Jing Long
RL-VLA$^3$: Reinforcement Learning VLA Accelerating via Full Asynchronism
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:In recent years, Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have emerged as a crucial pathway towards general embodied intelligence, yet their training efficiency has become a key bottleneck. Although existing reinforcement learning (RL)-based training frameworks like RLinf can enhance model generalization, they still rely on synchronous execution, leading to severe resource underutilization and throughput limitations during environment interaction, policy generation (rollout), and model update phases (actor). To overcome this challenge, this paper, for the first time, proposes and implements a fully-asynchronous policy training framework encompassing the entire pipeline from environment interaction, rollout generation, to actor policy updates. Systematically drawing inspiration from asynchronous optimization ideas in large model RL, our framework designs a multi-level decoupled architecture. This includes asynchronous parallelization of environment interaction and trajectory collection, streaming execution for policy generation, and decoupled scheduling for training updates. We validated the effectiveness of our method across diverse VLA models and environments. On the LIBERO benchmark, the framework achieves throughput improvements of up to 59.25\% compared to existing synchronous strategies. When deeply optimizing separation strategies, throughput can be increased by as much as 126.67\%. We verified the effectiveness of each asynchronous component via ablation studies. Scaling law validation across 8 to 256 GPUs demonstrates our method's excellent scalability under most conditions.
Towards Harmonized Uncertainty Estimation for Large Language Models
May 25, 2025Abstract:To facilitate robust and trustworthy deployment of large language models (LLMs), it is essential to quantify the reliability of their generations through uncertainty estimation. While recent efforts have made significant advancements by leveraging the internal logic and linguistic features of LLMs to estimate uncertainty scores, our empirical analysis highlights the pitfalls of these methods to strike a harmonized estimation between indication, balance, and calibration, which hinders their broader capability for accurate uncertainty estimation. To address this challenge, we propose CUE (Corrector for Uncertainty Estimation): A straightforward yet effective method that employs a lightweight model trained on data aligned with the target LLM's performance to adjust uncertainty scores. Comprehensive experiments across diverse models and tasks demonstrate its effectiveness, which achieves consistent improvements of up to 60% over existing methods.
Auxiliary Discrminator Sequence Generative Adversarial Networks (ADSeqGAN) for Few Sample Molecule Generation
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:In this work, we introduce Auxiliary Discriminator Sequence Generative Adversarial Networks (ADSeqGAN), a novel approach for molecular generation in small-sample datasets. Traditional generative models often struggle with limited training data, particularly in drug discovery, where molecular datasets for specific therapeutic targets, such as nucleic acids binders and central nervous system (CNS) drugs, are scarce. ADSeqGAN addresses this challenge by integrating an auxiliary random forest classifier as an additional discriminator into the GAN framework, significantly improves molecular generation quality and class specificity. Our method incorporates pretrained generator and Wasserstein distance to enhance training stability and diversity. We evaluate ADSeqGAN on a dataset comprising nucleic acid-targeting and protein-targeting small molecules, demonstrating its superior ability to generate nucleic acid binders compared to baseline models such as SeqGAN, ORGAN, and MolGPT. Through an oversampling strategy, ADSeqGAN also significantly improves CNS drug generation, achieving a higher yield than traditional de novo models. Critical assessments, including docking simulations and molecular property analysis, confirm that ADSeqGAN-generated molecules exhibit strong binding affinities, enhanced chemical diversity, and improved synthetic feasibility. Overall, ADSeqGAN presents a novel framework for generative molecular design in data-scarce scenarios, offering potential applications in computational drug discovery. We have demonstrated the successful applications of ADSeqGAN in generating synthetic nucleic acid-targeting and CNS drugs in this work.
Diffusion-Based Cloud-Edge-Device Collaborative Learning for Next POI Recommendations
May 22, 2024



Abstract:The rapid expansion of Location-Based Social Networks (LBSNs) has highlighted the importance of effective next Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendations, which leverage historical check-in data to predict users' next POIs to visit. Traditional centralized deep neural networks (DNNs) offer impressive POI recommendation performance but face challenges due to privacy concerns and limited timeliness. In response, on-device POI recommendations have been introduced, utilizing federated learning (FL) and decentralized approaches to ensure privacy and recommendation timeliness. However, these methods often suffer from computational strain on devices and struggle to adapt to new users and regions. This paper introduces a novel collaborative learning framework, Diffusion-Based Cloud-Edge-Device Collaborative Learning for Next POI Recommendations (DCPR), leveraging the diffusion model known for its success across various domains. DCPR operates with a cloud-edge-device architecture to offer region-specific and highly personalized POI recommendations while reducing on-device computational burdens. DCPR minimizes on-device computational demands through a unique blend of global and local learning processes. Our evaluation with two real-world datasets demonstrates DCPR's superior performance in recommendation accuracy, efficiency, and adaptability to new users and regions, marking a significant step forward in on-device POI recommendation technology.
Physical Trajectory Inference Attack and Defense in Decentralized POI Recommendation
Jan 26, 2024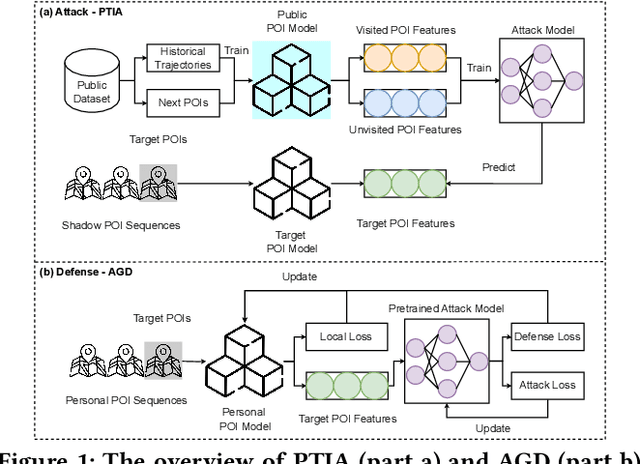
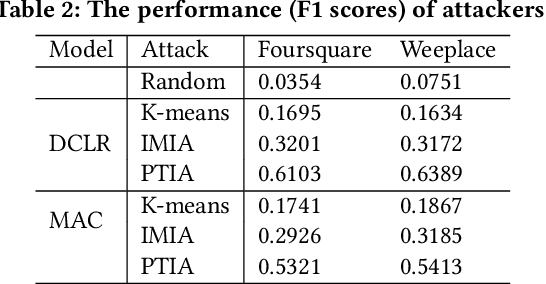
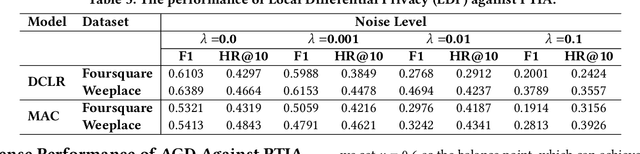
Abstract:As an indispensable personalized service within Location-Based Social Networks (LBSNs), the Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation aims to assist individuals in discovering attractive and engaging places. However, the accurate recommendation capability relies on the powerful server collecting a vast amount of users' historical check-in data, posing significant risks of privacy breaches. Although several collaborative learning (CL) frameworks for POI recommendation enhance recommendation resilience and allow users to keep personal data on-device, they still share personal knowledge to improve recommendation performance, thus leaving vulnerabilities for potential attackers. Given this, we design a new Physical Trajectory Inference Attack (PTIA) to expose users' historical trajectories. Specifically, for each user, we identify the set of interacted POIs by analyzing the aggregated information from the target POIs and their correlated POIs. We evaluate the effectiveness of PTIA on two real-world datasets across two types of decentralized CL frameworks for POI recommendation. Empirical results demonstrate that PTIA poses a significant threat to users' historical trajectories. Furthermore, Local Differential Privacy (LDP), the traditional privacy-preserving method for CL frameworks, has also been proven ineffective against PTIA. In light of this, we propose a novel defense mechanism (AGD) against PTIA based on an adversarial game to eliminate sensitive POIs and their information in correlated POIs. After conducting intensive experiments, AGD has been proven precise and practical, with minimal impact on recommendation performance.
On-Device Recommender Systems: A Comprehensive Survey
Jan 21, 2024



Abstract:Recommender systems have been widely deployed in various real-world applications to help users identify content of interest from massive amounts of information. Traditional recommender systems work by collecting user-item interaction data in a cloud-based data center and training a centralized model to perform the recommendation service. However, such cloud-based recommender systems (CloudRSs) inevitably suffer from excessive resource consumption, response latency, as well as privacy and security risks concerning both data and models. Recently, driven by the advances in storage, communication, and computation capabilities of edge devices, there has been a shift of focus from CloudRSs to on-device recommender systems (DeviceRSs), which leverage the capabilities of edge devices to minimize centralized data storage requirements, reduce the response latency caused by communication overheads, and enhance user privacy and security by localizing data processing and model training. Despite the rapid rise of DeviceRSs, there is a clear absence of timely literature reviews that systematically introduce, categorize and contrast these methods. To bridge this gap, we aim to provide a comprehensive survey of DeviceRSs, covering three main aspects: (1) the deployment and inference of DeviceRSs (2) the training and update of DeviceRSs (3) the security and privacy of DeviceRSs. Furthermore, we provide a fine-grained and systematic taxonomy of the methods involved in each aspect, followed by a discussion regarding challenges and future research directions. This is the first comprehensive survey on DeviceRSs that covers a spectrum of tasks to fit various needs. We believe this survey will help readers effectively grasp the current research status in this field, equip them with relevant technical foundations, and stimulate new research ideas for developing DeviceRSs.
Model-Agnostic Decentralized Collaborative Learning for On-Device POI Recommendation
Apr 08, 2023
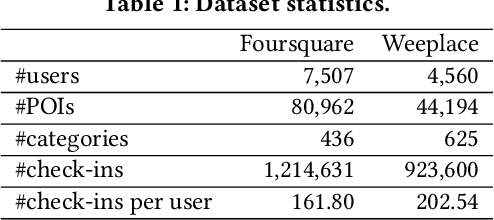
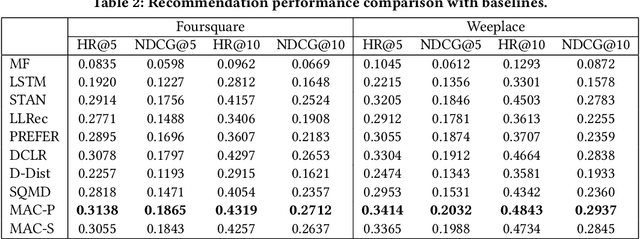
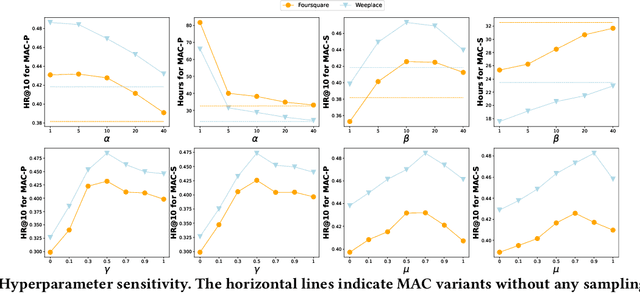
Abstract:As an indispensable personalized service in Location-based Social Networks (LBSNs), the next Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation aims to help people discover attractive and interesting places. Currently, most POI recommenders are based on the conventional centralized paradigm that heavily relies on the cloud to train the recommendation models with large volumes of collected users' sensitive check-in data. Although a few recent works have explored on-device frameworks for resilient and privacy-preserving POI recommendations, they invariably hold the assumption of model homogeneity for parameters/gradients aggregation and collaboration. However, users' mobile devices in the real world have various hardware configurations (e.g., compute resources), leading to heterogeneous on-device models with different architectures and sizes. In light of this, We propose a novel on-device POI recommendation framework, namely Model-Agnostic Collaborative learning for on-device POI recommendation (MAC), allowing users to customize their own model structures (e.g., dimension \& number of hidden layers). To counteract the sparsity of on-device user data, we propose to pre-select neighbors for collaboration based on physical distances, category-level preferences, and social networks. To assimilate knowledge from the above-selected neighbors in an efficient and secure way, we adopt the knowledge distillation framework with mutual information maximization. Instead of sharing sensitive models/gradients, clients in MAC only share their soft decisions on a preloaded reference dataset. To filter out low-quality neighbors, we propose two sampling strategies, performance-triggered sampling and similarity-based sampling, to speed up the training process and obtain optimal recommenders. In addition, we design two novel approaches to generate more effective reference datasets while protecting users' privacy.
Thinking inside The Box: Learning Hypercube Representations for Group Recommendation
Apr 06, 2022



Abstract:As a step beyond traditional personalized recommendation, group recommendation is the task of suggesting items that can satisfy a group of users. In group recommendation, the core is to design preference aggregation functions to obtain a quality summary of all group members' preferences. Such user and group preferences are commonly represented as points in the vector space (i.e., embeddings), where multiple user embeddings are compressed into one to facilitate ranking for group-item pairs. However, the resulted group representations, as points, lack adequate flexibility and capacity to account for the multi-faceted user preferences. Also, the point embedding-based preference aggregation is a less faithful reflection of a group's decision-making process, where all users have to agree on a certain value in each embedding dimension instead of a negotiable interval. In this paper, we propose a novel representation of groups via the notion of hypercubes, which are subspaces containing innumerable points in the vector space. Specifically, we design the hypercube recommender (CubeRec) to adaptively learn group hypercubes from user embeddings with minimal information loss during preference aggregation, and to leverage a revamped distance metric to measure the affinity between group hypercubes and item points. Moreover, to counteract the long-standing issue of data sparsity in group recommendation, we make full use of the geometric expressiveness of hypercubes and innovatively incorporate self-supervision by intersecting two groups. Experiments on four real-world datasets have validated the superiority of CubeRec over state-of-the-art baselines.
Decentralized Collaborative Learning Framework for Next POI Recommendation
Mar 30, 2022



Abstract:Next Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation has become an indispensable functionality in Location-based Social Networks (LBSNs) due to its effectiveness in helping people decide the next POI to visit. However, accurate recommendation requires a vast amount of historical check-in data, thus threatening user privacy as the location-sensitive data needs to be handled by cloud servers. Although there have been several on-device frameworks for privacy-preserving POI recommendations, they are still resource-intensive when it comes to storage and computation, and show limited robustness to the high sparsity of user-POI interactions. On this basis, we propose a novel decentralized collaborative learning framework for POI recommendation (DCLR), which allows users to train their personalized models locally in a collaborative manner. DCLR significantly reduces the local models' dependence on the cloud for training, and can be used to expand arbitrary centralized recommendation models. To counteract the sparsity of on-device user data when learning each local model, we design two self-supervision signals to pretrain the POI representations on the server with geographical and categorical correlations of POIs. To facilitate collaborative learning, we innovatively propose to incorporate knowledge from either geographically or semantically similar users into each local model with attentive aggregation and mutual information maximization. The collaborative learning process makes use of communications between devices while requiring only minor engagement from the central server for identifying user groups, and is compatible with common privacy preservation mechanisms like differential privacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge