Luke Zettlemoyer
University of Washington
Beyond Language Modeling: An Exploration of Multimodal Pretraining
Mar 03, 2026Abstract:The visual world offers a critical axis for advancing foundation models beyond language. Despite growing interest in this direction, the design space for native multimodal models remains opaque. We provide empirical clarity through controlled, from-scratch pretraining experiments, isolating the factors that govern multimodal pretraining without interference from language pretraining. We adopt the Transfusion framework, using next-token prediction for language and diffusion for vision, to train on diverse data including text, video, image-text pairs, and even action-conditioned video. Our experiments yield four key insights: (i) Representation Autoencoder (RAE) provides an optimal unified visual representation by excelling at both visual understanding and generation; (ii) visual and language data are complementary and yield synergy for downstream capabilities; (iii) unified multimodal pretraining leads naturally to world modeling, with capabilities emerging from general training; and (iv) Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) enables efficient and effective multimodal scaling while naturally inducing modality specialization. Through IsoFLOP analysis, we compute scaling laws for both modalities and uncover a scaling asymmetry: vision is significantly more data-hungry than language. We demonstrate that the MoE architecture harmonizes this scaling asymmetry by providing the high model capacity required by language while accommodating the data-intensive nature of vision, paving the way for truly unified multimodal models.
Robometer: Scaling General-Purpose Robotic Reward Models via Trajectory Comparisons
Mar 02, 2026Abstract:General-purpose robot reward models are typically trained to predict absolute task progress from expert demonstrations, providing only local, frame-level supervision. While effective for expert demonstrations, this paradigm scales poorly to large-scale robotics datasets where failed and suboptimal trajectories are abundant and assigning dense progress labels is ambiguous. We introduce Robometer, a scalable reward modeling framework that combines intra-trajectory progress supervision with inter-trajectory preference supervision. Robometer is trained with a dual objective: a frame-level progress loss that anchors reward magnitude on expert data, and a trajectory-comparison preference loss that imposes global ordering constraints across trajectories of the same task, enabling effective learning from both real and augmented failed trajectories. To support this formulation at scale, we curate RBM-1M, a reward-learning dataset comprising over one million trajectories spanning diverse robot embodiments and tasks, including substantial suboptimal and failure data. Across benchmarks and real-world evaluations, Robometer learns more generalizable reward functions than prior methods and improves robot learning performance across a diverse set of downstream applications. Code, model weights, and videos at https://robometer.github.io/.
Anchored Decoding: Provably Reducing Copyright Risk for Any Language Model
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Modern language models (LMs) tend to memorize portions of their training data and emit verbatim spans. When the underlying sources are sensitive or copyright-protected, such reproduction raises issues of consent and compensation for creators and compliance risks for developers. We propose Anchored Decoding, a plug-and-play inference-time method for suppressing verbatim copying: it enables decoding from any risky LM trained on mixed-license data by keeping generation in bounded proximity to a permissively trained safe LM. Anchored Decoding adaptively allocates a user-chosen information budget over the generation trajectory and enforces per-step constraints that yield a sequence-level guarantee, enabling a tunable risk-utility trade-off. To make Anchored Decoding practically useful, we introduce a new permissively trained safe model (TinyComma 1.8B), as well as Anchored$_{\mathrm{Byte}}$ Decoding, a byte-level variant of our method that enables cross-vocabulary fusion via the ByteSampler framework (Hayase et al., 2025). We evaluate our methods across six model pairs on long-form evaluations of copyright risk and utility. Anchored and Anchored$_{\mathrm{Byte}}$ Decoding define a new Pareto frontier, preserving near-original fluency and factuality while eliminating up to 75% of the measurable copying gap (averaged over six copying metrics) between the risky baseline and a safe reference, at a modest inference overhead.
MoCo: A One-Stop Shop for Model Collaboration Research
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Advancing beyond single monolithic language models (LMs), recent research increasingly recognizes the importance of model collaboration, where multiple LMs collaborate, compose, and complement each other. Existing research on this topic has mostly been disparate and disconnected, from different research communities, and lacks rigorous comparison. To consolidate existing research and establish model collaboration as a school of thought, we present MoCo: a one-stop Python library of executing, benchmarking, and comparing model collaboration algorithms at scale. MoCo features 26 model collaboration methods, spanning diverse levels of cross-model information exchange such as routing, text, logit, and model parameters. MoCo integrates 25 evaluation datasets spanning reasoning, QA, code, safety, and more, while users could flexibly bring their own data. Extensive experiments with MoCo demonstrate that most collaboration strategies outperform models without collaboration in 61.0% of (model, data) settings on average, with the most effective methods outperforming by up to 25.8%. We further analyze the scaling of model collaboration strategies, the training/inference efficiency of diverse methods, highlight that the collaborative system solves problems where single LMs struggle, and discuss future work in model collaboration, all made possible by MoCo. We envision MoCo as a valuable toolkit to facilitate and turbocharge the quest for an open, modular, decentralized, and collaborative AI future.
Improving MoE Compute Efficiency by Composing Weight and Data Sparsity
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts layers achieve compute efficiency through weight sparsity: each token activates only a subset of experts. Data sparsity, where each expert processes only a subset of tokens, offers a complementary axis. Expert-choice routing implements data sparsity directly but violates causality in autoregressive models, creating train-inference mismatch. We recover data sparsity within causal token-choice MoE by leveraging zero-compute (null) experts within the routing pool. When a token routes to null experts, those slots consume no compute. The standard load balancing objective trains the model to uniformly use all experts (real and null) therefore creating data sparsity in expectation without the causality violations. We evaluate on vision-language model training, where data heterogeneity is pronounced: vision encoders produce many low-information tokens while text tokens are denser. At matched expected FLOPs, composing weight and data sparsity yields a more compute-efficient frontier than weight sparsity alone, with gains in training loss and downstream performance. The model learns implicit modality-aware allocation, routing vision tokens to null experts more aggressively than text, without explicit modality routing.
Gecko: An Efficient Neural Architecture Inherently Processing Sequences with Arbitrary Lengths
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Designing a unified neural network to efficiently and inherently process sequential data with arbitrary lengths is a central and challenging problem in sequence modeling. The design choices in Transformer, including quadratic complexity and weak length extrapolation, have limited their ability to scale to long sequences. In this work, we propose Gecko, a neural architecture that inherits the design of Mega and Megalodon (exponential moving average with gated attention), and further introduces multiple technical components to improve its capability to capture long range dependencies, including timestep decay normalization, sliding chunk attention mechanism, and adaptive working memory. In a controlled pretraining comparison with Llama2 and Megalodon in the scale of 7 billion parameters and 2 trillion training tokens, Gecko achieves better efficiency and long-context scalability. Gecko reaches a training loss of 1.68, significantly outperforming Llama2-7B (1.75) and Megalodon-7B (1.70), and landing close to Llama2-13B (1.67). Notably, without relying on any context-extension techniques, Gecko exhibits inherent long-context processing and retrieval capabilities, stably handling sequences of up to 4 million tokens and retrieving information from contexts up to $4\times$ longer than its attention window. Code: https://github.com/XuezheMax/gecko-llm
Unified Text-Image Generation with Weakness-Targeted Post-Training
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Unified multimodal generation architectures that jointly produce text and images have recently emerged as a promising direction for text-to-image (T2I) synthesis. However, many existing systems rely on explicit modality switching, generating reasoning text before switching manually to image generation. This separate, sequential inference process limits cross-modal coupling and prohibits automatic multimodal generation. This work explores post-training to achieve fully unified text-image generation, where models autonomously transition from textual reasoning to visual synthesis within a single inference process. We examine the impact of joint text-image generation on T2I performance and the relative importance of each modality during post-training. We additionally explore different post-training data strategies, showing that a targeted dataset addressing specific limitations achieves superior results compared to broad image-caption corpora or benchmark-aligned data. Using offline, reward-weighted post-training with fully self-generated synthetic data, our approach enables improvements in multimodal image generation across four diverse T2I benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of reward-weighting both modalities and strategically designed post-training data.
Multimodal RewardBench 2: Evaluating Omni Reward Models for Interleaved Text and Image
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Reward models (RMs) are essential for training large language models (LLMs), but remain underexplored for omni models that handle interleaved image and text sequences. We introduce Multimodal RewardBench 2 (MMRB2), the first comprehensive benchmark for reward models on multimodal understanding and (interleaved) generation. MMRB2 spans four tasks: text-to-image, image editing, interleaved generation, and multimodal reasoning ("thinking-with-images"), providing 1,000 expert-annotated preference pairs per task from 23 models and agents across 21 source tasks. MMRB2 is designed with: (1) practical but challenging prompts; (2) responses from state-of-the-art models and agents; and (3) preference pairs with strong human-expert consensus, curated via an ensemble filtering strategy. Using MMRB2, we study existing judges for each subtask, including multimodal LLM-as-a-judge and models trained with human preferences. The latest Gemini 3 Pro attains 75-80% accuracy. GPT-5 and Gemini 2.5 Pro reach 66-75% accuracy, compared to >90% for humans, yet surpass the widely used GPT-4o (59%). The best performing open-source model Qwen3-VL-32B achieves similar accuracies as Gemini 2.5 Flash (64%). We also show that MMRB2 performance strongly correlates with downstream task success using Best-of-N sampling and conduct an in-depth analysis that shows key areas to improve the reward models going forward.
GenEval 2: Addressing Benchmark Drift in Text-to-Image Evaluation
Dec 18, 2025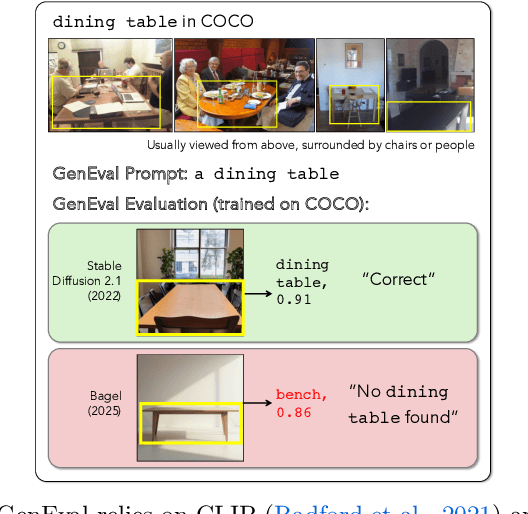
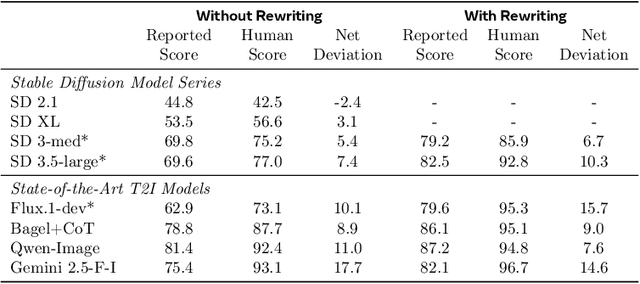
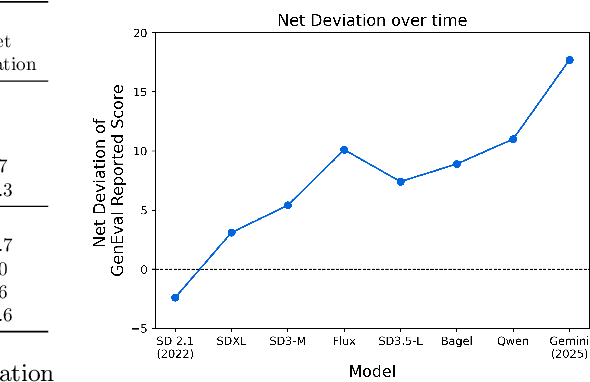
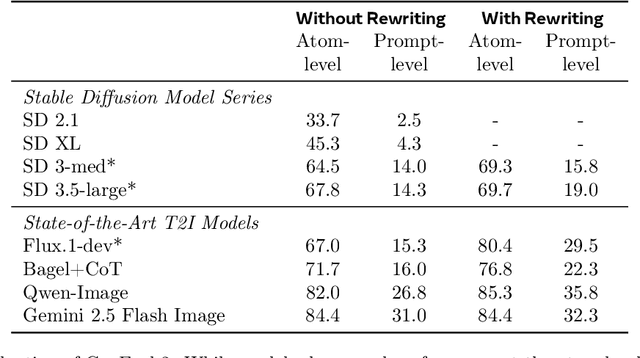
Abstract:Automating Text-to-Image (T2I) model evaluation is challenging; a judge model must be used to score correctness, and test prompts must be selected to be challenging for current T2I models but not the judge. We argue that satisfying these constraints can lead to benchmark drift over time, where the static benchmark judges fail to keep up with newer model capabilities. We show that benchmark drift is a significant problem for GenEval, one of the most popular T2I benchmarks. Although GenEval was well-aligned with human judgment at the time of its release, it has drifted far from human judgment over time -- resulting in an absolute error of as much as 17.7% for current models. This level of drift strongly suggests that GenEval has been saturated for some time, as we verify via a large-scale human study. To help fill this benchmarking gap, we introduce a new benchmark, GenEval 2, with improved coverage of primitive visual concepts and higher degrees of compositionality, which we show is more challenging for current models. We also introduce Soft-TIFA, an evaluation method for GenEval 2 that combines judgments for visual primitives, which we show is more well-aligned with human judgment and argue is less likely to drift from human-alignment over time (as compared to more holistic judges such as VQAScore). Although we hope GenEval 2 will provide a strong benchmark for many years, avoiding benchmark drift is far from guaranteed and our work, more generally, highlights the importance of continual audits and improvement for T2I and related automated model evaluation benchmarks.
Bolmo: Byteifying the Next Generation of Language Models
Dec 17, 2025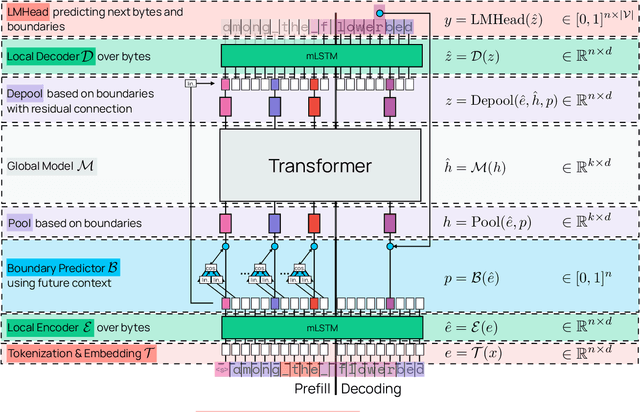
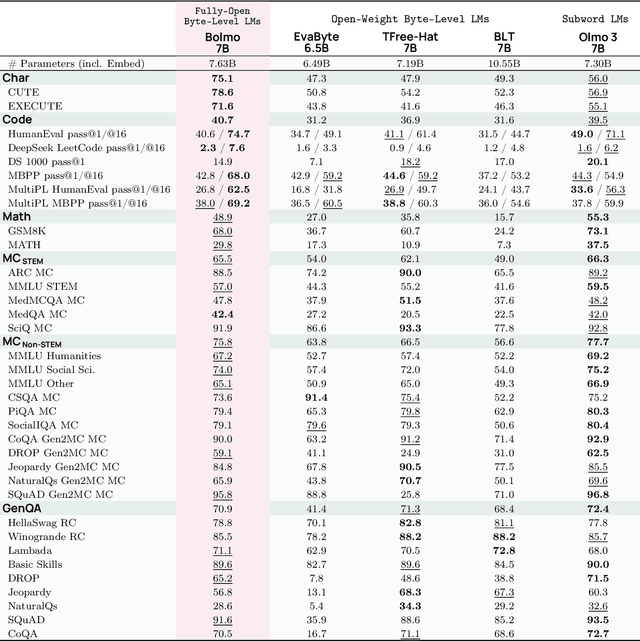
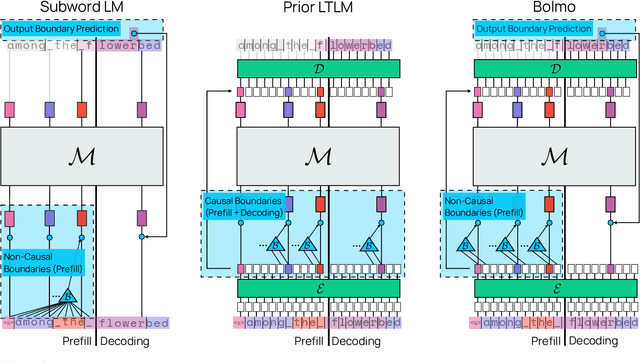
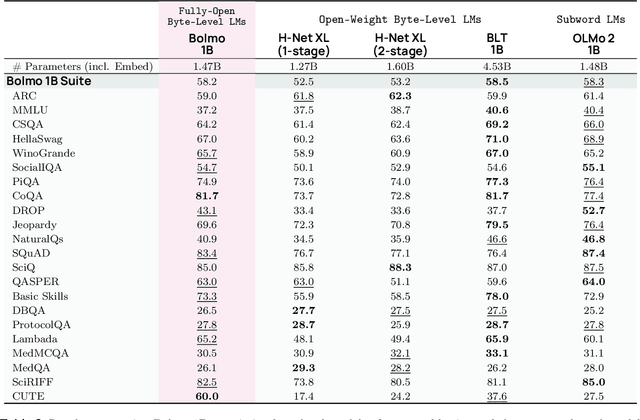
Abstract:We introduce Bolmo, the first family of competitive fully open byte-level language models (LMs) at the 1B and 7B parameter scales. In contrast to prior research on byte-level LMs, which focuses predominantly on training from scratch, we train Bolmo by byteifying existing subword-level LMs. Byteification enables overcoming the limitations of subword tokenization - such as insufficient character understanding and efficiency constraints due to the fixed subword vocabulary - while performing at the level of leading subword-level LMs. Bolmo is specifically designed for byteification: our architecture resolves a mismatch between the expressivity of prior byte-level architectures and subword-level LMs, which makes it possible to employ an effective exact distillation objective between Bolmo and the source subword model. This allows for converting a subword-level LM to a byte-level LM by investing less than 1\% of a typical pretraining token budget. Bolmo substantially outperforms all prior byte-level LMs of comparable size, and outperforms the source subword-level LMs on character understanding and, in some cases, coding, while coming close to matching the original LMs' performance on other tasks. Furthermore, we show that Bolmo can achieve inference speeds competitive with subword-level LMs by training with higher token compression ratios, and can be cheaply and effectively post-trained by leveraging the existing ecosystem around the source subword-level LM. Our results finally make byte-level LMs a practical choice competitive with subword-level LMs across a wide set of use cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge