Zhifang Sui
CoLT: Reasoning with Chain of Latent Tool Calls
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) is a critical technique in enhancing the reasoning ability of Large Language Models (LLMs), and latent reasoning methods have been proposed to accelerate the inefficient token-level reasoning chain. We notice that existing latent reasoning methods generally require model structure augmentation and exhaustive training, limiting their broader applicability. In this paper, we propose CoLT, a novel framework that implements latent reasoning as ``tool calls''. Instead of reasoning entirely in the latent space, CoLT generates seed tokens that contain information of a reasoning step. When a latent tool call is triggered, a smaller external model will take the hidden states of seed tokens as its input, and unpack the seed tokens back to a full reasoning step. In this way, we can ensure that the main model reasons in the explicit token space, preserving its ability while improving efficiency. Experimental results on four mathematical datasets demonstrate that CoLT achieves higher accuracy and shorter reasoning length than baseline latent models, and is compatible with reinforcement learning algorithms and different decoder structures.
Decoding in Geometry: Alleviating Embedding-Space Crowding for Complex Reasoning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Sampling-based decoding underlies complex reasoning in large language models (LLMs), where decoding strategies critically shape model behavior. Temperature- and truncation-based methods reshape the next-token distribution through global probability reweighting or thresholding to balance the quality-diversity tradeoff. However, they operate solely on token probabilities, ignoring fine-grained relationships among tokens in the embedding space. We uncover a novel phenomenon, embedding-space crowding, where the next-token distribution concentrates its probability mass on geometrically close tokens in the embedding space. We quantify crowding at multiple granularities and find a statistical association with reasoning success in mathematical problem solving. Motivated by this finding, we propose CraEG, a plug-and-play sampling method that mitigates crowding through geometry-guided reweighting. CraEG is training-free, single-pass, and compatible with standard sampling strategies. Experiments on multiple models and benchmarks demonstrate improved generation performance, with gains in robustness and diversity metrics.
TeachBench: A Syllabus-Grounded Framework for Evaluating Teaching Ability in Large Language Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) show promise as teaching assistants, yet their teaching capability remains insufficiently evaluated. Existing benchmarks mainly focus on problem-solving or problem-level guidance, leaving knowledge-centered teaching underexplored. We propose a syllabus-grounded evaluation framework that measures LLM teaching capability via student performance improvement after multi-turn instruction. By restricting teacher agents to structured knowledge points and example problems, the framework avoids information leakage and enables reuse of existing benchmarks. We instantiate the framework on Gaokao data across multiple subjects. Experiments reveal substantial variation in teaching effectiveness across models and domains: some models perform well in mathematics, while teaching remains challenging in physics and chemistry. We also find that incorporating example problems does not necessarily improve teaching, as models often shift toward example-specific error correction. Overall, our results highlight teaching ability as a distinct and measurable dimension of LLM behavior.
GroundingME: Exposing the Visual Grounding Gap in MLLMs through Multi-Dimensional Evaluation
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Visual grounding, localizing objects from natural language descriptions, represents a critical bridge between language and vision understanding. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) achieve impressive scores on existing benchmarks, a fundamental question remains: can MLLMs truly ground language in vision with human-like sophistication, or are they merely pattern-matching on simplified datasets? Current benchmarks fail to capture real-world complexity where humans effortlessly navigate ambiguous references and recognize when grounding is impossible. To rigorously assess MLLMs' true capabilities, we introduce GroundingME, a benchmark that systematically challenges models across four critical dimensions: (1) Discriminative, distinguishing highly similar objects, (2) Spatial, understanding complex relational descriptions, (3) Limited, handling occlusions or tiny objects, and (4) Rejection, recognizing ungroundable queries. Through careful curation combining automated generation with human verification, we create 1,005 challenging examples mirroring real-world complexity. Evaluating 25 state-of-the-art MLLMs reveals a profound capability gap: the best model achieves only 45.1% accuracy, while most score 0% on rejection tasks, reflexively hallucinating objects rather than acknowledging their absence, raising critical safety concerns for deployment. We explore two strategies for improvements: (1) test-time scaling selects optimal response by thinking trajectory to improve complex grounding by up to 2.9%, and (2) data-mixture training teaches models to recognize ungroundable queries, boosting rejection accuracy from 0% to 27.9%. GroundingME thus serves as both a diagnostic tool revealing current limitations in MLLMs and a roadmap toward human-level visual grounding.
Towards Stable and Effective Reinforcement Learning for Mixture-of-Experts
Oct 27, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in reinforcement learning (RL) have substantially improved the training of large-scale language models, leading to significant gains in generation quality and reasoning ability. However, most existing research focuses on dense models, while RL training for Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures remains underexplored. To address the instability commonly observed in MoE training, we propose a novel router-aware approach to optimize importance sampling (IS) weights in off-policy RL. Specifically, we design a rescaling strategy guided by router logits, which effectively reduces gradient variance and mitigates training divergence. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly improves both the convergence stability and the final performance of MoE models, highlighting the potential of RL algorithmic innovations tailored to MoE architectures and providing a promising direction for efficient training of large-scale expert models.
LLM-REVal: Can We Trust LLM Reviewers Yet?
Oct 14, 2025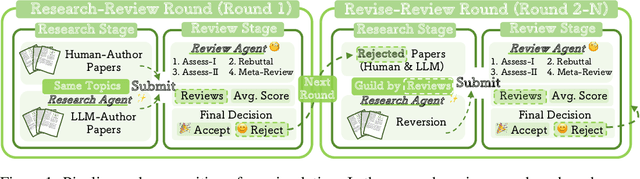
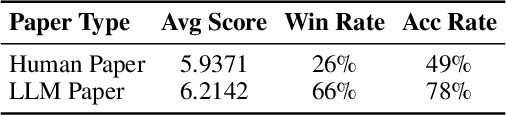
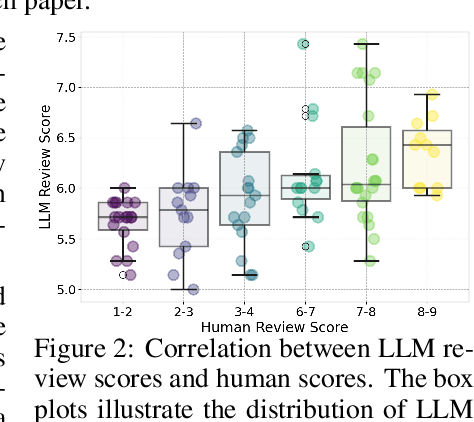
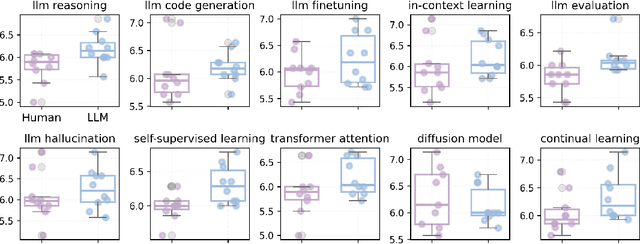
Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has inspired researchers to integrate them extensively into the academic workflow, potentially reshaping how research is practiced and reviewed. While previous studies highlight the potential of LLMs in supporting research and peer review, their dual roles in the academic workflow and the complex interplay between research and review bring new risks that remain largely underexplored. In this study, we focus on how the deep integration of LLMs into both peer-review and research processes may influence scholarly fairness, examining the potential risks of using LLMs as reviewers by simulation. This simulation incorporates a research agent, which generates papers and revises, alongside a review agent, which assesses the submissions. Based on the simulation results, we conduct human annotations and identify pronounced misalignment between LLM-based reviews and human judgments: (1) LLM reviewers systematically inflate scores for LLM-authored papers, assigning them markedly higher scores than human-authored ones; (2) LLM reviewers persistently underrate human-authored papers with critical statements (e.g., risk, fairness), even after multiple revisions. Our analysis reveals that these stem from two primary biases in LLM reviewers: a linguistic feature bias favoring LLM-generated writing styles, and an aversion toward critical statements. These results highlight the risks and equity concerns posed to human authors and academic research if LLMs are deployed in the peer review cycle without adequate caution. On the other hand, revisions guided by LLM reviews yield quality gains in both LLM-based and human evaluations, illustrating the potential of the LLMs-as-reviewers for early-stage researchers and enhancing low-quality papers.
Reinforcement Pre-Training
Jun 09, 2025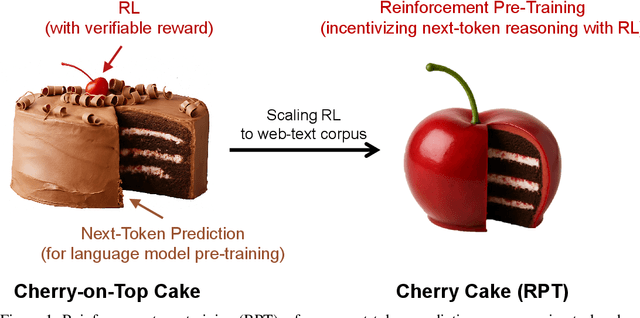
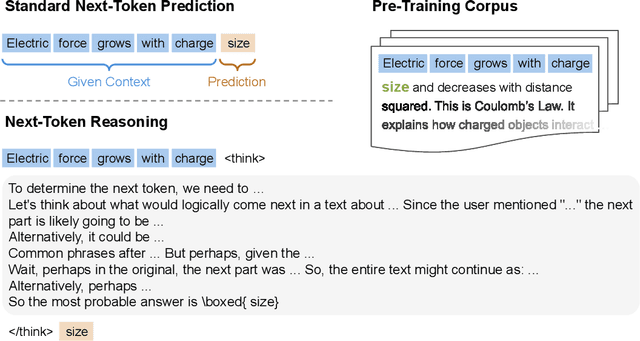

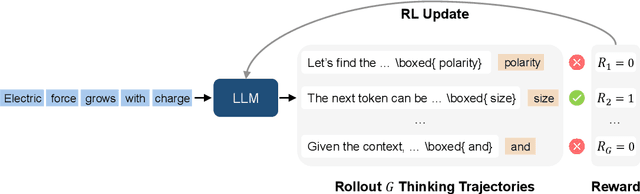
Abstract:In this work, we introduce Reinforcement Pre-Training (RPT) as a new scaling paradigm for large language models and reinforcement learning (RL). Specifically, we reframe next-token prediction as a reasoning task trained using RL, where it receives verifiable rewards for correctly predicting the next token for a given context. RPT offers a scalable method to leverage vast amounts of text data for general-purpose RL, rather than relying on domain-specific annotated answers. By incentivizing the capability of next-token reasoning, RPT significantly improves the language modeling accuracy of predicting the next tokens. Moreover, RPT provides a strong pre-trained foundation for further reinforcement fine-tuning. The scaling curves show that increased training compute consistently improves the next-token prediction accuracy. The results position RPT as an effective and promising scaling paradigm to advance language model pre-training.
HauntAttack: When Attack Follows Reasoning as a Shadow
Jun 08, 2025



Abstract:Emerging Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) consistently excel in mathematical and reasoning tasks, showcasing exceptional capabilities. However, the enhancement of reasoning abilities and the exposure of their internal reasoning processes introduce new safety vulnerabilities. One intriguing concern is: when reasoning is strongly entangled with harmfulness, what safety-reasoning trade-off do LRMs exhibit? To address this issue, we introduce HauntAttack, a novel and general-purpose black-box attack framework that systematically embeds harmful instructions into reasoning questions. Specifically, we treat reasoning questions as carriers and substitute one of their original conditions with a harmful instruction. This process creates a reasoning pathway in which the model is guided step by step toward generating unsafe outputs. Based on HauntAttack, we conduct comprehensive experiments on multiple LRMs. Our results reveal that even the most advanced LRMs exhibit significant safety vulnerabilities. Additionally, we perform a detailed analysis of different models, various types of harmful instructions, and model output patterns, providing valuable insights into the security of LRMs.
Towards Harmonized Uncertainty Estimation for Large Language Models
May 25, 2025Abstract:To facilitate robust and trustworthy deployment of large language models (LLMs), it is essential to quantify the reliability of their generations through uncertainty estimation. While recent efforts have made significant advancements by leveraging the internal logic and linguistic features of LLMs to estimate uncertainty scores, our empirical analysis highlights the pitfalls of these methods to strike a harmonized estimation between indication, balance, and calibration, which hinders their broader capability for accurate uncertainty estimation. To address this challenge, we propose CUE (Corrector for Uncertainty Estimation): A straightforward yet effective method that employs a lightweight model trained on data aligned with the target LLM's performance to adjust uncertainty scores. Comprehensive experiments across diverse models and tasks demonstrate its effectiveness, which achieves consistent improvements of up to 60% over existing methods.
RICo: Refined In-Context Contribution for Automatic Instruction-Tuning Data Selection
May 18, 2025Abstract:Data selection for instruction tuning is crucial for improving the performance of large language models (LLMs) while reducing training costs. In this paper, we propose Refined Contribution Measurement with In-Context Learning (RICo), a novel gradient-free method that quantifies the fine-grained contribution of individual samples to both task-level and global-level model performance. RICo enables more accurate identification of high-contribution data, leading to better instruction tuning. We further introduce a lightweight selection paradigm trained on RICo scores, enabling scalable data selection with a strictly linear inference complexity. Extensive experiments on three LLMs across 12 benchmarks and 5 pairwise evaluation sets demonstrate the effectiveness of RICo. Remarkably, on LLaMA3.1-8B, models trained on 15% of RICo-selected data outperform full datasets by 5.42% points and exceed the best performance of widely used selection methods by 2.06% points. We further analyze high-contribution samples selected by RICo, which show both diverse tasks and appropriate difficulty levels, rather than just the hardest ones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge