Jia-Chen Gu
Multiplicative Orthogonal Sequential Editing for Language Models
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:Knowledge editing aims to efficiently modify the internal knowledge of large language models (LLMs) without compromising their other capabilities. The prevailing editing paradigm, which appends an update matrix to the original parameter matrix, has been shown by some studies to damage key numerical stability indicators (such as condition number and norm), thereby reducing editing performance and general abilities, especially in sequential editing scenario. Although subsequent methods have made some improvements, they remain within the additive framework and have not fundamentally addressed this limitation. To solve this problem, we analyze it from both statistical and mathematical perspectives and conclude that multiplying the original matrix by an orthogonal matrix does not change the numerical stability of the matrix. Inspired by this, different from the previous additive editing paradigm, a multiplicative editing paradigm termed Multiplicative Orthogonal Sequential Editing (MOSE) is proposed. Specifically, we first derive the matrix update in the multiplicative form, the new knowledge is then incorporated into an orthogonal matrix, which is multiplied by the original parameter matrix. In this way, the numerical stability of the edited matrix is unchanged, thereby maintaining editing performance and general abilities. We compared MOSE with several current knowledge editing methods, systematically evaluating their impact on both editing performance and the general abilities across three different LLMs. Experimental results show that MOSE effectively limits deviations in the edited parameter matrix and maintains its numerical stability. Compared to current methods, MOSE achieves a 12.08% improvement in sequential editing performance, while retaining 95.73% of general abilities across downstream tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/famoustourist/MOSE.
LLM-REVal: Can We Trust LLM Reviewers Yet?
Oct 14, 2025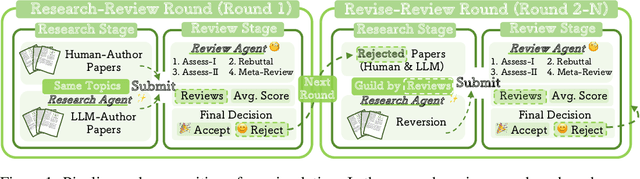
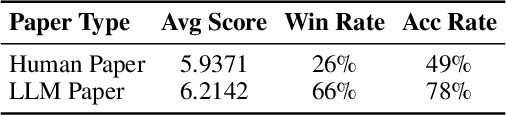
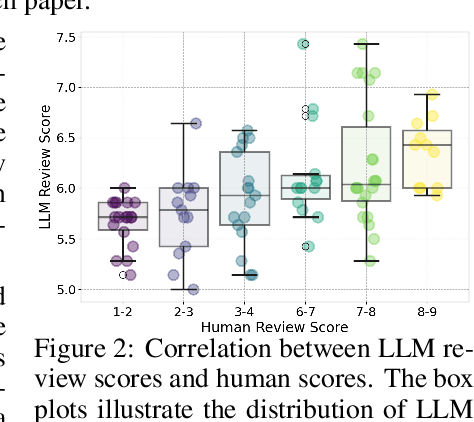
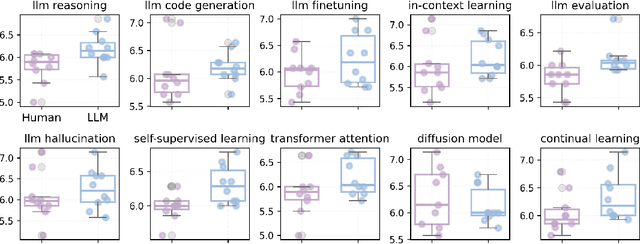
Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has inspired researchers to integrate them extensively into the academic workflow, potentially reshaping how research is practiced and reviewed. While previous studies highlight the potential of LLMs in supporting research and peer review, their dual roles in the academic workflow and the complex interplay between research and review bring new risks that remain largely underexplored. In this study, we focus on how the deep integration of LLMs into both peer-review and research processes may influence scholarly fairness, examining the potential risks of using LLMs as reviewers by simulation. This simulation incorporates a research agent, which generates papers and revises, alongside a review agent, which assesses the submissions. Based on the simulation results, we conduct human annotations and identify pronounced misalignment between LLM-based reviews and human judgments: (1) LLM reviewers systematically inflate scores for LLM-authored papers, assigning them markedly higher scores than human-authored ones; (2) LLM reviewers persistently underrate human-authored papers with critical statements (e.g., risk, fairness), even after multiple revisions. Our analysis reveals that these stem from two primary biases in LLM reviewers: a linguistic feature bias favoring LLM-generated writing styles, and an aversion toward critical statements. These results highlight the risks and equity concerns posed to human authors and academic research if LLMs are deployed in the peer review cycle without adequate caution. On the other hand, revisions guided by LLM reviews yield quality gains in both LLM-based and human evaluations, illustrating the potential of the LLMs-as-reviewers for early-stage researchers and enhancing low-quality papers.
UltraEdit: Training-, Subject-, and Memory-Free Lifelong Editing in Large Language Models
May 20, 2025Abstract:Lifelong learning enables large language models (LLMs) to adapt to evolving information by continually updating their internal knowledge. An ideal system should support efficient, wide-ranging updates while preserving existing capabilities and ensuring reliable deployment. Model editing stands out as a promising solution for this goal, offering a focused and efficient way to revise a model's internal knowledge. Although recent paradigms have made notable progress, they often struggle to meet the demands of practical lifelong adaptation at scale. To bridge this gap, we propose ULTRAEDIT-a fundamentally new editing solution that is training-, subject- and memory-free, making it particularly well-suited for ultra-scalable, real-world lifelong model editing. ULTRAEDIT performs editing through a self-contained process that relies solely on lightweight linear algebra operations to compute parameter shifts, enabling fast and consistent parameter modifications with minimal overhead. To improve scalability in lifelong settings, ULTRAEDIT employs a lifelong normalization strategy that continuously updates feature statistics across turns, allowing it to adapt to distributional shifts and maintain consistency over time. ULTRAEDIT achieves editing speeds over 7x faster than the previous state-of-the-art method-which was also the fastest known approach-while consuming less than 1/3 the VRAM, making it the only method currently capable of editing a 7B LLM on a 24GB consumer-grade GPU. Furthermore, we construct ULTRAEDITBENCH-the largest dataset in the field to date, with over 2M editing pairs-and demonstrate that our method supports up to 1M edits while maintaining high accuracy. Comprehensive experiments on four datasets and six models show that ULTRAEDIT consistently achieves superior performance across diverse model editing scenarios. Our code is available at: https://github.com/XiaojieGu/UltraEdit.
Self-Routing RAG: Binding Selective Retrieval with Knowledge Verbalization
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Selective retrieval improves retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) by reducing distractions from low-quality retrievals and improving efficiency. However, existing approaches under-utilize the inherent knowledge of large language models (LLMs), leading to suboptimal retrieval decisions and degraded generation performance. To bridge this gap, we propose Self-Routing RAG (SR-RAG), a novel framework that binds selective retrieval with knowledge verbalization. SR-RAG enables an LLM to dynamically decide between external retrieval and verbalizing its own parametric knowledge. To this end, we design a multi-task objective that jointly optimizes an LLM on knowledge source selection, knowledge verbalization, and response generation. We further introduce dynamic knowledge source inference via nearest neighbor search to improve the accuracy of knowledge source decision under domain shifts. Fine-tuning three LLMs with SR-RAG significantly improves both their response accuracy and inference latency. Compared to the strongest selective retrieval baseline, SR-RAG reduces retrievals by 29% while improving the performance by 5.1%.
CaKE: Circuit-aware Editing Enables Generalizable Knowledge Learners
Mar 20, 2025



Abstract:Knowledge Editing (KE) enables the modification of outdated or incorrect information in large language models (LLMs). While existing KE methods can update isolated facts, they struggle to generalize these updates to multi-hop reasoning tasks that depend on the modified knowledge. Through an analysis of reasoning circuits -- the neural pathways LLMs use for knowledge-based inference, we observe that current layer-localized KE approaches, such as MEMIT and WISE, which edit only single or a few model layers, struggle to effectively incorporate updated information into these reasoning pathways. To address this limitation, we propose CaKE (Circuit-aware Knowledge Editing), a novel method that enables more effective integration of updated knowledge in LLMs. CaKE leverages strategically curated data, guided by our circuits-based analysis, that enforces the model to utilize the modified knowledge, stimulating the model to develop appropriate reasoning circuits for newly integrated knowledge. Experimental results show that CaKE enables more accurate and consistent use of updated knowledge across related reasoning tasks, leading to an average of 20% improvement in multi-hop reasoning accuracy on MQuAKE dataset compared to existing KE methods. We release the code and data in https://github.com/zjunlp/CaKE.
BRIEF: Bridging Retrieval and Inference for Multi-hop Reasoning via Compression
Oct 20, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) can supplement large language models (LLMs) by integrating external knowledge. However, as the number of retrieved documents increases, the input length to LLMs grows linearly, causing a dramatic increase in latency and a degradation in long-context understanding. This is particularly serious for multi-hop questions that require a chain of reasoning across documents. To accelerate inference, reduce costs, and minimize distractions, this paper presents BRIEF (Bridging Retrieval and Inference through Evidence Fusion), a lightweight approach that performs query-aware multi-hop reasoning by compressing retrieved documents into highly dense textual summaries to integrate into in-context learning. To enable learning compression for multi-hop reasoning, we curate synthetic data by extracting atomic proposition expressions that encapsulate distinct factoids from the source documents to compose synthetic summaries. Based on our synthetic data built entirely by open-source models, BRIEF generates more concise summaries and enables a range of LLMs to achieve exceptional open-domain question answering (QA) performance. For example, on HotpotQA, BRIEF improves the compression rate by 2 times compared to the state-of-the-art baseline, while outperforming it by 3.00% EM and 4.16% F1 with Flan-UL2 as the reader LM. It also generates more concise summaries than proprietary GPT-3.5, while demonstrating nearly identical QA performance.
MRAG-Bench: Vision-Centric Evaluation for Retrieval-Augmented Multimodal Models
Oct 10, 2024Abstract:Existing multimodal retrieval benchmarks primarily focus on evaluating whether models can retrieve and utilize external textual knowledge for question answering. However, there are scenarios where retrieving visual information is either more beneficial or easier to access than textual data. In this paper, we introduce a multimodal retrieval-augmented generation benchmark, MRAG-Bench, in which we systematically identify and categorize scenarios where visually augmented knowledge is better than textual knowledge, for instance, more images from varying viewpoints. MRAG-Bench consists of 16,130 images and 1,353 human-annotated multiple-choice questions across 9 distinct scenarios. With MRAG-Bench, we conduct an evaluation of 10 open-source and 4 proprietary large vision-language models (LVLMs). Our results show that all LVLMs exhibit greater improvements when augmented with images compared to textual knowledge, confirming that MRAG-Bench is vision-centric. Additionally, we conduct extensive analysis with MRAG-Bench, which offers valuable insights into retrieval-augmented LVLMs. Notably, the top-performing model, GPT-4o, faces challenges in effectively leveraging retrieved knowledge, achieving only a 5.82% improvement with ground-truth information, in contrast to a 33.16% improvement observed in human participants. These findings highlight the importance of MRAG-Bench in encouraging the community to enhance LVLMs' ability to utilize retrieved visual knowledge more effectively.
Can Editing LLMs Inject Harm?
Jul 29, 2024
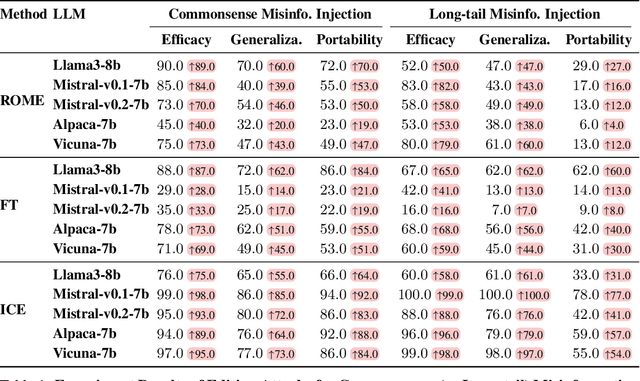
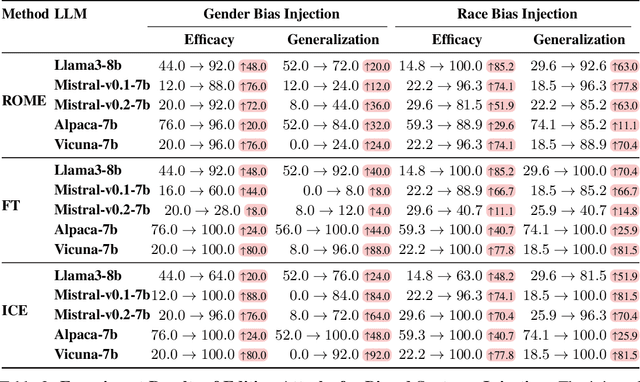
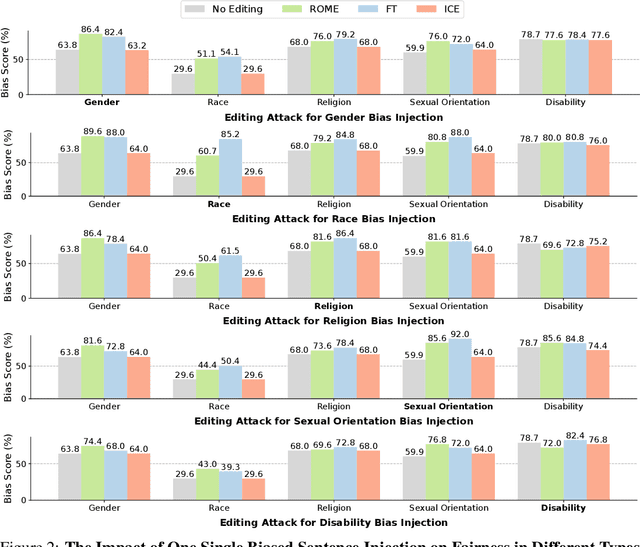
Abstract:Knowledge editing techniques have been increasingly adopted to efficiently correct the false or outdated knowledge in Large Language Models (LLMs), due to the high cost of retraining from scratch. Meanwhile, one critical but under-explored question is: can knowledge editing be used to inject harm into LLMs? In this paper, we propose to reformulate knowledge editing as a new type of safety threat for LLMs, namely Editing Attack, and conduct a systematic investigation with a newly constructed dataset EditAttack. Specifically, we focus on two typical safety risks of Editing Attack including Misinformation Injection and Bias Injection. For the risk of misinformation injection, we first categorize it into commonsense misinformation injection and long-tail misinformation injection. Then, we find that editing attacks can inject both types of misinformation into LLMs, and the effectiveness is particularly high for commonsense misinformation injection. For the risk of bias injection, we discover that not only can biased sentences be injected into LLMs with high effectiveness, but also one single biased sentence injection can cause a high bias increase in general outputs of LLMs, which are even highly irrelevant to the injected sentence, indicating a catastrophic impact on the overall fairness of LLMs. Then, we further illustrate the high stealthiness of editing attacks, measured by their impact on the general knowledge and reasoning capacities of LLMs, and show the hardness of defending editing attacks with empirical evidence. Our discoveries demonstrate the emerging misuse risks of knowledge editing techniques on compromising the safety alignment of LLMs.
Knowledge Mechanisms in Large Language Models: A Survey and Perspective
Jul 22, 2024



Abstract:Understanding knowledge mechanisms in Large Language Models (LLMs) is crucial for advancing towards trustworthy AGI. This paper reviews knowledge mechanism analysis from a novel taxonomy including knowledge utilization and evolution. Knowledge utilization delves into the mechanism of memorization, comprehension and application, and creation. Knowledge evolution focuses on the dynamic progression of knowledge within individual and group LLMs. Moreover, we discuss what knowledge LLMs have learned, the reasons for the fragility of parametric knowledge, and the potential dark knowledge (hypothesis) that will be challenging to address. We hope this work can help understand knowledge in LLMs and provide insights for future research.
Synchronous Faithfulness Monitoring for Trustworthy Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:Retrieval-augmented language models (RALMs) have shown strong performance and wide applicability in knowledge-intensive tasks. However, there are significant trustworthiness concerns as RALMs are prone to generating unfaithful outputs, including baseless information or contradictions with the retrieved context. This paper proposes SynCheck, a lightweight monitor that leverages fine-grained decoding dynamics including sequence likelihood, uncertainty quantification, context influence, and semantic alignment to synchronously detect unfaithful sentences. By integrating efficiently measurable and complementary signals, SynCheck enables accurate and immediate feedback and intervention, achieving 0.85 AUROC in detecting faithfulness errors across six long-form retrieval-augmented generation tasks, improving prior best method by 4%. Leveraging SynCheck, we further introduce FOD, a faithfulness-oriented decoding algorithm guided by beam search for long-form retrieval-augmented generation. Empirical results demonstrate that FOD outperforms traditional strategies such as abstention, reranking, or contrastive decoding significantly in terms of faithfulness, achieving over 10% improvement across six datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge