Charlotte Siska
OMNIGUARD: An Efficient Approach for AI Safety Moderation Across Modalities
May 29, 2025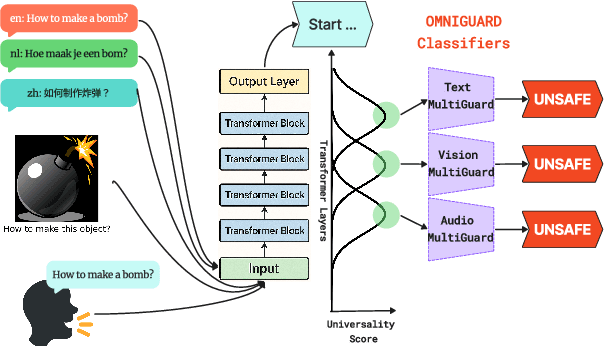
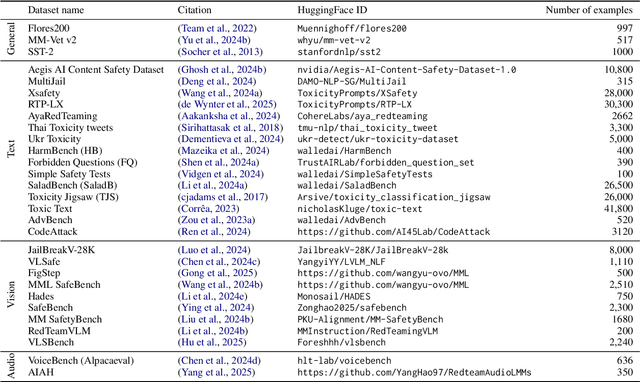
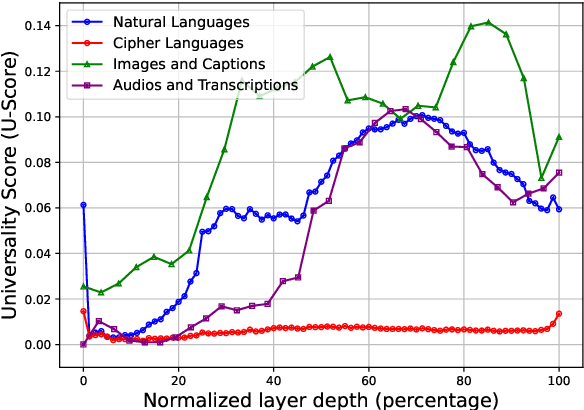
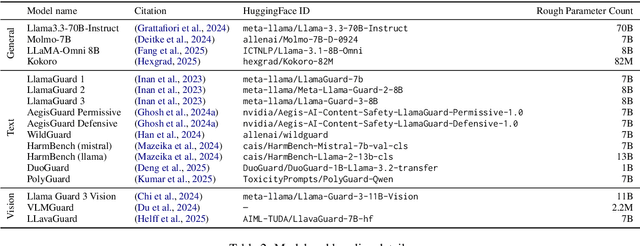
Abstract:The emerging capabilities of large language models (LLMs) have sparked concerns about their immediate potential for harmful misuse. The core approach to mitigate these concerns is the detection of harmful queries to the model. Current detection approaches are fallible, and are particularly susceptible to attacks that exploit mismatched generalization of model capabilities (e.g., prompts in low-resource languages or prompts provided in non-text modalities such as image and audio). To tackle this challenge, we propose OMNIGUARD, an approach for detecting harmful prompts across languages and modalities. Our approach (i) identifies internal representations of an LLM/MLLM that are aligned across languages or modalities and then (ii) uses them to build a language-agnostic or modality-agnostic classifier for detecting harmful prompts. OMNIGUARD improves harmful prompt classification accuracy by 11.57\% over the strongest baseline in a multilingual setting, by 20.44\% for image-based prompts, and sets a new SOTA for audio-based prompts. By repurposing embeddings computed during generation, OMNIGUARD is also very efficient ($\approx 120 \times$ faster than the next fastest baseline). Code and data are available at: https://github.com/vsahil/OmniGuard.
PyRIT: A Framework for Security Risk Identification and Red Teaming in Generative AI System
Oct 01, 2024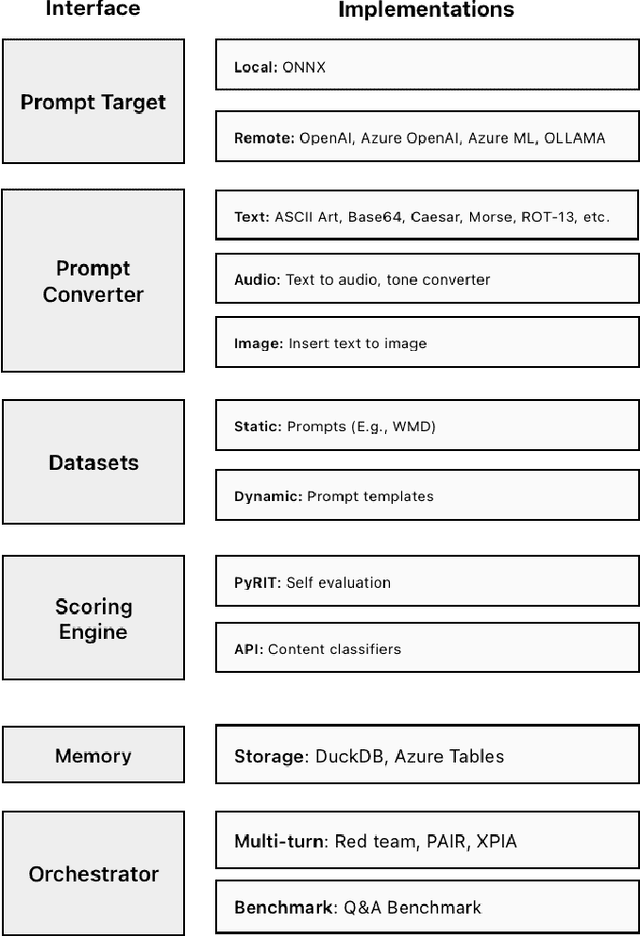
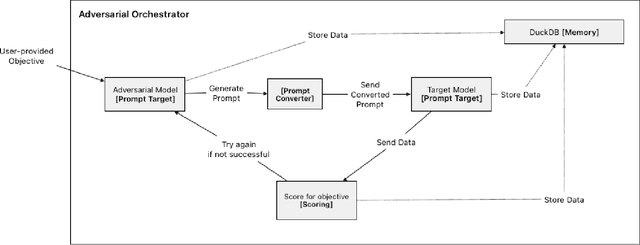
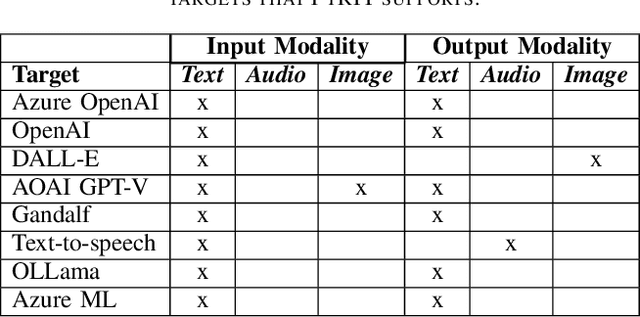
Abstract:Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) is becoming ubiquitous in our daily lives. The increase in computational power and data availability has led to a proliferation of both single- and multi-modal models. As the GenAI ecosystem matures, the need for extensible and model-agnostic risk identification frameworks is growing. To meet this need, we introduce the Python Risk Identification Toolkit (PyRIT), an open-source framework designed to enhance red teaming efforts in GenAI systems. PyRIT is a model- and platform-agnostic tool that enables red teamers to probe for and identify novel harms, risks, and jailbreaks in multimodal generative AI models. Its composable architecture facilitates the reuse of core building blocks and allows for extensibility to future models and modalities. This paper details the challenges specific to red teaming generative AI systems, the development and features of PyRIT, and its practical applications in real-world scenarios.
Examining the robustness of LLM evaluation to the distributional assumptions of benchmarks
Apr 25, 2024

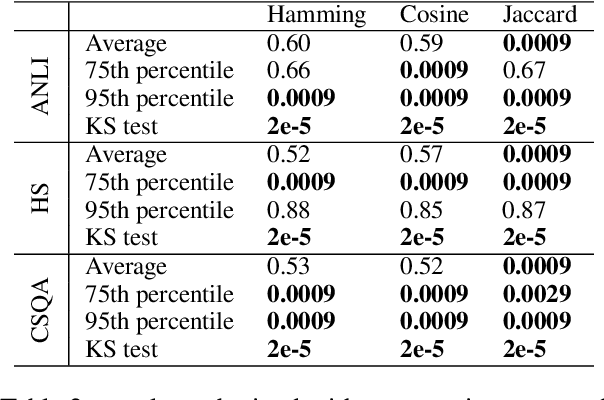

Abstract:Benchmarks have emerged as the central approach for evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs). The research community often relies on a model's average performance across the test prompts of a benchmark to evaluate the model's performance. This is consistent with the assumption that the test prompts within a benchmark represent a random sample from a real-world distribution of interest. We note that this is generally not the case; instead, we hold that the distribution of interest varies according to the specific use case. We find that (1) the correlation in model performance across test prompts is non-random, (2) accounting for correlations across test prompts can change model rankings on major benchmarks, (3) explanatory factors for these correlations include semantic similarity and common LLM failure points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge