Scott Geng
Olmo 3
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce Olmo 3, a family of state-of-the-art, fully-open language models at the 7B and 32B parameter scales. Olmo 3 model construction targets long-context reasoning, function calling, coding, instruction following, general chat, and knowledge recall. This release includes the entire model flow, i.e., the full lifecycle of the family of models, including every stage, checkpoint, data point, and dependency used to build it. Our flagship model, Olmo 3 Think 32B, is the strongest fully-open thinking model released to-date.
The Delta Learning Hypothesis: Preference Tuning on Weak Data can Yield Strong Gains
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:Improvements in language models are often driven by improving the quality of the data we train them on, which can be limiting when strong supervision is scarce. In this work, we show that paired preference data consisting of individually weak data points can enable gains beyond the strength of each individual data point. We formulate the delta learning hypothesis to explain this phenomenon, positing that the relative quality delta between points suffices to drive learning via preference tuning--even when supervised finetuning on the weak data hurts. We validate our hypothesis in controlled experiments and at scale, where we post-train 8B models on preference data generated by pairing a small 3B model's responses with outputs from an even smaller 1.5B model to create a meaningful delta. Strikingly, on a standard 11-benchmark evaluation suite (MATH, MMLU, etc.), our simple recipe matches the performance of Tulu 3, a state-of-the-art open model tuned from the same base model while relying on much stronger supervisors (e.g., GPT-4o). Thus, delta learning enables simpler and cheaper open recipes for state-of-the-art post-training. To better understand delta learning, we prove in logistic regression that the performance gap between two weak teacher models provides useful signal for improving a stronger student. Overall, our work shows that models can learn surprisingly well from paired data that might typically be considered weak.
Spurious Rewards: Rethinking Training Signals in RLVR
Jun 12, 2025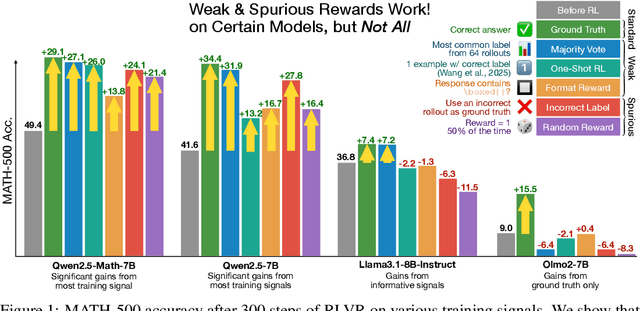
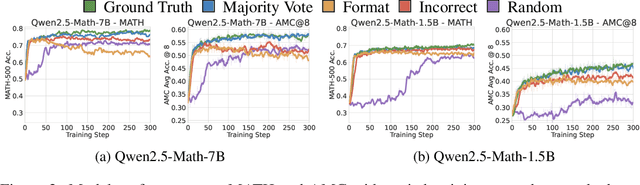
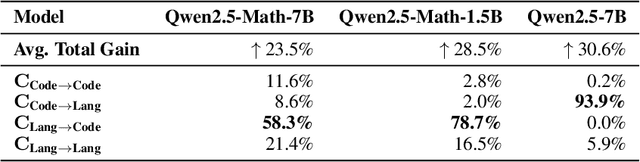
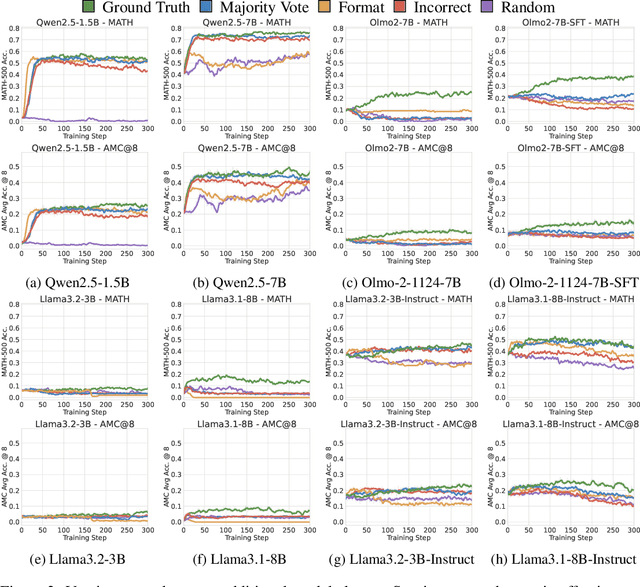
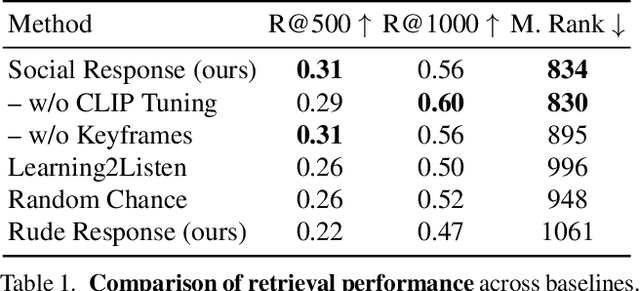
Abstract:We show that reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) can elicit strong mathematical reasoning in certain models even with spurious rewards that have little, no, or even negative correlation with the correct answer. For example, RLVR improves MATH-500 performance for Qwen2.5-Math-7B in absolute points by 21.4% (random reward), 13.8% (format reward), 24.1% (incorrect label), 26.0% (1-shot RL), and 27.1% (majority voting) -- nearly matching the 29.1% gained with ground truth rewards. However, the spurious rewards that work for Qwen often fail to yield gains with other model families like Llama3 or OLMo2. In particular, we find code reasoning -- thinking in code without actual code execution -- to be a distinctive Qwen2.5-Math behavior that becomes significantly more frequent after RLVR, from 65% to over 90%, even with spurious rewards. Overall, we hypothesize that, given the lack of useful reward signal, RLVR must somehow be surfacing useful reasoning representations learned during pretraining, although the exact mechanism remains a topic for future work. We suggest that future RLVR research should possibly be validated on diverse models rather than a single de facto choice, as we show that it is easy to get significant performance gains on Qwen models even with completely spurious reward signals.
The Unmet Promise of Synthetic Training Images: Using Retrieved Real Images Performs Better
Jun 07, 2024Abstract:Generative text-to-image models enable us to synthesize unlimited amounts of images in a controllable manner, spurring many recent efforts to train vision models with synthetic data. However, every synthetic image ultimately originates from the upstream data used to train the generator. What additional value does the intermediate generator provide over directly training on relevant parts of the upstream data? Grounding this question in the setting of image classification, we compare finetuning on task-relevant, targeted synthetic data generated by Stable Diffusion -- a generative model trained on the LAION-2B dataset -- against finetuning on targeted real images retrieved directly from LAION-2B. We show that while synthetic data can benefit some downstream tasks, it is universally matched or outperformed by real data from our simple retrieval baseline. Our analysis suggests that this underperformance is partially due to generator artifacts and inaccurate task-relevant visual details in the synthetic images. Overall, we argue that retrieval is a critical baseline to consider when training with synthetic data -- a baseline that current methods do not yet surpass. We release code, data, and models at https://github.com/scottgeng00/unmet-promise.
Symmetry-Preserving Program Representations for Learning Code Semantics
Aug 07, 2023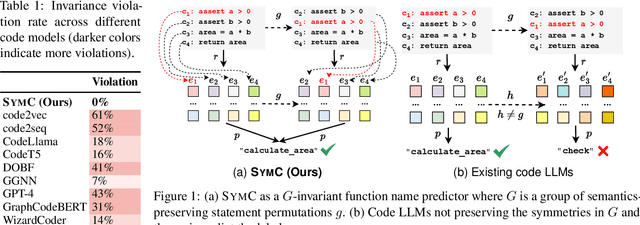
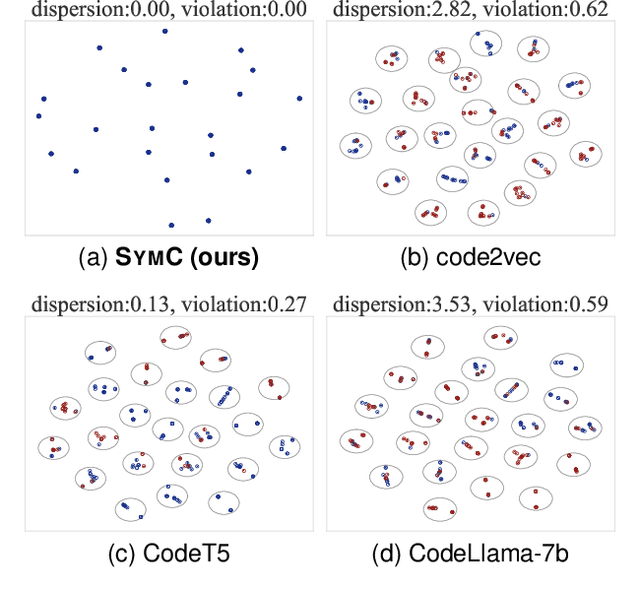
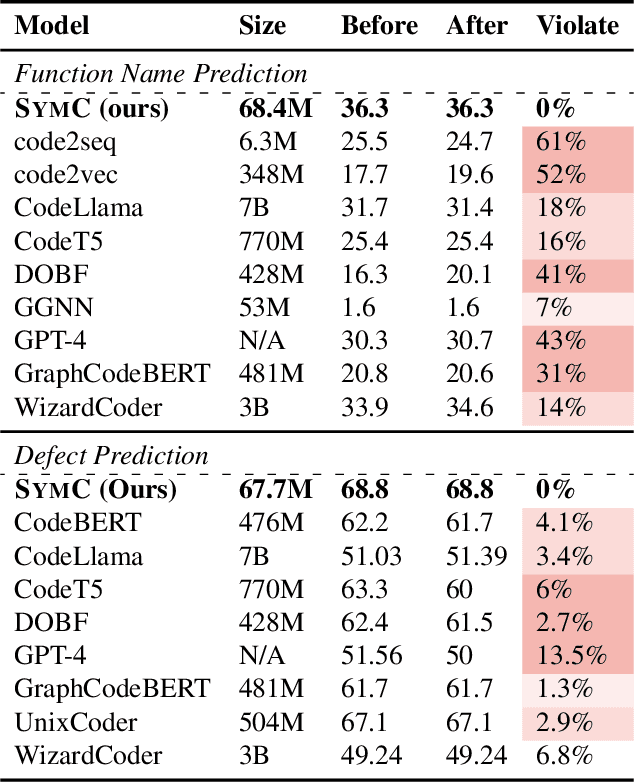
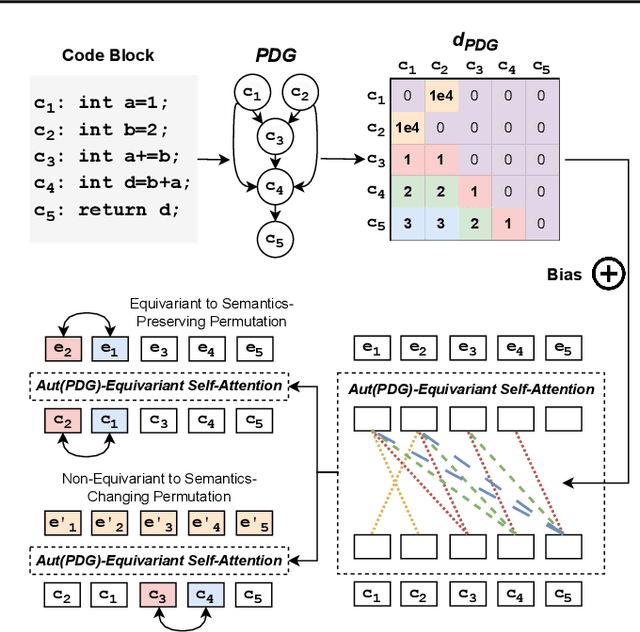
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in automated program reasoning, a crucial aspect of many security tasks. However, existing LLM architectures for code are often borrowed from other domains like natural language processing, raising concerns about their generalization and robustness to unseen code. A key generalization challenge is to incorporate the knowledge of code semantics, including control and data flow, into the LLM architectures. Drawing inspiration from examples of convolution layers exploiting translation symmetry, we explore how code symmetries can enhance LLM architectures for program analysis and modeling. We present a rigorous group-theoretic framework that formally defines code symmetries as semantics-preserving transformations and provides techniques for precisely reasoning about symmetry preservation within LLM architectures. Using this framework, we introduce a novel variant of self-attention that preserves program symmetries, demonstrating its effectiveness in generalization and robustness through detailed experimental evaluations across different binary and source code analysis tasks. Overall, our code symmetry framework offers rigorous and powerful reasoning techniques that can guide the future development of specialized LLMs for code and advance LLM-guided program reasoning tasks.
Affective Faces for Goal-Driven Dyadic Communication
Jan 26, 2023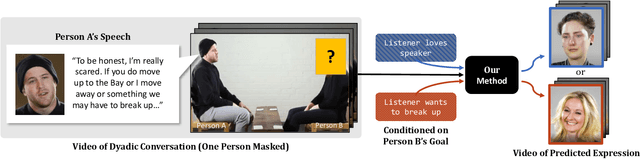
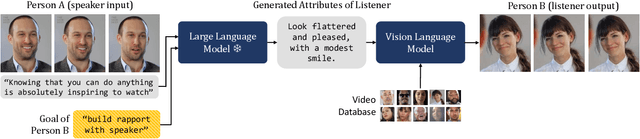

Abstract:We introduce a video framework for modeling the association between verbal and non-verbal communication during dyadic conversation. Given the input speech of a speaker, our approach retrieves a video of a listener, who has facial expressions that would be socially appropriate given the context. Our approach further allows the listener to be conditioned on their own goals, personalities, or backgrounds. Our approach models conversations through a composition of large language models and vision-language models, creating internal representations that are interpretable and controllable. To study multimodal communication, we propose a new video dataset of unscripted conversations covering diverse topics and demographics. Experiments and visualizations show our approach is able to output listeners that are significantly more socially appropriate than baselines. However, many challenges remain, and we release our dataset publicly to spur further progress. See our website for video results, data, and code: https://realtalk.cs.columbia.edu.
Understanding Zero-Shot Adversarial Robustness for Large-Scale Models
Dec 14, 2022



Abstract:Pretrained large-scale vision-language models like CLIP have exhibited strong generalization over unseen tasks. Yet imperceptible adversarial perturbations can significantly reduce CLIP's performance on new tasks. In this work, we identify and explore the problem of \emph{adapting large-scale models for zero-shot adversarial robustness}. We first identify two key factors during model adaption -- training losses and adaptation methods -- that affect the model's zero-shot adversarial robustness. We then propose a text-guided contrastive adversarial training loss, which aligns the text embeddings and the adversarial visual features with contrastive learning on a small set of training data. We apply this training loss to two adaption methods, model finetuning and visual prompt tuning. We find that visual prompt tuning is more effective in the absence of texts, while finetuning wins in the existence of text guidance. Overall, our approach significantly improves the zero-shot adversarial robustness over CLIP, seeing an average improvement of over 31 points over ImageNet and 15 zero-shot datasets. We hope this work can shed light on understanding the zero-shot adversarial robustness of large-scale models.
NeuDep: Neural Binary Memory Dependence Analysis
Oct 04, 2022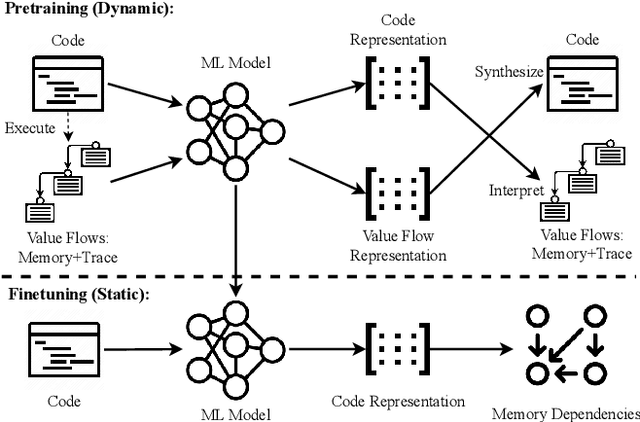
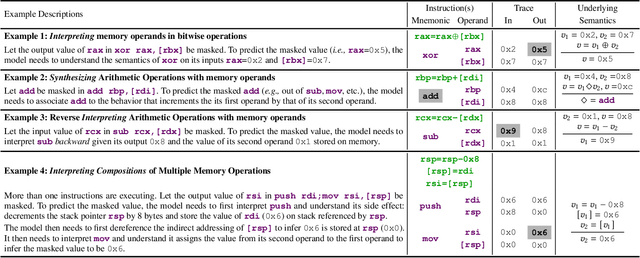
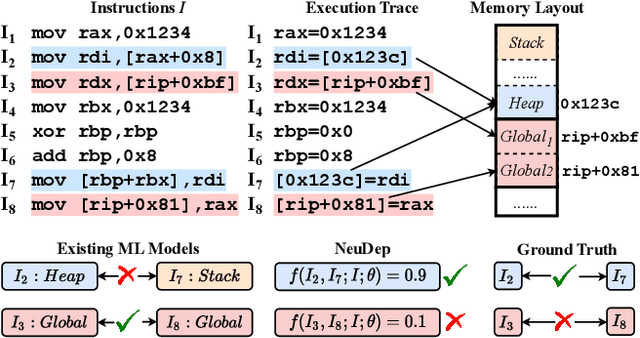
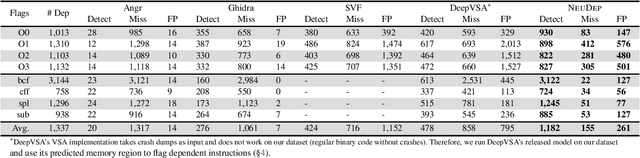
Abstract:Determining whether multiple instructions can access the same memory location is a critical task in binary analysis. It is challenging as statically computing precise alias information is undecidable in theory. The problem aggravates at the binary level due to the presence of compiler optimizations and the absence of symbols and types. Existing approaches either produce significant spurious dependencies due to conservative analysis or scale poorly to complex binaries. We present a new machine-learning-based approach to predict memory dependencies by exploiting the model's learned knowledge about how binary programs execute. Our approach features (i) a self-supervised procedure that pretrains a neural net to reason over binary code and its dynamic value flows through memory addresses, followed by (ii) supervised finetuning to infer the memory dependencies statically. To facilitate efficient learning, we develop dedicated neural architectures to encode the heterogeneous inputs (i.e., code, data values, and memory addresses from traces) with specific modules and fuse them with a composition learning strategy. We implement our approach in NeuDep and evaluate it on 41 popular software projects compiled by 2 compilers, 4 optimizations, and 4 obfuscation passes. We demonstrate that NeuDep is more precise (1.5x) and faster (3.5x) than the current state-of-the-art. Extensive probing studies on security-critical reverse engineering tasks suggest that NeuDep understands memory access patterns, learns function signatures, and is able to match indirect calls. All these tasks either assist or benefit from inferring memory dependencies. Notably, NeuDep also outperforms the current state-of-the-art on these tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge