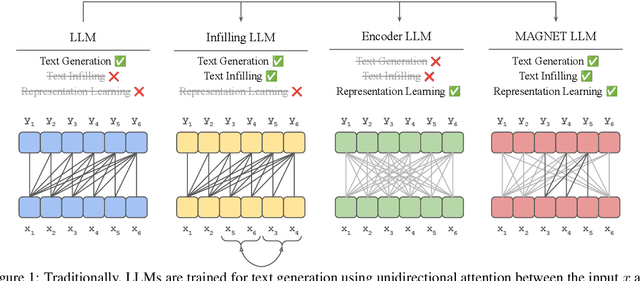
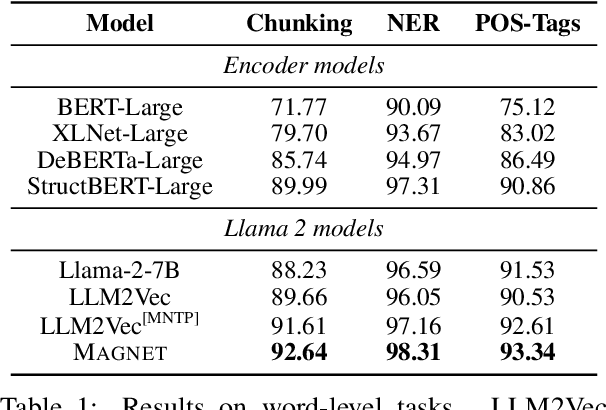
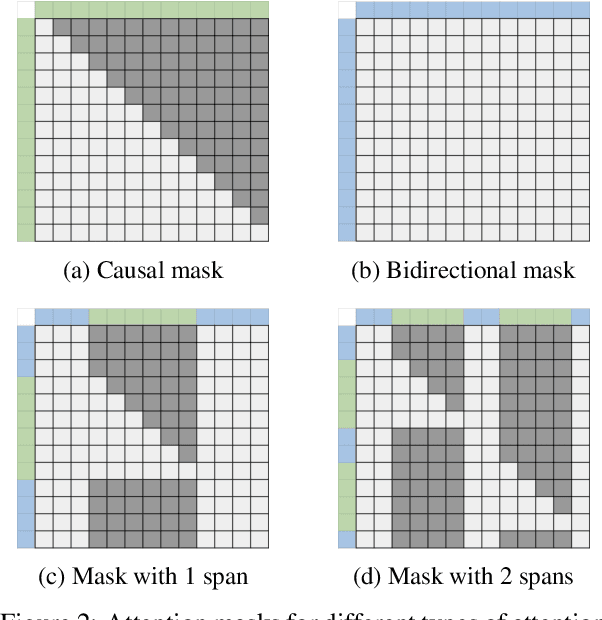
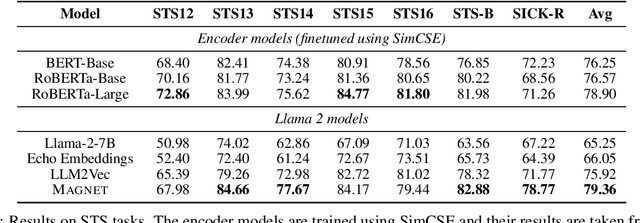
Abstract:While originally designed for unidirectional generative modeling, decoder-only large language models (LLMs) are increasingly being adapted for bidirectional modeling. However, unidirectional and bidirectional models are typically trained separately with distinct objectives (generation and representation learning, respectively). This separation overlooks the opportunity for developing a more versatile language model and for these objectives to complement each other. In this work, we introduce MAGNET, an adaptation of decoder-only LLMs that enhances their ability to generate robust representations and infill missing text spans, while preserving their knowledge and text generation capabilities. MAGNET employs three self-supervised training objectives and introduces an attention mechanism that combines bidirectional and causal attention, enabling unified training across all objectives. Our results demonstrate that LLMs adapted with MAGNET (1) surpass strong text encoders on token-level and sentence-level representation learning tasks, (2) generate contextually appropriate text infills by leveraging future context, (3) retain the ability for open-ended text generation without exhibiting repetition problem, and (4) preserve the knowledge gained by the LLM during pretraining.
Toward Robust Hyper-Detailed Image Captioning: A Multiagent Approach and Dual Evaluation Metrics for Factuality and Coverage
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) excel at generating highly detailed captions but often produce hallucinations. Our analysis reveals that existing hallucination detection methods struggle with detailed captions. We attribute this to the increasing reliance of MLLMs on their generated text, rather than the input image, as the sequence length grows. To address this issue, we propose a multiagent approach that leverages LLM-MLLM collaboration to correct given captions. Additionally, we introduce an evaluation framework and a benchmark dataset to facilitate the systematic analysis of detailed captions. Our experiments demonstrate that our proposed evaluation method better aligns with human judgments of factuality than existing metrics and that existing approaches to improve the MLLM factuality may fall short in hyper-detailed image captioning tasks. In contrast, our proposed method significantly enhances the factual accuracy of captions, even improving those generated by GPT-4V. Finally, we highlight a limitation of VQA-centric benchmarking by demonstrating that an MLLM's performance on VQA benchmarks may not correlate with its ability to generate detailed image captions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge