Allyson Ettinger
Olmo 3
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce Olmo 3, a family of state-of-the-art, fully-open language models at the 7B and 32B parameter scales. Olmo 3 model construction targets long-context reasoning, function calling, coding, instruction following, general chat, and knowledge recall. This release includes the entire model flow, i.e., the full lifecycle of the family of models, including every stage, checkpoint, data point, and dependency used to build it. Our flagship model, Olmo 3 Think 32B, is the strongest fully-open thinking model released to-date.
FlexOlmo: Open Language Models for Flexible Data Use
Jul 09, 2025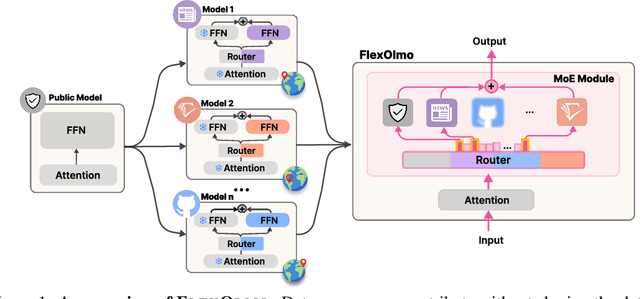
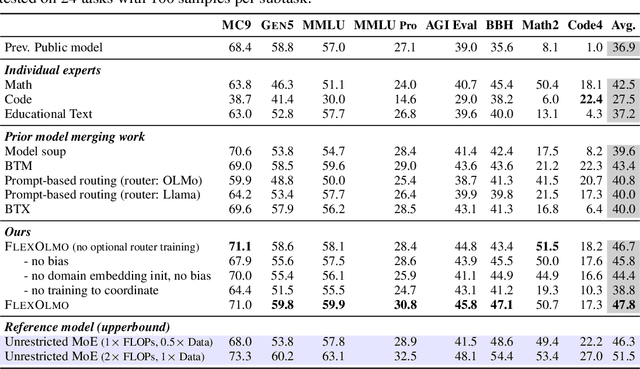
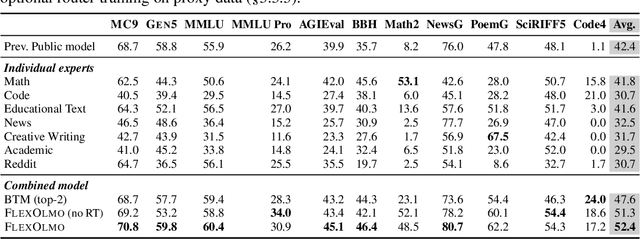
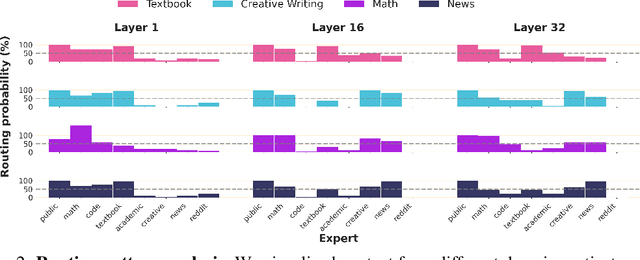
Abstract:We introduce FlexOlmo, a new class of language models (LMs) that supports (1) distributed training without data sharing, where different model parameters are independently trained on closed datasets, and (2) data-flexible inference, where these parameters along with their associated data can be flexibly included or excluded from model inferences with no further training. FlexOlmo employs a mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture where each expert is trained independently on closed datasets and later integrated through a new domain-informed routing without any joint training. FlexOlmo is trained on FlexMix, a corpus we curate comprising publicly available datasets alongside seven domain-specific sets, representing realistic approximations of closed sets. We evaluate models with up to 37 billion parameters (20 billion active) on 31 diverse downstream tasks. We show that a general expert trained on public data can be effectively combined with independently trained experts from other data owners, leading to an average 41% relative improvement while allowing users to opt out of certain data based on data licensing or permission requirements. Our approach also outperforms prior model merging methods by 10.1% on average and surpasses the standard MoE trained without data restrictions using the same training FLOPs. Altogether, this research presents a solution for both data owners and researchers in regulated industries with sensitive or protected data. FlexOlmo enables benefiting from closed data while respecting data owners' preferences by keeping their data local and supporting fine-grained control of data access during inference.
To Err is AI : A Case Study Informing LLM Flaw Reporting Practices
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:In August of 2024, 495 hackers generated evaluations in an open-ended bug bounty targeting the Open Language Model (OLMo) from The Allen Institute for AI. A vendor panel staffed by representatives of OLMo's safety program adjudicated changes to OLMo's documentation and awarded cash bounties to participants who successfully demonstrated a need for public disclosure clarifying the intent, capacities, and hazards of model deployment. This paper presents a collection of lessons learned, illustrative of flaw reporting best practices intended to reduce the likelihood of incidents and produce safer large language models (LLMs). These include best practices for safety reporting processes, their artifacts, and safety program staffing.
AI as Humanity's Salieri: Quantifying Linguistic Creativity of Language Models via Systematic Attribution of Machine Text against Web Text
Oct 05, 2024Abstract:Creativity has long been considered one of the most difficult aspect of human intelligence for AI to mimic. However, the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs), like ChatGPT, has raised questions about whether AI can match or even surpass human creativity. We present CREATIVITY INDEX as the first step to quantify the linguistic creativity of a text by reconstructing it from existing text snippets on the web. CREATIVITY INDEX is motivated by the hypothesis that the seemingly remarkable creativity of LLMs may be attributable in large part to the creativity of human-written texts on the web. To compute CREATIVITY INDEX efficiently, we introduce DJ SEARCH, a novel dynamic programming algorithm that can search verbatim and near-verbatim matches of text snippets from a given document against the web. Experiments reveal that the CREATIVITY INDEX of professional human authors is on average 66.2% higher than that of LLMs, and that alignment reduces the CREATIVITY INDEX of LLMs by an average of 30.1%. In addition, we find that distinguished authors like Hemingway exhibit measurably higher CREATIVITY INDEX compared to other human writers. Finally, we demonstrate that CREATIVITY INDEX can be used as a surprisingly effective criterion for zero-shot machine text detection, surpassing the strongest existing zero-shot system, DetectGPT, by a significant margin of 30.2%, and even outperforming the strongest supervised system, GhostBuster, in five out of six domains.
WildGuard: Open One-Stop Moderation Tools for Safety Risks, Jailbreaks, and Refusals of LLMs
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:We introduce WildGuard -- an open, light-weight moderation tool for LLM safety that achieves three goals: (1) identifying malicious intent in user prompts, (2) detecting safety risks of model responses, and (3) determining model refusal rate. Together, WildGuard serves the increasing needs for automatic safety moderation and evaluation of LLM interactions, providing a one-stop tool with enhanced accuracy and broad coverage across 13 risk categories. While existing open moderation tools such as Llama-Guard2 score reasonably well in classifying straightforward model interactions, they lag far behind a prompted GPT-4, especially in identifying adversarial jailbreaks and in evaluating models' refusals, a key measure for evaluating safety behaviors in model responses. To address these challenges, we construct WildGuardMix, a large-scale and carefully balanced multi-task safety moderation dataset with 92K labeled examples that cover vanilla (direct) prompts and adversarial jailbreaks, paired with various refusal and compliance responses. WildGuardMix is a combination of WildGuardTrain, the training data of WildGuard, and WildGuardTest, a high-quality human-annotated moderation test set with 5K labeled items covering broad risk scenarios. Through extensive evaluations on WildGuardTest and ten existing public benchmarks, we show that WildGuard establishes state-of-the-art performance in open-source safety moderation across all the three tasks compared to ten strong existing open-source moderation models (e.g., up to 26.4% improvement on refusal detection). Importantly, WildGuard matches and sometimes exceeds GPT-4 performance (e.g., up to 3.9% improvement on prompt harmfulness identification). WildGuard serves as a highly effective safety moderator in an LLM interface, reducing the success rate of jailbreak attacks from 79.8% to 2.4%.
WildTeaming at Scale: From In-the-Wild Jailbreaks to (Adversarially) Safer Language Models
Jun 26, 2024



Abstract:We introduce WildTeaming, an automatic LLM safety red-teaming framework that mines in-the-wild user-chatbot interactions to discover 5.7K unique clusters of novel jailbreak tactics, and then composes multiple tactics for systematic exploration of novel jailbreaks. Compared to prior work that performed red-teaming via recruited human workers, gradient-based optimization, or iterative revision with LLMs, our work investigates jailbreaks from chatbot users who were not specifically instructed to break the system. WildTeaming reveals previously unidentified vulnerabilities of frontier LLMs, resulting in up to 4.6x more diverse and successful adversarial attacks compared to state-of-the-art jailbreak methods. While many datasets exist for jailbreak evaluation, very few open-source datasets exist for jailbreak training, as safety training data has been closed even when model weights are open. With WildTeaming we create WildJailbreak, a large-scale open-source synthetic safety dataset with 262K vanilla (direct request) and adversarial (complex jailbreak) prompt-response pairs. To mitigate exaggerated safety behaviors, WildJailbreak provides two contrastive types of queries: 1) harmful queries (vanilla & adversarial) and 2) benign queries that resemble harmful queries in form but contain no harm. As WildJailbreak considerably upgrades the quality and scale of existing safety resources, it uniquely enables us to examine the scaling effects of data and the interplay of data properties and model capabilities during safety training. Through extensive experiments, we identify the training properties that enable an ideal balance of safety behaviors: appropriate safeguarding without over-refusal, effective handling of vanilla and adversarial queries, and minimal, if any, decrease in general capabilities. All components of WildJailbeak contribute to achieving balanced safety behaviors of models.
When Hindsight is Not 20/20: Testing Limits on Reflective Thinking in Large Language Models
Apr 14, 2024



Abstract:Recent studies suggest that self-reflective prompting can significantly enhance the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, the use of external feedback as a stop criterion raises doubts about the true extent of LLMs' ability to emulate human-like self-reflection. In this paper, we set out to clarify these capabilities under a more stringent evaluation setting in which we disallow any kind of external feedback. Our findings under this setting show a split: while self-reflection enhances performance in TruthfulQA, it adversely affects results in HotpotQA. We conduct follow-up analyses to clarify the contributing factors in these patterns, and find that the influence of self-reflection is impacted both by reliability of accuracy in models' initial responses, and by overall question difficulty: specifically, self-reflection shows the most benefit when models are less likely to be correct initially, and when overall question difficulty is higher. We also find that self-reflection reduces tendency toward majority voting. Based on our findings, we propose guidelines for decisions on when to implement self-reflection. We release the codebase for reproducing our experiments at https://github.com/yanhong-lbh/LLM-SelfReflection-Eval.
Experimental Contexts Can Facilitate Robust Semantic Property Inference in Language Models, but Inconsistently
Jan 12, 2024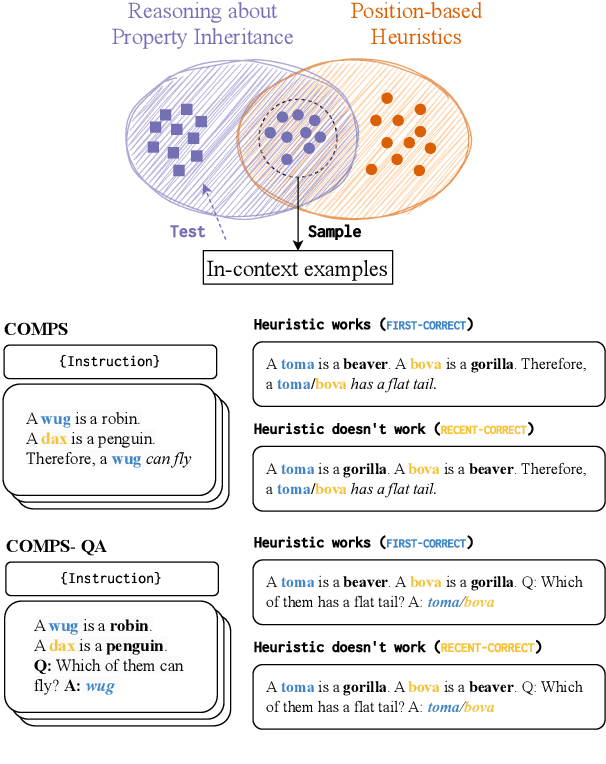
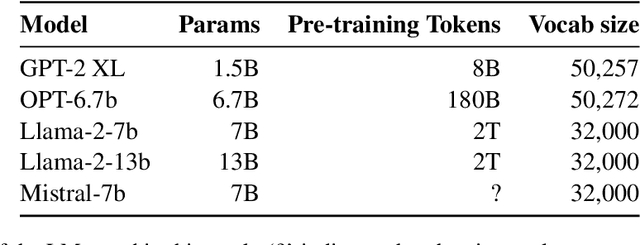
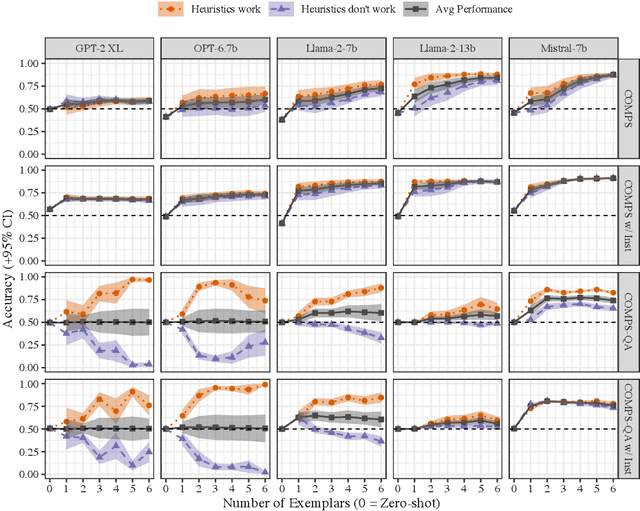

Abstract:Recent zero-shot evaluations have highlighted important limitations in the abilities of language models (LMs) to perform meaning extraction. However, it is now well known that LMs can demonstrate radical improvements in the presence of experimental contexts such as in-context examples and instructions. How well does this translate to previously studied meaning-sensitive tasks? We present a case-study on the extent to which experimental contexts can improve LMs' robustness in performing property inheritance -- predicting semantic properties of novel concepts, a task that they have been previously shown to fail on. Upon carefully controlling the nature of the in-context examples and the instructions, our work reveals that they can indeed lead to non-trivial property inheritance behavior in LMs. However, this ability is inconsistent: with a minimal reformulation of the task, some LMs were found to pick up on shallow, non-semantic heuristics from their inputs, suggesting that the computational principles of semantic property inference are yet to be mastered by LMs.
The Generative AI Paradox: "What It Can Create, It May Not Understand"
Oct 31, 2023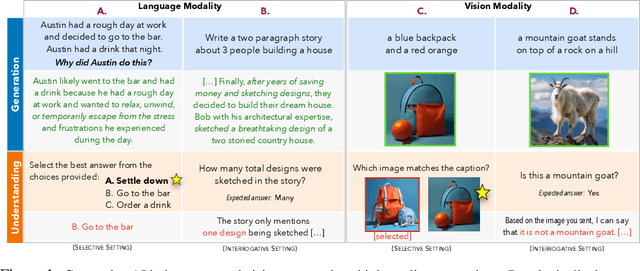
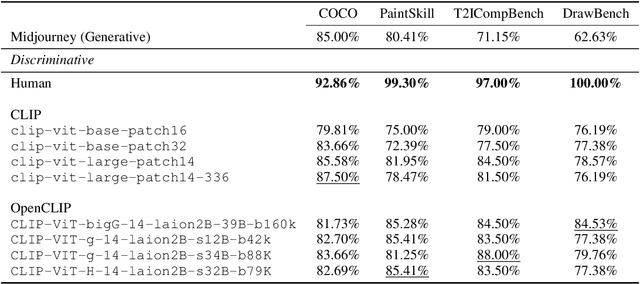
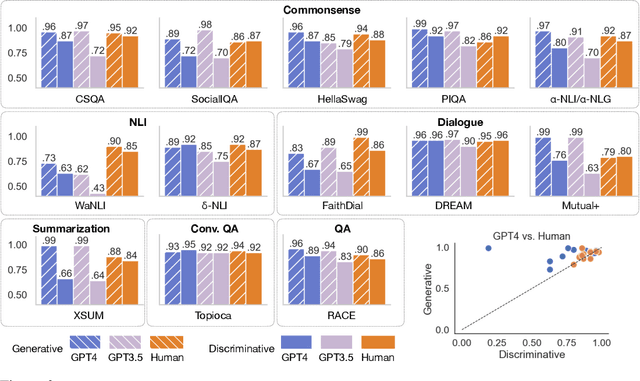
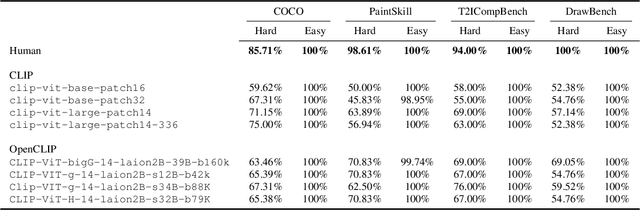
Abstract:The recent wave of generative AI has sparked unprecedented global attention, with both excitement and concern over potentially superhuman levels of artificial intelligence: models now take only seconds to produce outputs that would challenge or exceed the capabilities even of expert humans. At the same time, models still show basic errors in understanding that would not be expected even in non-expert humans. This presents us with an apparent paradox: how do we reconcile seemingly superhuman capabilities with the persistence of errors that few humans would make? In this work, we posit that this tension reflects a divergence in the configuration of intelligence in today's generative models relative to intelligence in humans. Specifically, we propose and test the Generative AI Paradox hypothesis: generative models, having been trained directly to reproduce expert-like outputs, acquire generative capabilities that are not contingent upon -- and can therefore exceed -- their ability to understand those same types of outputs. This contrasts with humans, for whom basic understanding almost always precedes the ability to generate expert-level outputs. We test this hypothesis through controlled experiments analyzing generation vs. understanding in generative models, across both language and image modalities. Our results show that although models can outperform humans in generation, they consistently fall short of human capabilities in measures of understanding, as well as weaker correlation between generation and understanding performance, and more brittleness to adversarial inputs. Our findings support the hypothesis that models' generative capability may not be contingent upon understanding capability, and call for caution in interpreting artificial intelligence by analogy to human intelligence.
"You Are An Expert Linguistic Annotator": Limits of LLMs as Analyzers of Abstract Meaning Representation
Oct 26, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) show amazing proficiency and fluency in the use of language. Does this mean that they have also acquired insightful linguistic knowledge about the language, to an extent that they can serve as an "expert linguistic annotator"? In this paper, we examine the successes and limitations of the GPT-3, ChatGPT, and GPT-4 models in analysis of sentence meaning structure, focusing on the Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR; Banarescu et al. 2013) parsing formalism, which provides rich graphical representations of sentence meaning structure while abstracting away from surface forms. We compare models' analysis of this semantic structure across two settings: 1) direct production of AMR parses based on zero- and few-shot prompts, and 2) indirect partial reconstruction of AMR via metalinguistic natural language queries (e.g., "Identify the primary event of this sentence, and the predicate corresponding to that event."). Across these settings, we find that models can reliably reproduce the basic format of AMR, and can often capture core event, argument, and modifier structure -- however, model outputs are prone to frequent and major errors, and holistic analysis of parse acceptability shows that even with few-shot demonstrations, models have virtually 0% success in producing fully accurate parses. Eliciting natural language responses produces similar patterns of errors. Overall, our findings indicate that these models out-of-the-box can capture aspects of semantic structure, but there remain key limitations in their ability to support fully accurate semantic analyses or parses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge