Jiuxiang Gu
MiLDEdit: Reasoning-Based Multi-Layer Design Document Editing
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Real-world design documents (e.g., posters) are inherently multi-layered, combining decoration, text, and images. Editing them from natural-language instructions requires fine-grained, layer-aware reasoning to identify relevant layers and coordinate modifications. Prior work largely overlooks multi-layer design document editing, focusing instead on single-layer image editing or multi-layer generation, which assume a flat canvas and lack the reasoning needed to determine what and where to modify. To address this gap, we introduce the Multi-Layer Document Editing Agent (MiLDEAgent), a reasoning-based framework that combines an RL-trained multimodal reasoner for layer-wise understanding with an image editor for targeted modifications. To systematically benchmark this setting, we introduce the MiLDEBench, a human-in-the-loop corpus of over 20K design documents paired with diverse editing instructions. The benchmark is complemented by a task-specific evaluation protocol, MiLDEEval, which spans four dimensions including instruction following, layout consistency, aesthetics, and text rendering. Extensive experiments on 14 open-source and 2 closed-source models reveal that existing approaches fail to generalize: open-source models often cannot complete multi-layer document editing tasks, while closed-source models suffer from format violations. In contrast, MiLDEAgent achieves strong layer-aware reasoning and precise editing, significantly outperforming all open-source baselines and attaining performance comparable to closed-source models, thereby establishing the first strong baseline for multi-layer document editing.
MMGR: Multi-Modal Generative Reasoning
Dec 17, 2025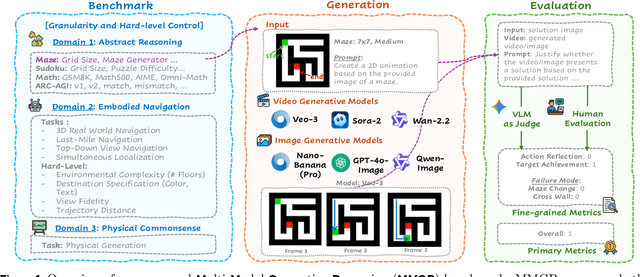
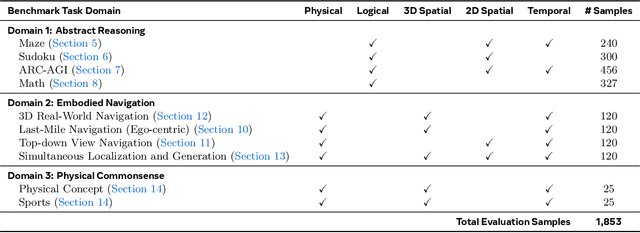
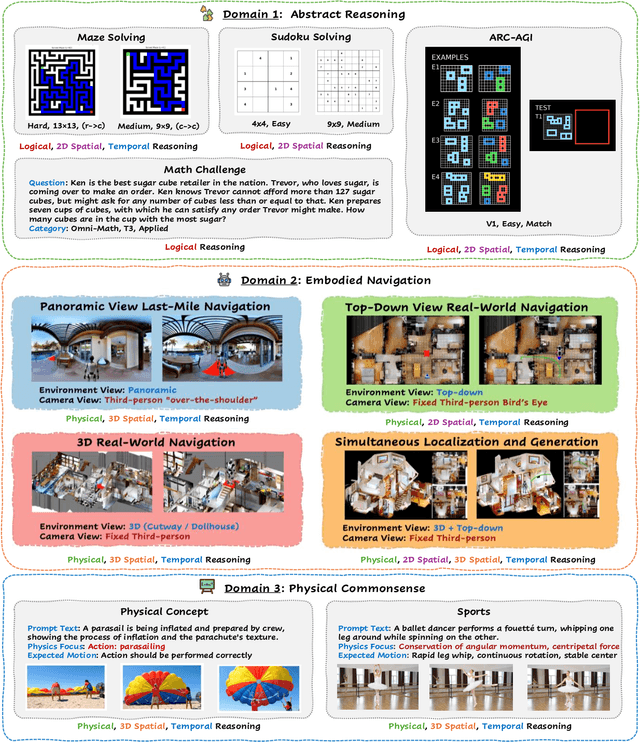
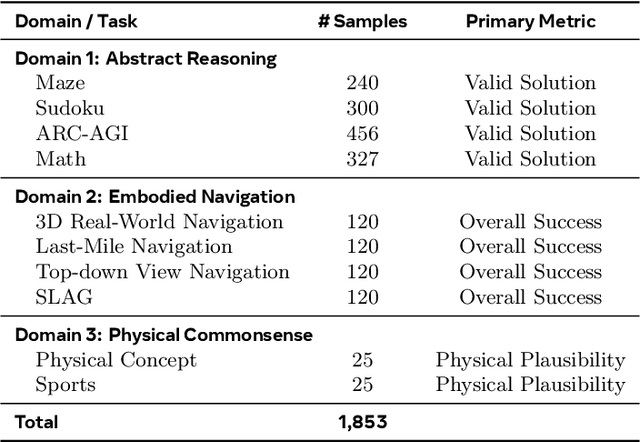
Abstract:Video foundation models generate visually realistic and temporally coherent content, but their reliability as world simulators depends on whether they capture physical, logical, and spatial constraints. Existing metrics such as Frechet Video Distance (FVD) emphasize perceptual quality and overlook reasoning failures, including violations of causality, physics, and global consistency. We introduce MMGR (Multi-Modal Generative Reasoning Evaluation and Benchmark), a principled evaluation framework based on five reasoning abilities: Physical, Logical, 3D Spatial, 2D Spatial, and Temporal. MMGR evaluates generative reasoning across three domains: Abstract Reasoning (ARC-AGI, Sudoku), Embodied Navigation (real-world 3D navigation and localization), and Physical Commonsense (sports and compositional interactions). MMGR applies fine-grained metrics that require holistic correctness across both video and image generation. We benchmark leading video models (Veo-3, Sora-2, Wan-2.2) and image models (Nano-banana, Nano-banana Pro, GPT-4o-image, Qwen-image), revealing strong performance gaps across domains. Models show moderate success on Physical Commonsense tasks but perform poorly on Abstract Reasoning (below 10 percent accuracy on ARC-AGI) and struggle with long-horizon spatial planning in embodied settings. Our analysis highlights key limitations in current models, including overreliance on perceptual data, weak global state consistency, and objectives that reward visual plausibility over causal correctness. MMGR offers a unified diagnostic benchmark and a path toward reasoning-aware generative world models.
Sparse-LaViDa: Sparse Multimodal Discrete Diffusion Language Models
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Masked Discrete Diffusion Models (MDMs) have achieved strong performance across a wide range of multimodal tasks, including image understanding, generation, and editing. However, their inference speed remains suboptimal due to the need to repeatedly process redundant masked tokens at every sampling step. In this work, we propose Sparse-LaViDa, a novel modeling framework that dynamically truncates unnecessary masked tokens at each inference step to accelerate MDM sampling. To preserve generation quality, we introduce specialized register tokens that serve as compact representations for the truncated tokens. Furthermore, to ensure consistency between training and inference, we design a specialized attention mask that faithfully matches the truncated sampling procedure during training. Built upon the state-of-the-art unified MDM LaViDa-O, Sparse-LaViDa achieves up to a 2x speedup across diverse tasks including text-to-image generation, image editing, and mathematical reasoning, while maintaining generation quality.
More Than the Final Answer: Improving Visual Extraction and Logical Consistency in Vision-Language Models
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (RLVR) has recently been extended from text-only LLMs to vision-language models (VLMs) to elicit long-chain multimodal reasoning. However, RLVR-trained VLMs still exhibit two persistent failure modes: inaccurate visual extraction (missing or hallucinating details) and logically inconsistent chains-of-thought, largely because verifiable signals supervise only the final answer. We propose PeRL-VL (Perception and Reasoning Learning for Vision-Language Models), a decoupled framework that separately improves visual perception and textual reasoning on top of RLVR. For perception, PeRL-VL introduces a VLM-based description reward that scores the model's self-generated image descriptions for faithfulness and sufficiency. For reasoning, PeRL-VL adds a text-only Reasoning SFT stage on logic-rich chain-of-thought data, enhancing coherence and logical consistency independently of vision. Across diverse multimodal benchmarks, PeRL-VL improves average Pass@1 accuracy from 63.3% (base Qwen2.5-VL-7B) to 68.8%, outperforming standard RLVR, text-only reasoning SFT, and naive multimodal distillation from GPT-4o.
OIDA-QA: A Multimodal Benchmark for Analyzing the Opioid Industry Documents Archive
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:The opioid crisis represents a significant moment in public health that reveals systemic shortcomings across regulatory systems, healthcare practices, corporate governance, and public policy. Analyzing how these interconnected systems simultaneously failed to protect public health requires innovative analytic approaches for exploring the vast amounts of data and documents disclosed in the UCSF-JHU Opioid Industry Documents Archive (OIDA). The complexity, multimodal nature, and specialized characteristics of these healthcare-related legal and corporate documents necessitate more advanced methods and models tailored to specific data types and detailed annotations, ensuring the precision and professionalism in the analysis. In this paper, we tackle this challenge by organizing the original dataset according to document attributes and constructing a benchmark with 400k training documents and 10k for testing. From each document, we extract rich multimodal information-including textual content, visual elements, and layout structures-to capture a comprehensive range of features. Using multiple AI models, we then generate a large-scale dataset comprising 360k training QA pairs and 10k testing QA pairs. Building on this foundation, we develop domain-specific multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) and explore the impact of multimodal inputs on task performance. To further enhance response accuracy, we incorporate historical QA pairs as contextual grounding for answering current queries. Additionally, we incorporate page references within the answers and introduce an importance-based page classifier, further improving the precision and relevance of the information provided. Preliminary results indicate the improvements with our AI assistant in document information extraction and question-answering tasks. The dataset is available at: https://huggingface.co/datasets/opioidarchive/oida-qa
Image Tokenizer Needs Post-Training
Sep 15, 2025Abstract:Recent image generative models typically capture the image distribution in a pre-constructed latent space, relying on a frozen image tokenizer. However, there exists a significant discrepancy between the reconstruction and generation distribution, where current tokenizers only prioritize the reconstruction task that happens before generative training without considering the generation errors during sampling. In this paper, we comprehensively analyze the reason for this discrepancy in a discrete latent space, and, from which, we propose a novel tokenizer training scheme including both main-training and post-training, focusing on improving latent space construction and decoding respectively. During the main training, a latent perturbation strategy is proposed to simulate sampling noises, \ie, the unexpected tokens generated in generative inference. Specifically, we propose a plug-and-play tokenizer training scheme, which significantly enhances the robustness of tokenizer, thus boosting the generation quality and convergence speed, and a novel tokenizer evaluation metric, \ie, pFID, which successfully correlates the tokenizer performance to generation quality. During post-training, we further optimize the tokenizer decoder regarding a well-trained generative model to mitigate the distribution difference between generated and reconstructed tokens. With a $\sim$400M generator, a discrete tokenizer trained with our proposed main training achieves a notable 1.60 gFID and further obtains 1.36 gFID with the additional post-training. Further experiments are conducted to broadly validate the effectiveness of our post-training strategy on off-the-shelf discrete and continuous tokenizers, coupled with autoregressive and diffusion-based generators.
MS4UI: A Dataset for Multi-modal Summarization of User Interface Instructional Videos
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:We study multi-modal summarization for instructional videos, whose goal is to provide users an efficient way to learn skills in the form of text instructions and key video frames. We observe that existing benchmarks focus on generic semantic-level video summarization, and are not suitable for providing step-by-step executable instructions and illustrations, both of which are crucial for instructional videos. We propose a novel benchmark for user interface (UI) instructional video summarization to fill the gap. We collect a dataset of 2,413 UI instructional videos, which spans over 167 hours. These videos are manually annotated for video segmentation, text summarization, and video summarization, which enable the comprehensive evaluations for concise and executable video summarization. We conduct extensive experiments on our collected MS4UI dataset, which suggest that state-of-the-art multi-modal summarization methods struggle on UI video summarization, and highlight the importance of new methods for UI instructional video summarization.
Refer to Anything with Vision-Language Prompts
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Recent image segmentation models have advanced to segment images into high-quality masks for visual entities, and yet they cannot provide comprehensive semantic understanding for complex queries based on both language and vision. This limitation reduces their effectiveness in applications that require user-friendly interactions driven by vision-language prompts. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel task of omnimodal referring expression segmentation (ORES). In this task, a model produces a group of masks based on arbitrary prompts specified by text only or text plus reference visual entities. To address this new challenge, we propose a novel framework to "Refer to Any Segmentation Mask Group" (RAS), which augments segmentation models with complex multimodal interactions and comprehension via a mask-centric large multimodal model. For training and benchmarking ORES models, we create datasets MaskGroups-2M and MaskGroups-HQ to include diverse mask groups specified by text and reference entities. Through extensive evaluation, we demonstrate superior performance of RAS on our new ORES task, as well as classic referring expression segmentation (RES) and generalized referring expression segmentation (GRES) tasks. Project page: https://Ref2Any.github.io.
R-KV: Redundancy-aware KV Cache Compression for Training-Free Reasoning Models Acceleration
May 30, 2025Abstract:Reasoning models have demonstrated impressive performance in self-reflection and chain-of-thought reasoning. However, they often produce excessively long outputs, leading to prohibitively large key-value (KV) caches during inference. While chain-of-thought inference significantly improves performance on complex reasoning tasks, it can also lead to reasoning failures when deployed with existing KV cache compression approaches. To address this, we propose Redundancy-aware KV Cache Compression for Reasoning models (R-KV), a novel method specifically targeting redundant tokens in reasoning models. Our method preserves nearly 100% of the full KV cache performance using only 10% of the KV cache, substantially outperforming existing KV cache baselines, which reach only 60% of the performance. Remarkably, R-KV even achieves 105% of full KV cache performance with 16% of the KV cache. This KV-cache reduction also leads to a 90% memory saving and a 6.6X throughput over standard chain-of-thought reasoning inference. Experimental results show that R-KV consistently outperforms existing KV cache compression baselines across two mathematical reasoning datasets.
Towards Visual Text Grounding of Multimodal Large Language Model
Apr 07, 2025


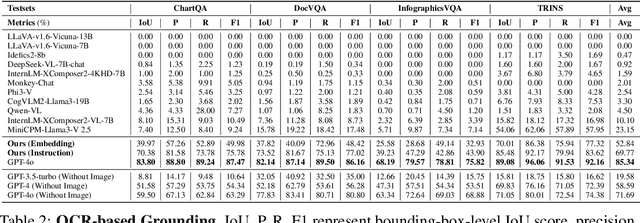
Abstract:Despite the existing evolution of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), a non-neglectable limitation remains in their struggle with visual text grounding, especially in text-rich images of documents. Document images, such as scanned forms and infographics, highlight critical challenges due to their complex layouts and textual content. However, current benchmarks do not fully address these challenges, as they mostly focus on visual grounding on natural images, rather than text-rich document images. Thus, to bridge this gap, we introduce TRIG, a novel task with a newly designed instruction dataset for benchmarking and improving the Text-Rich Image Grounding capabilities of MLLMs in document question-answering. Specifically, we propose an OCR-LLM-human interaction pipeline to create 800 manually annotated question-answer pairs as a benchmark and a large-scale training set of 90$ synthetic data based on four diverse datasets. A comprehensive evaluation of various MLLMs on our proposed benchmark exposes substantial limitations in their grounding capability on text-rich images. In addition, we propose two simple and effective TRIG methods based on general instruction tuning and plug-and-play efficient embedding, respectively. By finetuning MLLMs on our synthetic dataset, they promisingly improve spatial reasoning and grounding capabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge