Lucas Bandarkar
Translation as a Scalable Proxy for Multilingual Evaluation
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:The rapid proliferation of LLMs has created a critical evaluation paradox: while LLMs claim multilingual proficiency, comprehensive non-machine-translated benchmarks exist for fewer than 30 languages, leaving >98% of the world's 7,000 languages in an empirical void. Traditional benchmark construction faces scaling challenges such as cost, scarcity of domain experts, and data contamination. We evaluate the validity of a simpler alternative: can translation quality alone indicate a model's broader multilingual capabilities? Through systematic evaluation of 14 models (1B-72B parameters) across 9 diverse benchmarks and 7 translation metrics, we find that translation performance is a good indicator of downstream task success (e.g., Phi-4, median Pearson r: MetricX = 0.89, xCOMET = 0.91, SSA-COMET = 0.87). These results suggest that the representational abilities supporting faithful translation overlap with those required for multilingual understanding. Translation quality, thus emerges as a strong, inexpensive first-pass proxy of multilingual performance, enabling a translation-first screening with targeted follow-up for specific tasks.
Multilingual Routing in Mixture-of-Experts
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures have become the key to scaling modern LLMs, yet little is understood about how their sparse routing dynamics respond to multilingual data. In this work, we analyze expert routing patterns using parallel multilingual datasets and present highly interpretable layer-wise phenomena. We find that MoE models route tokens in language-specific ways in the early and late decoder layers but exhibit significant cross-lingual routing alignment in middle layers, mirroring parameter-sharing trends observed in dense LLMs. In particular, we reveal a clear, strong correlation between a model's performance in a given language and how similarly its tokens are routed to English in these layers. Extending beyond correlation, we explore inference-time interventions that induce higher cross-lingual routing alignment. We introduce a method that steers the router by promoting middle-layer task experts frequently activated in English, and it successfully increases multilingual performance. These 1-2% gains are remarkably consistent across two evaluation tasks, three models, and 15+ languages, especially given that these simple interventions override routers of extensively trained, state-of-the-art LLMs. In comparison, interventions outside of the middle layers or targeting multilingual-specialized experts only yield performance degradation. Altogether, we present numerous findings that explain how MoEs process non-English text and demonstrate that generalization is limited by the model's ability to leverage language-universal experts in all languages.
The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Model Merging for Cross-Lingual Transfer in LLMs
May 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) still struggle across tasks outside of high-resource languages. In this work, we investigate cross-lingual transfer to lower-resource languages where task-specific post-training data is scarce. Building on prior work, we first validate that the subsets of model parameters that matter most for mathematical reasoning and multilingual capabilities are distinctly non-overlapping. To exploit this implicit separability between task and target language parameterization, we develop and analyze numerous modular frameworks to improve the composition of the two during fine-tuning. These methods generally employ freezing parameters or post hoc model merging to assign math and language improvement to different key parts of the LLM. In the absence of in-language math data, we demonstrate that the modular approaches successfully improve upon baselines across three languages, four models, and two fine-tuning paradigms (full and LoRA). Furthermore, we identify the most consistently successful modular method to be fine-tuning separate language and math experts and model merging via Layer-Swapping, somewhat surprisingly. We offer possible explanations for this result via recent works on the linearity of task vectors. We further explain this by empirically showing that reverting less useful fine-tuning updates after training often outperforms freezing them from the start.
FIG: Forward-Inverse Generation for Low-Resource Domain-specific Event Detection
Feb 24, 2025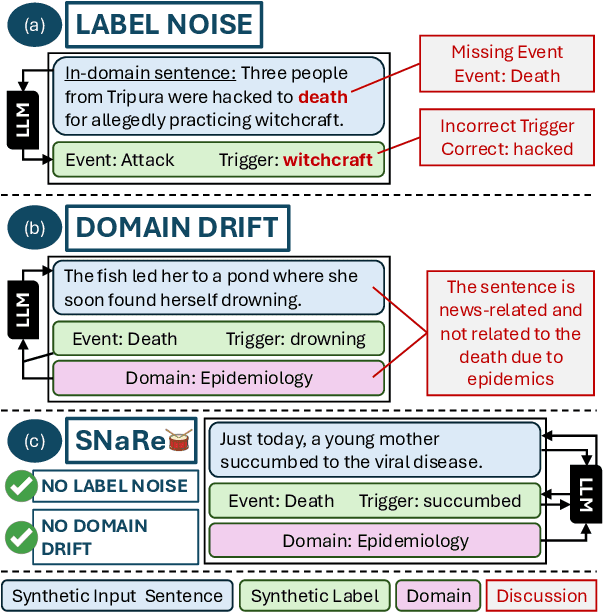
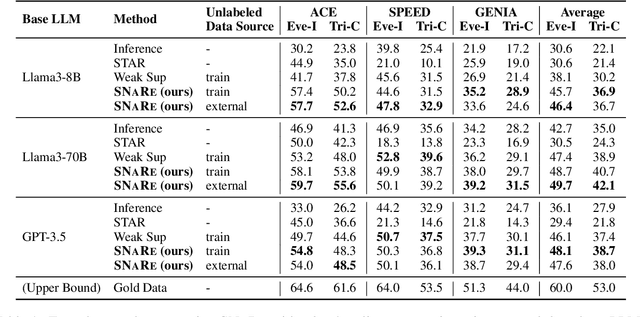
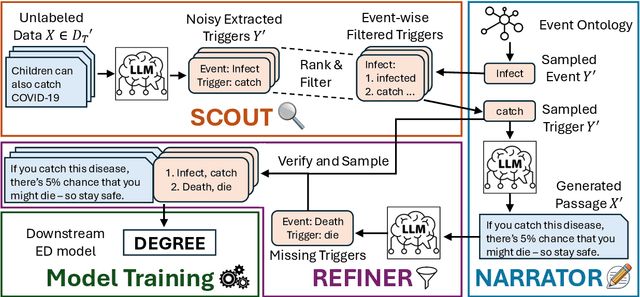
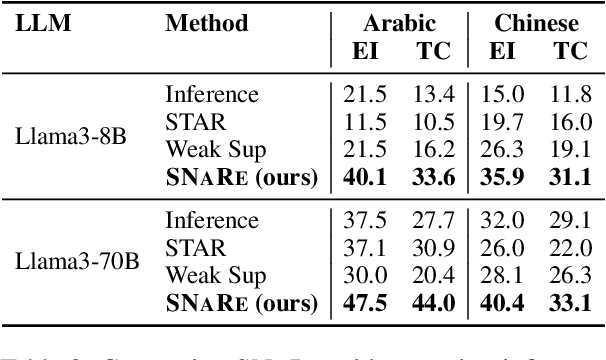
Abstract:Event Detection (ED) is the task of identifying typed event mentions of interest from natural language text, which benefits domain-specific reasoning in biomedical, legal, and epidemiological domains. However, procuring supervised data for thousands of events for various domains is a laborious and expensive task. To this end, existing works have explored synthetic data generation via forward (generating labels for unlabeled sentences) and inverse (generating sentences from generated labels) generations. However, forward generation often produces noisy labels, while inverse generation struggles with domain drift and incomplete event annotations. To address these challenges, we introduce FIG, a hybrid approach that leverages inverse generation for high-quality data synthesis while anchoring it to domain-specific cues extracted via forward generation on unlabeled target data. FIG further enhances its synthetic data by adding missing annotations through forward generation-based refinement. Experimentation on three ED datasets from diverse domains reveals that FIG outperforms the best baseline achieving average gains of 3.3% F1 and 5.4% F1 in the zero-shot and few-shot settings respectively. Analyzing the generated trigger hit rate and human evaluation substantiates FIG's superior domain alignment and data quality compared to existing baselines.
Layer Swapping for Zero-Shot Cross-Lingual Transfer in Large Language Models
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:Model merging, such as model souping, is the practice of combining different models with the same architecture together without further training. In this work, we present a model merging methodology that addresses the difficulty of fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) for target tasks in non-English languages, where task-specific data is often unavailable. We focus on mathematical reasoning and without in-language math data, facilitate cross-lingual transfer by composing language and math capabilities. Starting from the same pretrained model, we fine-tune separate "experts" on math instruction data in English and on generic instruction data in the target language. We then replace the top and bottom transformer layers of the math expert directly with layers from the language expert, which consequently enhances math performance in the target language. The resulting merged models outperform the individual experts and other merging methods on the math benchmark, MGSM, by 10% across four major languages where math instruction data is scarce. In addition, this layer swapping is simple, inexpensive, and intuitive, as it is based on an interpretative analysis of the most important parameter changes during the fine-tuning of each expert. The ability to successfully re-compose LLMs for cross-lingual transfer in this manner opens up future possibilities to combine model expertise, create modular solutions, and transfer reasoning capabilities across languages all post hoc.
The Belebele Benchmark: a Parallel Reading Comprehension Dataset in 122 Language Variants
Aug 31, 2023



Abstract:We present Belebele, a multiple-choice machine reading comprehension (MRC) dataset spanning 122 language variants. Significantly expanding the language coverage of natural language understanding (NLU) benchmarks, this dataset enables the evaluation of text models in high-, medium-, and low-resource languages. Each question is based on a short passage from the Flores-200 dataset and has four multiple-choice answers. The questions were carefully curated to discriminate between models with different levels of general language comprehension. The English dataset on its own proves difficult enough to challenge state-of-the-art language models. Being fully parallel, this dataset enables direct comparison of model performance across all languages. We use this dataset to evaluate the capabilities of multilingual masked language models (MLMs) and large language models (LLMs). We present extensive results and find that despite significant cross-lingual transfer in English-centric LLMs, much smaller MLMs pretrained on balanced multilingual data still understand far more languages. We also observe that larger vocabulary size and conscious vocabulary construction correlate with better performance on low-resource languages. Overall, Belebele opens up new avenues for evaluating and analyzing the multilingual capabilities of NLP systems.
Can Transformer Models Measure Coherence In Text? Re-Thinking the Shuffle Test
Jul 07, 2021



Abstract:The Shuffle Test is the most common task to evaluate whether NLP models can measure coherence in text. Most recent work uses direct supervision on the task; we show that by simply finetuning a RoBERTa model, we can achieve a near perfect accuracy of 97.8%, a state-of-the-art. We argue that this outstanding performance is unlikely to lead to a good model of text coherence, and suggest that the Shuffle Test should be approached in a Zero-Shot setting: models should be evaluated without being trained on the task itself. We evaluate common models in this setting, such as Generative and Bi-directional Transformers, and find that larger architectures achieve high-performance out-of-the-box. Finally, we suggest the k-Block Shuffle Test, a modification of the original by increasing the size of blocks shuffled. Even though human reader performance remains high (around 95% accuracy), model performance drops from 94% to 78% as block size increases, creating a conceptually simple challenge to benchmark NLP models. Code available: https://github.com/tingofurro/shuffle_test/
* Accepted at ACL-IJCNLP 2021 (short paper), 7 pages, 4 figures
News Headline Grouping as a Challenging NLU Task
May 12, 2021



Abstract:Recent progress in Natural Language Understanding (NLU) has seen the latest models outperform human performance on many standard tasks. These impressive results have led the community to introspect on dataset limitations, and iterate on more nuanced challenges. In this paper, we introduce the task of HeadLine Grouping (HLG) and a corresponding dataset (HLGD) consisting of 20,056 pairs of news headlines, each labeled with a binary judgement as to whether the pair belongs within the same group. On HLGD, human annotators achieve high performance of around 0.9 F-1, while current state-of-the art Transformer models only reach 0.75 F-1, opening the path for further improvements. We further propose a novel unsupervised Headline Generator Swap model for the task of HeadLine Grouping that achieves within 3 F-1 of the best supervised model. Finally, we analyze high-performing models with consistency tests, and find that models are not consistent in their predictions, revealing modeling limits of current architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge