Suhaila Shakiah
DISPO: Enhancing Training Efficiency and Stability in Reinforcement Learning for Large Language Model Mathematical Reasoning
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards has emerged as a promising paradigm for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models particularly in mathematics. Current approaches in this domain present a clear trade-off: PPO-style methods (e.g., GRPO/DAPO) offer training stability but exhibit slow learning trajectories due to their trust-region constraints on policy updates, while REINFORCE-style approaches (e.g., CISPO) demonstrate improved learning efficiency but suffer from performance instability as they clip importance sampling weights while still permitting non-zero gradients outside the trust-region. To address these limitations, we introduce DISPO, a simple yet effective REINFORCE-style algorithm that decouples the up-clipping and down-clipping of importance sampling weights for correct and incorrect responses, yielding four controllable policy update regimes. Through targeted ablations, we uncover how each regime impacts training: for correct responses, weights >1 increase the average token entropy (i.e., exploration) while weights <1 decrease it (i.e., distillation) -- both beneficial but causing gradual performance degradation when excessive. For incorrect responses, overly restrictive clipping triggers sudden performance collapse through repetitive outputs (when weights >1) or vanishing response lengths (when weights <1). By separately tuning these four clipping parameters, DISPO maintains the exploration-distillation balance while preventing catastrophic failures, achieving 61.04% on AIME'24 (vs. 55.42% CISPO and 50.21% DAPO) with similar gains across various benchmarks and models.
VaPR -- Vision-language Preference alignment for Reasoning
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Preference finetuning methods like Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with AI-generated feedback have shown promise in aligning Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) with human preferences. However, existing techniques overlook the prevalence of noise in synthetic preference annotations in the form of stylistic and length biases. To this end, we introduce a hard-negative response generation framework based on LLM-guided response editing, that produces rejected responses with targeted errors, maintaining stylistic and length similarity to the accepted ones. Using this framework, we develop the VaPR dataset, comprising 30K high-quality samples, to finetune three LVLM families: LLaVA-V1.5, Qwen2VL & Qwen2.5VL (2B-13B sizes). Our VaPR models deliver significant performance improvements across ten benchmarks, achieving average gains of 6.5% (LLaVA), 4.0% (Qwen2VL), and 1.5% (Qwen2.5VL), with notable improvements on reasoning tasks. A scaling analysis shows that performance consistently improves with data size, with LLaVA models benefiting even at smaller scales. Moreover, VaPR reduces the tendency to answer "Yes" in binary questions - addressing a common failure mode in LVLMs like LLaVA. Lastly, we show that the framework generalizes to open-source LLMs as editors, with models trained on VaPR-OS achieving ~99% of the performance of models trained on \name, which is synthesized using GPT-4o. Our data, models, and code can be found on the project page https://vap-r.github.io
GROUNDHOG: Grounding Large Language Models to Holistic Segmentation
Feb 26, 2024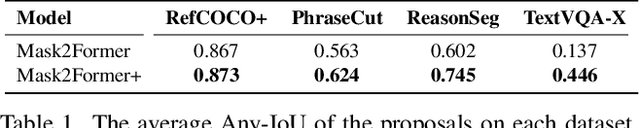
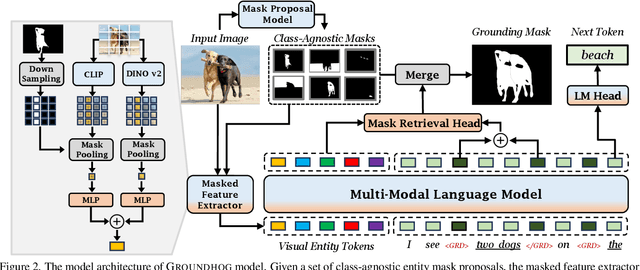
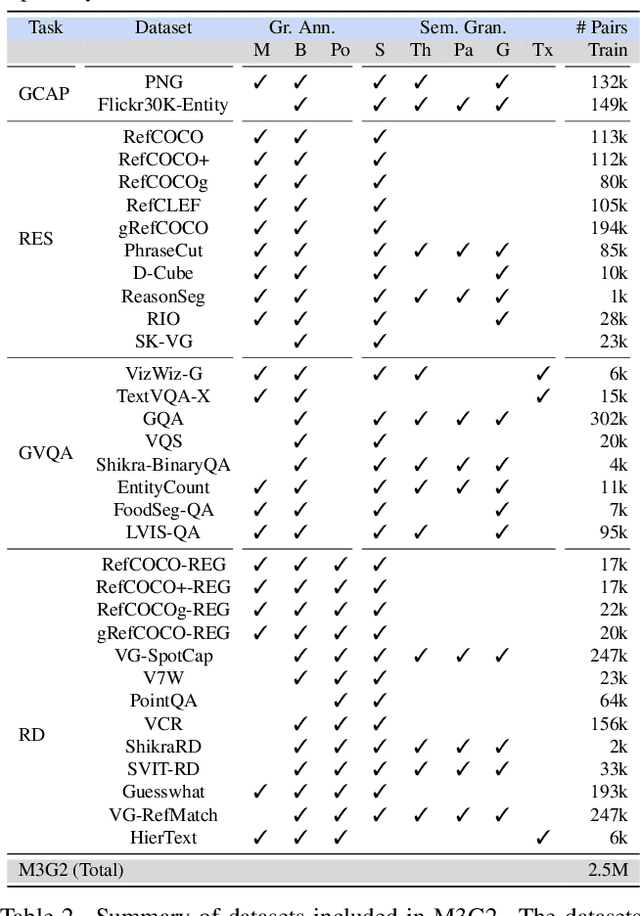
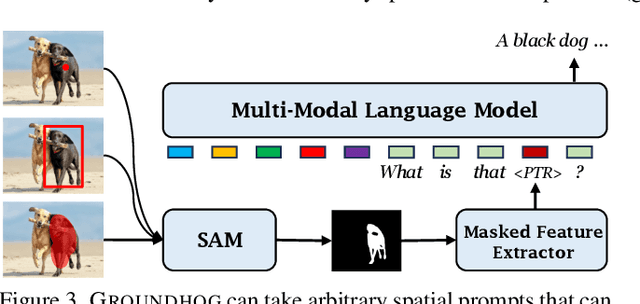
Abstract:Most multimodal large language models (MLLMs) learn language-to-object grounding through causal language modeling where grounded objects are captured by bounding boxes as sequences of location tokens. This paradigm lacks pixel-level representations that are important for fine-grained visual understanding and diagnosis. In this work, we introduce GROUNDHOG, an MLLM developed by grounding Large Language Models to holistic segmentation. GROUNDHOG incorporates a masked feature extractor and converts extracted features into visual entity tokens for the MLLM backbone, which then connects groundable phrases to unified grounding masks by retrieving and merging the entity masks. To train GROUNDHOG, we carefully curated M3G2, a grounded visual instruction tuning dataset with Multi-Modal Multi-Grained Grounding, by harvesting a collection of segmentation-grounded datasets with rich annotations. Our experimental results show that GROUNDHOG achieves superior performance on various language grounding tasks without task-specific fine-tuning, and significantly reduces object hallucination. GROUNDHOG also demonstrates better grounding towards complex forms of visual input and provides easy-to-understand diagnosis in failure cases.
Mastering Robot Manipulation with Multimodal Prompts through Pretraining and Multi-task Fine-tuning
Oct 14, 2023Abstract:Prompt-based learning has been demonstrated as a compelling paradigm contributing to large language models' tremendous success (LLMs). Inspired by their success in language tasks, existing research has leveraged LLMs in embodied instruction following and task planning. However, not much attention has been paid to embodied tasks with multimodal prompts, combining vision signals with text descriptions. This type of task poses a major challenge to robots' capability to understand the interconnection and complementarity between vision and language signals. In this work, we introduce an effective framework that learns a policy to perform robot manipulation with multimodal prompts from multi-task expert trajectories. Our methods consist of a two-stage training pipeline that performs inverse dynamics pretraining and multi-task finetuning. To facilitate multimodal understanding, we design our multimodal prompt encoder by augmenting a pretrained LM with a residual connection to the visual input and model the dependencies among action dimensions. Empirically, we evaluate the efficacy of our method on the VIMA-BENCH and establish a new state-of-the-art (10% improvement in success rate). Moreover, we demonstrate that our model exhibits remarkable in-context learning ability.
Alexa, play with robot: Introducing the First Alexa Prize SimBot Challenge on Embodied AI
Aug 09, 2023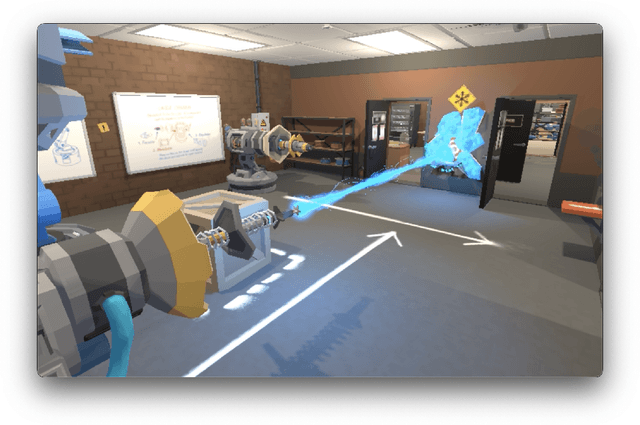



Abstract:The Alexa Prize program has empowered numerous university students to explore, experiment, and showcase their talents in building conversational agents through challenges like the SocialBot Grand Challenge and the TaskBot Challenge. As conversational agents increasingly appear in multimodal and embodied contexts, it is important to explore the affordances of conversational interaction augmented with computer vision and physical embodiment. This paper describes the SimBot Challenge, a new challenge in which university teams compete to build robot assistants that complete tasks in a simulated physical environment. This paper provides an overview of the SimBot Challenge, which included both online and offline challenge phases. We describe the infrastructure and support provided to the teams including Alexa Arena, the simulated environment, and the ML toolkit provided to teams to accelerate their building of vision and language models. We summarize the approaches the participating teams took to overcome research challenges and extract key lessons learned. Finally, we provide analysis of the performance of the competing SimBots during the competition.
LEMMA: Learning Language-Conditioned Multi-Robot Manipulation
Aug 02, 2023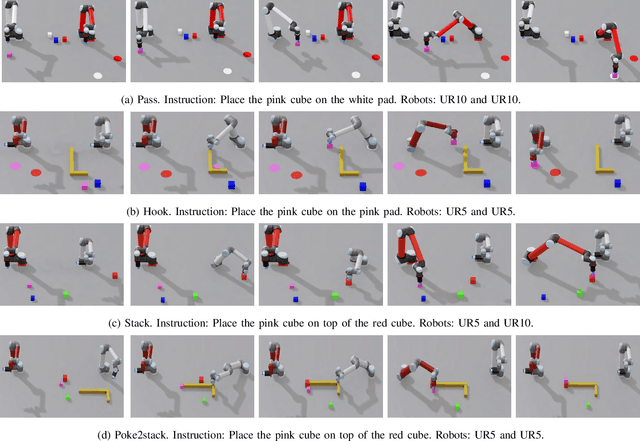
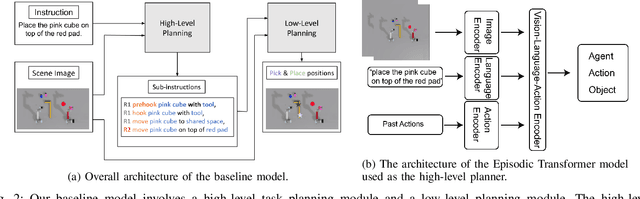

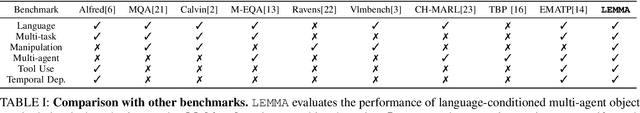
Abstract:Complex manipulation tasks often require robots with complementary capabilities to collaborate. We introduce a benchmark for LanguagE-Conditioned Multi-robot MAnipulation (LEMMA) focused on task allocation and long-horizon object manipulation based on human language instructions in a tabletop setting. LEMMA features 8 types of procedurally generated tasks with varying degree of complexity, some of which require the robots to use tools and pass tools to each other. For each task, we provide 800 expert demonstrations and human instructions for training and evaluations. LEMMA poses greater challenges compared to existing benchmarks, as it requires the system to identify each manipulator's limitations and assign sub-tasks accordingly while also handling strong temporal dependencies in each task. To address these challenges, we propose a modular hierarchical planning approach as a baseline. Our results highlight the potential of LEMMA for developing future language-conditioned multi-robot systems.
Alexa Arena: A User-Centric Interactive Platform for Embodied AI
Mar 02, 2023



Abstract:We introduce Alexa Arena, a user-centric simulation platform for Embodied AI (EAI) research. Alexa Arena provides a variety of multi-room layouts and interactable objects, for the creation of human-robot interaction (HRI) missions. With user-friendly graphics and control mechanisms, Alexa Arena supports the development of gamified robotic tasks readily accessible to general human users, thus opening a new venue for high-efficiency HRI data collection and EAI system evaluation. Along with the platform, we introduce a dialog-enabled instruction-following benchmark and provide baseline results for it. We make Alexa Arena publicly available to facilitate research in building generalizable and assistive embodied agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge