Nanyun Peng
Shammie
Translation as a Scalable Proxy for Multilingual Evaluation
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:The rapid proliferation of LLMs has created a critical evaluation paradox: while LLMs claim multilingual proficiency, comprehensive non-machine-translated benchmarks exist for fewer than 30 languages, leaving >98% of the world's 7,000 languages in an empirical void. Traditional benchmark construction faces scaling challenges such as cost, scarcity of domain experts, and data contamination. We evaluate the validity of a simpler alternative: can translation quality alone indicate a model's broader multilingual capabilities? Through systematic evaluation of 14 models (1B-72B parameters) across 9 diverse benchmarks and 7 translation metrics, we find that translation performance is a good indicator of downstream task success (e.g., Phi-4, median Pearson r: MetricX = 0.89, xCOMET = 0.91, SSA-COMET = 0.87). These results suggest that the representational abilities supporting faithful translation overlap with those required for multilingual understanding. Translation quality, thus emerges as a strong, inexpensive first-pass proxy of multilingual performance, enabling a translation-first screening with targeted follow-up for specific tasks.
MMGR: Multi-Modal Generative Reasoning
Dec 17, 2025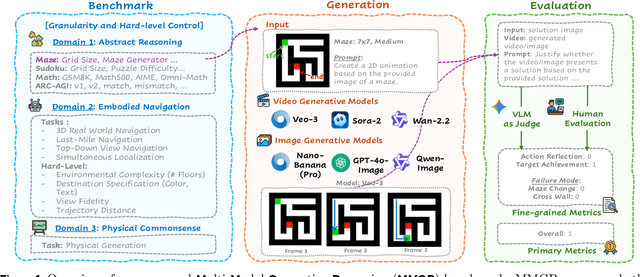
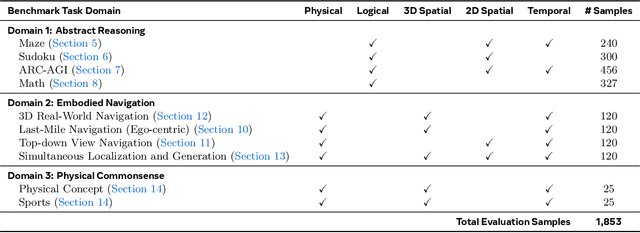
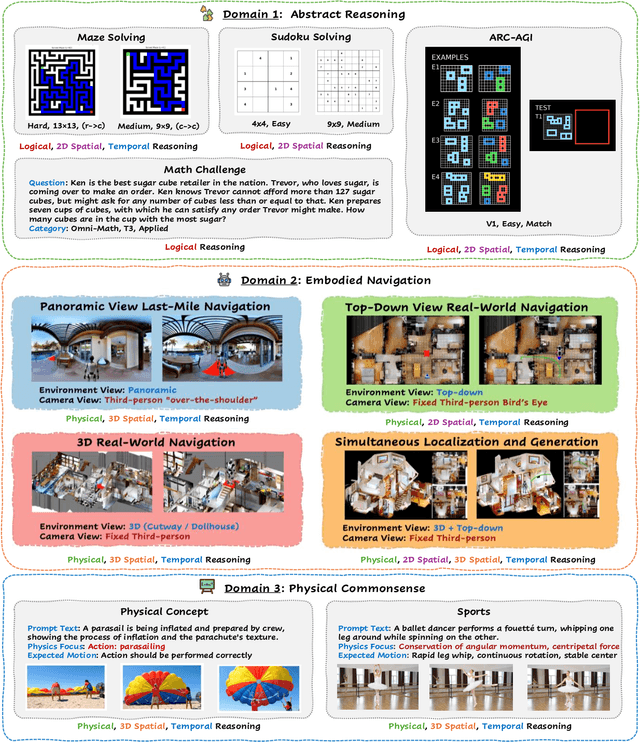
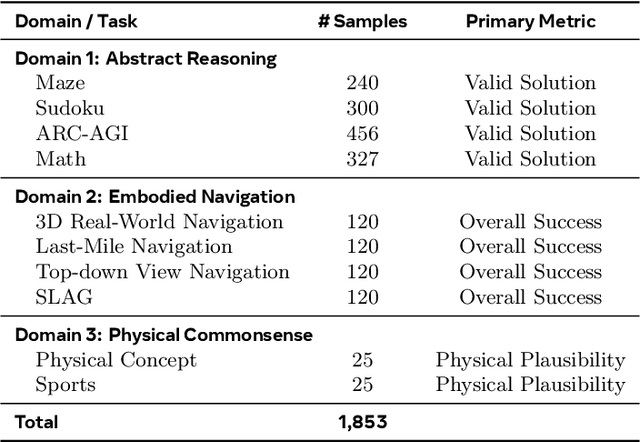
Abstract:Video foundation models generate visually realistic and temporally coherent content, but their reliability as world simulators depends on whether they capture physical, logical, and spatial constraints. Existing metrics such as Frechet Video Distance (FVD) emphasize perceptual quality and overlook reasoning failures, including violations of causality, physics, and global consistency. We introduce MMGR (Multi-Modal Generative Reasoning Evaluation and Benchmark), a principled evaluation framework based on five reasoning abilities: Physical, Logical, 3D Spatial, 2D Spatial, and Temporal. MMGR evaluates generative reasoning across three domains: Abstract Reasoning (ARC-AGI, Sudoku), Embodied Navigation (real-world 3D navigation and localization), and Physical Commonsense (sports and compositional interactions). MMGR applies fine-grained metrics that require holistic correctness across both video and image generation. We benchmark leading video models (Veo-3, Sora-2, Wan-2.2) and image models (Nano-banana, Nano-banana Pro, GPT-4o-image, Qwen-image), revealing strong performance gaps across domains. Models show moderate success on Physical Commonsense tasks but perform poorly on Abstract Reasoning (below 10 percent accuracy on ARC-AGI) and struggle with long-horizon spatial planning in embodied settings. Our analysis highlights key limitations in current models, including overreliance on perceptual data, weak global state consistency, and objectives that reward visual plausibility over causal correctness. MMGR offers a unified diagnostic benchmark and a path toward reasoning-aware generative world models.
MMPersuade: A Dataset and Evaluation Framework for Multimodal Persuasion
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:As Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) are increasingly deployed in domains such as shopping, health, and news, they are exposed to pervasive persuasive content. A critical question is how these models function as persuadees-how and why they can be influenced by persuasive multimodal inputs. Understanding both their susceptibility to persuasion and the effectiveness of different persuasive strategies is crucial, as overly persuadable models may adopt misleading beliefs, override user preferences, or generate unethical or unsafe outputs when exposed to manipulative messages. We introduce MMPersuade, a unified framework for systematically studying multimodal persuasion dynamics in LVLMs. MMPersuade contributes (i) a comprehensive multimodal dataset that pairs images and videos with established persuasion principles across commercial, subjective and behavioral, and adversarial contexts, and (ii) an evaluation framework that quantifies both persuasion effectiveness and model susceptibility via third-party agreement scoring and self-estimated token probabilities on conversation histories. Our study of six leading LVLMs as persuadees yields three key insights: (i) multimodal inputs substantially increase persuasion effectiveness-and model susceptibility-compared to text alone, especially in misinformation scenarios; (ii) stated prior preferences decrease susceptibility, yet multimodal information maintains its persuasive advantage; and (iii) different strategies vary in effectiveness across contexts, with reciprocity being most potent in commercial and subjective contexts, and credibility and logic prevailing in adversarial contexts. By jointly analyzing persuasion effectiveness and susceptibility, MMPersuade provides a principled foundation for developing models that are robust, preference-consistent, and ethically aligned when engaging with persuasive multimodal content.
DialectGen: Benchmarking and Improving Dialect Robustness in Multimodal Generation
Oct 16, 2025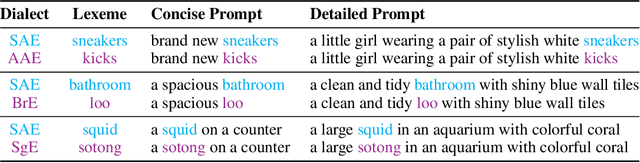
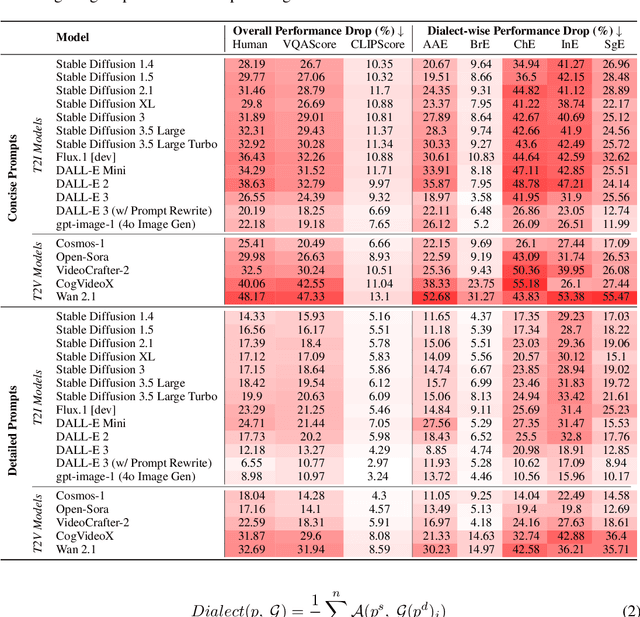
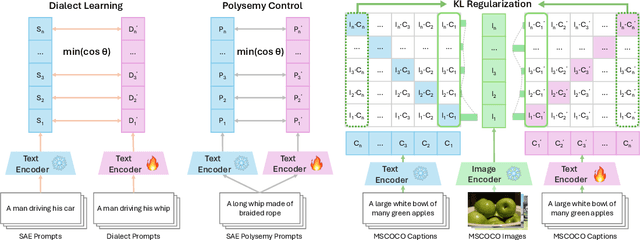
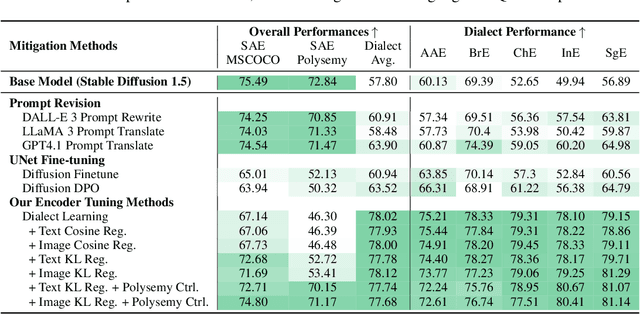
Abstract:Contact languages like English exhibit rich regional variations in the form of dialects, which are often used by dialect speakers interacting with generative models. However, can multimodal generative models effectively produce content given dialectal textual input? In this work, we study this question by constructing a new large-scale benchmark spanning six common English dialects. We work with dialect speakers to collect and verify over 4200 unique prompts and evaluate on 17 image and video generative models. Our automatic and human evaluation results show that current state-of-the-art multimodal generative models exhibit 32.26% to 48.17% performance degradation when a single dialect word is used in the prompt. Common mitigation methods such as fine-tuning and prompt rewriting can only improve dialect performance by small margins (< 7%), while potentially incurring significant performance degradation in Standard American English (SAE). To this end, we design a general encoder-based mitigation strategy for multimodal generative models. Our method teaches the model to recognize new dialect features while preserving SAE performance. Experiments on models such as Stable Diffusion 1.5 show that our method is able to simultaneously raise performance on five dialects to be on par with SAE (+34.4%), while incurring near zero cost to SAE performance.
LLM-REVal: Can We Trust LLM Reviewers Yet?
Oct 14, 2025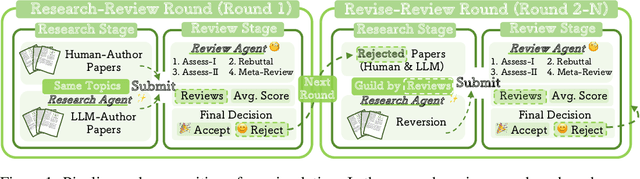
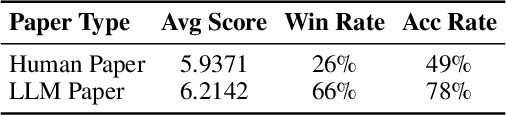
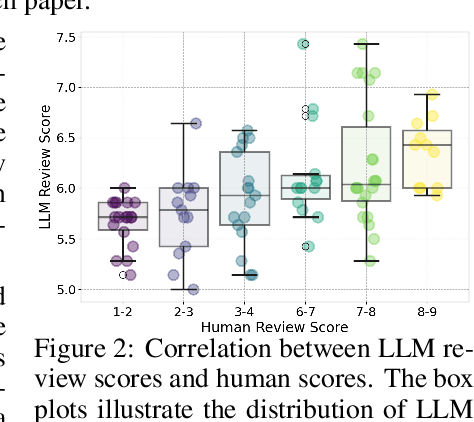
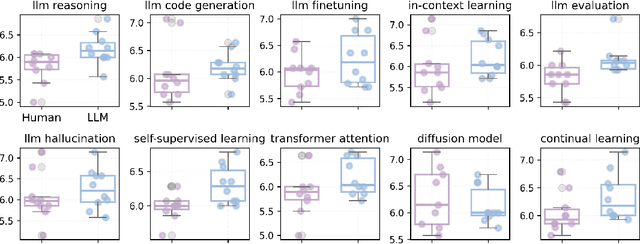
Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has inspired researchers to integrate them extensively into the academic workflow, potentially reshaping how research is practiced and reviewed. While previous studies highlight the potential of LLMs in supporting research and peer review, their dual roles in the academic workflow and the complex interplay between research and review bring new risks that remain largely underexplored. In this study, we focus on how the deep integration of LLMs into both peer-review and research processes may influence scholarly fairness, examining the potential risks of using LLMs as reviewers by simulation. This simulation incorporates a research agent, which generates papers and revises, alongside a review agent, which assesses the submissions. Based on the simulation results, we conduct human annotations and identify pronounced misalignment between LLM-based reviews and human judgments: (1) LLM reviewers systematically inflate scores for LLM-authored papers, assigning them markedly higher scores than human-authored ones; (2) LLM reviewers persistently underrate human-authored papers with critical statements (e.g., risk, fairness), even after multiple revisions. Our analysis reveals that these stem from two primary biases in LLM reviewers: a linguistic feature bias favoring LLM-generated writing styles, and an aversion toward critical statements. These results highlight the risks and equity concerns posed to human authors and academic research if LLMs are deployed in the peer review cycle without adequate caution. On the other hand, revisions guided by LLM reviews yield quality gains in both LLM-based and human evaluations, illustrating the potential of the LLMs-as-reviewers for early-stage researchers and enhancing low-quality papers.
Multilingual Routing in Mixture-of-Experts
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures have become the key to scaling modern LLMs, yet little is understood about how their sparse routing dynamics respond to multilingual data. In this work, we analyze expert routing patterns using parallel multilingual datasets and present highly interpretable layer-wise phenomena. We find that MoE models route tokens in language-specific ways in the early and late decoder layers but exhibit significant cross-lingual routing alignment in middle layers, mirroring parameter-sharing trends observed in dense LLMs. In particular, we reveal a clear, strong correlation between a model's performance in a given language and how similarly its tokens are routed to English in these layers. Extending beyond correlation, we explore inference-time interventions that induce higher cross-lingual routing alignment. We introduce a method that steers the router by promoting middle-layer task experts frequently activated in English, and it successfully increases multilingual performance. These 1-2% gains are remarkably consistent across two evaluation tasks, three models, and 15+ languages, especially given that these simple interventions override routers of extensively trained, state-of-the-art LLMs. In comparison, interventions outside of the middle layers or targeting multilingual-specialized experts only yield performance degradation. Altogether, we present numerous findings that explain how MoEs process non-English text and demonstrate that generalization is limited by the model's ability to leverage language-universal experts in all languages.
VaPR -- Vision-language Preference alignment for Reasoning
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Preference finetuning methods like Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with AI-generated feedback have shown promise in aligning Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) with human preferences. However, existing techniques overlook the prevalence of noise in synthetic preference annotations in the form of stylistic and length biases. To this end, we introduce a hard-negative response generation framework based on LLM-guided response editing, that produces rejected responses with targeted errors, maintaining stylistic and length similarity to the accepted ones. Using this framework, we develop the VaPR dataset, comprising 30K high-quality samples, to finetune three LVLM families: LLaVA-V1.5, Qwen2VL & Qwen2.5VL (2B-13B sizes). Our VaPR models deliver significant performance improvements across ten benchmarks, achieving average gains of 6.5% (LLaVA), 4.0% (Qwen2VL), and 1.5% (Qwen2.5VL), with notable improvements on reasoning tasks. A scaling analysis shows that performance consistently improves with data size, with LLaVA models benefiting even at smaller scales. Moreover, VaPR reduces the tendency to answer "Yes" in binary questions - addressing a common failure mode in LVLMs like LLaVA. Lastly, we show that the framework generalizes to open-source LLMs as editors, with models trained on VaPR-OS achieving ~99% of the performance of models trained on \name, which is synthesized using GPT-4o. Our data, models, and code can be found on the project page https://vap-r.github.io
Steering MoE LLMs via Expert (De)Activation
Sep 11, 2025



Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) in Large Language Models (LLMs) routes each token through a subset of specialized Feed-Forward Networks (FFN), known as experts. We present SteerMoE, a framework for steering MoE models by detecting and controlling behavior-linked experts. Our detection method identifies experts with distinct activation patterns across paired inputs exhibiting contrasting behaviors. By selectively (de)activating such experts during inference, we control behaviors like faithfulness and safety without retraining or modifying weights. Across 11 benchmarks and 6 LLMs, our steering raises safety by up to +20% and faithfulness by +27%. In adversarial attack mode, it drops safety by -41% alone, and -100% when combined with existing jailbreak methods, bypassing all safety guardrails and exposing a new dimension of alignment faking hidden within experts.
Rethinking Creativity Evaluation: A Critical Analysis of Existing Creativity Evaluations
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:We systematically examine, analyze, and compare representative creativity measures--creativity index, perplexity, syntactic templates, and LLM-as-a-Judge--across diverse creative domains, including creative writing, unconventional problem-solving, and research ideation. Our analyses reveal that these metrics exhibit limited consistency, capturing different dimensions of creativity. We highlight key limitations, including the creativity index's focus on lexical diversity, perplexity's sensitivity to model confidence, and syntactic templates' inability to capture conceptual creativity. Additionally, LLM-as-a-Judge shows instability and bias. Our findings underscore the need for more robust, generalizable evaluation frameworks that better align with human judgments of creativity.
Scaling Probabilistic Circuits via Monarch Matrices
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Probabilistic Circuits (PCs) are tractable representations of probability distributions allowing for exact and efficient computation of likelihoods and marginals. Recent advancements have improved the scalability of PCs either by leveraging their sparse properties or through the use of tensorized operations for better hardware utilization. However, no existing method fully exploits both aspects simultaneously. In this paper, we propose a novel sparse and structured parameterization for the sum blocks in PCs. By replacing dense matrices with sparse Monarch matrices, we significantly reduce the memory and computation costs, enabling unprecedented scaling of PCs. From a theory perspective, our construction arises naturally from circuit multiplication; from a practical perspective, compared to previous efforts on scaling up tractable probabilistic models, our approach not only achieves state-of-the-art generative modeling performance on challenging benchmarks like Text8, LM1B and ImageNet, but also demonstrates superior scaling behavior, achieving the same performance with substantially less compute as measured by the number of floating-point operations (FLOPs) during training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge