Ruiqi Zheng
SCaLRec: Semantic Calibration for LLM-enabled Cloud-Device Sequential Recommendation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Cloud-device collaborative recommendation partitions computation across the cloud and user devices: the cloud provides semantic user modeling, while the device leverages recent interactions and cloud semantic signals for privacy-preserving, responsive reranking. With large language models (LLMs) on the cloud, semantic user representations can improve sequential recommendation by capturing high-level intent. However, regenerating such representations via cloud LLM inference for every request is often infeasible at real-world scale. As a result, on-device reranking commonly reuses a cached cloud semantic user embedding across requests. We empirically identify a cloud semantic staleness effect: reused embeddings become less aligned with the user's latest interactions, leading to measurable ranking degradation. Most existing LLM-enabled cloud-device recommenders are typically designed around on-demand cloud semantics, either by assuming low-latency cloud LLM access or by regenerating semantic embeddings per request. When per-request regeneration is infeasible and cached semantics must be reused, two technical challenges arise: (1) deciding when cached cloud semantics remain useful for on-device reranking, and (2) maintaining ranking quality when the cloud LLM cannot be invoked and only cached semantics are available. To address this gap, we introduce the Semantic Calibration for LLM-enabled Cloud-Device Recommendation (SCaLRec). First, it estimates the reliability of cached semantics under the user's latest interactions. Second, an on-device semantic calibration module is proposed to adjusts the cached semantic embedding on-device using up-to-date interaction evidence, without per-request cloud LLM involvement. Experiments on real-world datasets show that SCaLRec consistently improves recommendation performance over strong baselines under cloud semantic staleness.
DecKG: Decentralized Collaborative Learning with Knowledge Graph Enhancement for POI Recommendation
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Decentralized collaborative learning for Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation has gained research interest due to its advantages in privacy preservation and efficiency, as it keeps data locally and leverages collaborative learning among clients to train models in a decentralized manner. However, since local data is often limited and insufficient for training accurate models, a common solution is integrating external knowledge as auxiliary information to enhance model performance. Nevertheless, this solution poses challenges for decentralized collaborative learning. Due to private nature of local data, identifying relevant auxiliary information specific to each user is non-trivial. Furthermore, resource-constrained local devices struggle to accommodate all auxiliary information, which places heavy burden on local storage. To fill the gap, we propose a novel decentralized collaborative learning with knowledge graph enhancement framework for POI recommendation (DecKG). Instead of directly uploading interacted items, users generate desensitized check-in data by uploading general categories of interacted items and sampling similar items from same category. The server then pretrains KG without sensitive user-item interactions and deploys relevant partitioned sub-KGs to individual users. Entities are further refined on the device, allowing client to client communication to exchange knowledge learned from local data and sub-KGs. Evaluations across two real-world datasets demonstrate DecKG's effectiveness recommendation performance.
Poisoning Decentralized Collaborative Recommender System and Its Countermeasures
Apr 01, 2024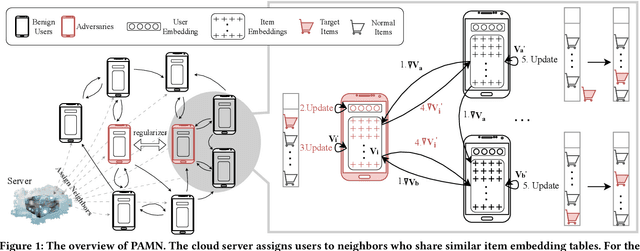
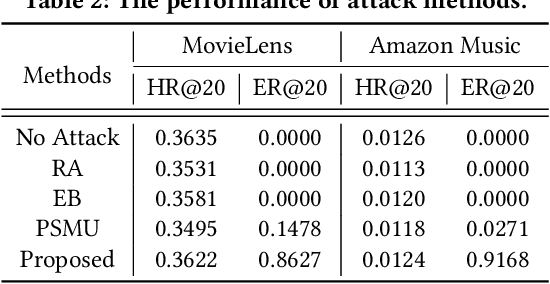
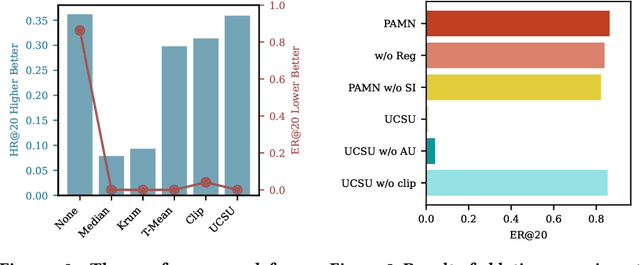
Abstract:To make room for privacy and efficiency, the deployment of many recommender systems is experiencing a shift from central servers to personal devices, where the federated recommender systems (FedRecs) and decentralized collaborative recommender systems (DecRecs) are arguably the two most representative paradigms. While both leverage knowledge (e.g., gradients) sharing to facilitate learning local models, FedRecs rely on a central server to coordinate the optimization process, yet in DecRecs, the knowledge sharing directly happens between clients. Knowledge sharing also opens a backdoor for model poisoning attacks, where adversaries disguise themselves as benign clients and disseminate polluted knowledge to achieve malicious goals like promoting an item's exposure rate. Although research on such poisoning attacks provides valuable insights into finding security loopholes and corresponding countermeasures, existing attacks mostly focus on FedRecs, and are either inapplicable or ineffective for DecRecs. Compared with FedRecs where the tampered information can be universally distributed to all clients once uploaded to the cloud, each adversary in DecRecs can only communicate with neighbor clients of a small size, confining its impact to a limited range. To fill the gap, we present a novel attack method named Poisoning with Adaptive Malicious Neighbors (PAMN). With item promotion in top-K recommendation as the attack objective, PAMN effectively boosts target items' ranks with several adversaries that emulate benign clients and transfers adaptively crafted gradients conditioned on each adversary's neighbors. Moreover, with the vulnerabilities of DecRecs uncovered, a dedicated defensive mechanism based on user-level gradient clipping with sparsified updating is proposed. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the poisoning attack and the robustness of our defensive mechanism.
Towards Personalized Privacy: User-Governed Data Contribution for Federated Recommendation
Jan 31, 2024
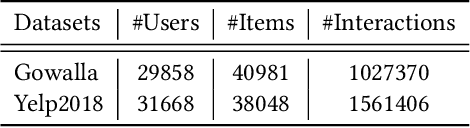


Abstract:Federated recommender systems (FedRecs) have gained significant attention for their potential to protect user's privacy by keeping user privacy data locally and only communicating model parameters/gradients to the server. Nevertheless, the currently existing architecture of FedRecs assumes that all users have the same 0-privacy budget, i.e., they do not upload any data to the server, thus overlooking those users who are less concerned about privacy and are willing to upload data to get a better recommendation service. To bridge this gap, this paper explores a user-governed data contribution federated recommendation architecture where users are free to take control of whether they share data and the proportion of data they share to the server. To this end, this paper presents a cloud-device collaborative graph neural network federated recommendation model, named CDCGNNFed. It trains user-centric ego graphs locally, and high-order graphs based on user-shared data in the server in a collaborative manner via contrastive learning. Furthermore, a graph mending strategy is utilized to predict missing links in the graph on the server, thus leveraging the capabilities of graph neural networks over high-order graphs. Extensive experiments were conducted on two public datasets, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Decentralized Collaborative Learning with Adaptive Reference Data for On-Device POI Recommendation
Jan 25, 2024



Abstract:In Location-based Social Networks, Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation helps users discover interesting places. There is a trend to move from the cloud-based model to on-device recommendations for privacy protection and reduced server reliance. Due to the scarcity of local user-item interactions on individual devices, solely relying on local instances is not adequate. Collaborative Learning (CL) emerges to promote model sharing among users, where reference data is an intermediary that allows users to exchange their soft decisions without directly sharing their private data or parameters, ensuring privacy and benefiting from collaboration. However, existing CL-based recommendations typically use a single reference for all users. Reference data valuable for one user might be harmful to another, given diverse user preferences. Users may not offer meaningful soft decisions on items outside their interest scope. Consequently, using the same reference data for all collaborations can impede knowledge exchange and lead to sub-optimal performance. To address this gap, we introduce the Decentralized Collaborative Learning with Adaptive Reference Data (DARD) framework, which crafts adaptive reference data for effective user collaboration. It first generates a desensitized public reference data pool with transformation and probability data generation methods. For each user, the selection of adaptive reference data is executed in parallel by training loss tracking and influence function. Local models are trained with individual private data and collaboratively with the geographical and semantic neighbors. During the collaboration between two users, they exchange soft decisions based on a combined set of their adaptive reference data. Our evaluations across two real-world datasets highlight DARD's superiority in recommendation performance and addressing the scarcity of available reference data.
On-Device Recommender Systems: A Comprehensive Survey
Jan 21, 2024



Abstract:Recommender systems have been widely deployed in various real-world applications to help users identify content of interest from massive amounts of information. Traditional recommender systems work by collecting user-item interaction data in a cloud-based data center and training a centralized model to perform the recommendation service. However, such cloud-based recommender systems (CloudRSs) inevitably suffer from excessive resource consumption, response latency, as well as privacy and security risks concerning both data and models. Recently, driven by the advances in storage, communication, and computation capabilities of edge devices, there has been a shift of focus from CloudRSs to on-device recommender systems (DeviceRSs), which leverage the capabilities of edge devices to minimize centralized data storage requirements, reduce the response latency caused by communication overheads, and enhance user privacy and security by localizing data processing and model training. Despite the rapid rise of DeviceRSs, there is a clear absence of timely literature reviews that systematically introduce, categorize and contrast these methods. To bridge this gap, we aim to provide a comprehensive survey of DeviceRSs, covering three main aspects: (1) the deployment and inference of DeviceRSs (2) the training and update of DeviceRSs (3) the security and privacy of DeviceRSs. Furthermore, we provide a fine-grained and systematic taxonomy of the methods involved in each aspect, followed by a discussion regarding challenges and future research directions. This is the first comprehensive survey on DeviceRSs that covers a spectrum of tasks to fit various needs. We believe this survey will help readers effectively grasp the current research status in this field, equip them with relevant technical foundations, and stimulate new research ideas for developing DeviceRSs.
Personalized Elastic Embedding Learning for On-Device Recommendation
Jun 18, 2023



Abstract:To address privacy concerns and reduce network latency, there has been a recent trend of compressing cumbersome recommendation models trained on the cloud and deploying compact recommender models to resource-limited devices for real-time recommendation. Existing solutions generally overlook device heterogeneity and user heterogeneity. They either require all devices to share the same compressed model or the devices with the same resource budget to share the same model. However, even users with the same devices may have different preferences. In addition, they assume the available resources (e.g., memory) for the recommender on a device are constant, which is not reflective of reality. In light of device and user heterogeneities as well as dynamic resource constraints, this paper proposes a Personalized Elastic Embedding Learning framework (PEEL) for on-device recommendation, which generates personalized embeddings for devices with various memory budgets in once-for-all manner, efficiently adapting to new or dynamic budgets, and effectively addressing user preference diversity by assigning personalized embeddings for different groups of users. Specifically, it pretrains using user-item interaction instances to generate the global embedding table and cluster users into groups. Then, it refines the embedding tables with local interaction instances within each group. Personalized elastic embedding is generated from the group-wise embedding blocks and their weights that indicate the contribution of each embedding block to the local recommendation performance. PEEL efficiently generates personalized elastic embeddings by selecting embedding blocks with the largest weights, making it adaptable to dynamic memory budgets. Extensive experiments are conducted on two public datasets, and the results show that PEEL yields superior performance on devices with heterogeneous and dynamic memory budgets.
Semi-decentralized Federated Ego Graph Learning for Recommendation
Feb 10, 2023



Abstract:Collaborative filtering (CF) based recommender systems are typically trained based on personal interaction data (e.g., clicks and purchases) that could be naturally represented as ego graphs. However, most existing recommendation methods collect these ego graphs from all users to compose a global graph to obtain high-order collaborative information between users and items, and these centralized CF recommendation methods inevitably lead to a high risk of user privacy leakage. Although recently proposed federated recommendation systems can mitigate the privacy problem, they either restrict the on-device local training to an isolated ego graph or rely on an additional third-party server to access other ego graphs resulting in a cumbersome pipeline, which is hard to work in practice. In addition, existing federated recommendation systems require resource-limited devices to maintain the entire embedding tables resulting in high communication costs. In light of this, we propose a semi-decentralized federated ego graph learning framework for on-device recommendations, named SemiDFEGL, which introduces new device-to-device collaborations to improve scalability and reduce communication costs and innovatively utilizes predicted interacted item nodes to connect isolated ego graphs to augment local subgraphs such that the high-order user-item collaborative information could be used in a privacy-preserving manner. Furthermore, the proposed framework is model-agnostic, meaning that it could be seamlessly integrated with existing graph neural network-based recommendation methods and privacy protection techniques. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed SemiDFEGL, extensive experiments are conducted on three public datasets, and the results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed SemiDFEGL compared to other federated recommendation methods.
AutoML for Deep Recommender Systems: A Survey
Mar 25, 2022



Abstract:Recommender systems play a significant role in information filtering and have been utilised in different scenarios, such as e-commerce and social media. With the prosperity of deep learning, deep recommender systems show superior performance by capturing non-linear information and item-user relationships. However, the design of deep recommender systems heavily relies on human experiences and expert knowledge. To tackle this problem, Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) is introduced to automatically search for the proper candidates for different parts of deep recommender systems. This survey performs a comprehensive review of the literature in this field. Firstly, we propose an abstract concept for AutoML for deep recommender systems (AutoRecSys) that describes its building blocks and distinguishes it from conventional AutoML techniques and recommender systems. Secondly, we present a taxonomy as a classification framework containing embedding dimension search, feature interaction search, model design search and other components search. Furthermore, we put a particular emphasis on the search space and search strategy, as they are the common thread to connect all methods within each category and enable practitioners to analyse and compare various approaches. Finally, we propose four future promising research directions that will lead this line of research.
ImGAGN:Imbalanced Network Embedding via Generative Adversarial Graph Networks
Jun 05, 2021



Abstract:Imbalanced classification on graphs is ubiquitous yet challenging in many real-world applications, such as fraudulent node detection. Recently, graph neural networks (GNNs) have shown promising performance on many network analysis tasks. However, most existing GNNs have almost exclusively focused on the balanced networks, and would get unappealing performance on the imbalanced networks. To bridge this gap, in this paper, we present a generative adversarial graph network model, called ImGAGN to address the imbalanced classification problem on graphs. It introduces a novel generator for graph structure data, named GraphGenerator, which can simulate both the minority class nodes' attribute distribution and network topological structure distribution by generating a set of synthetic minority nodes such that the number of nodes in different classes can be balanced. Then a graph convolutional network (GCN) discriminator is trained to discriminate between real nodes and fake (i.e., generated) nodes, and also between minority nodes and majority nodes on the synthetic balanced network. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, extensive experiments are conducted on four real-world imbalanced network datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method ImGAGN outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms for semi-supervised imbalanced node classification task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge