Symmetry-Preserving Program Representations for Learning Code Semantics
Paper and Code
Aug 07, 2023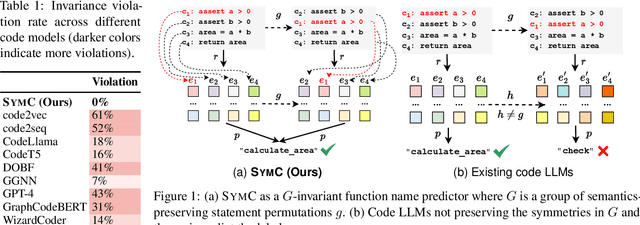
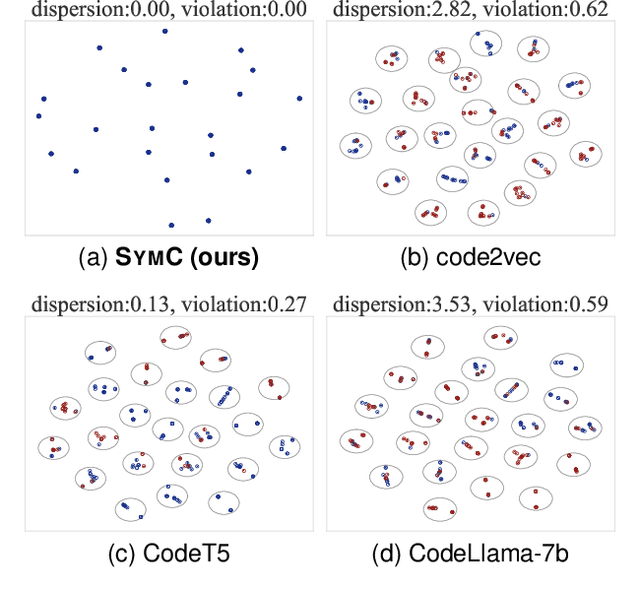
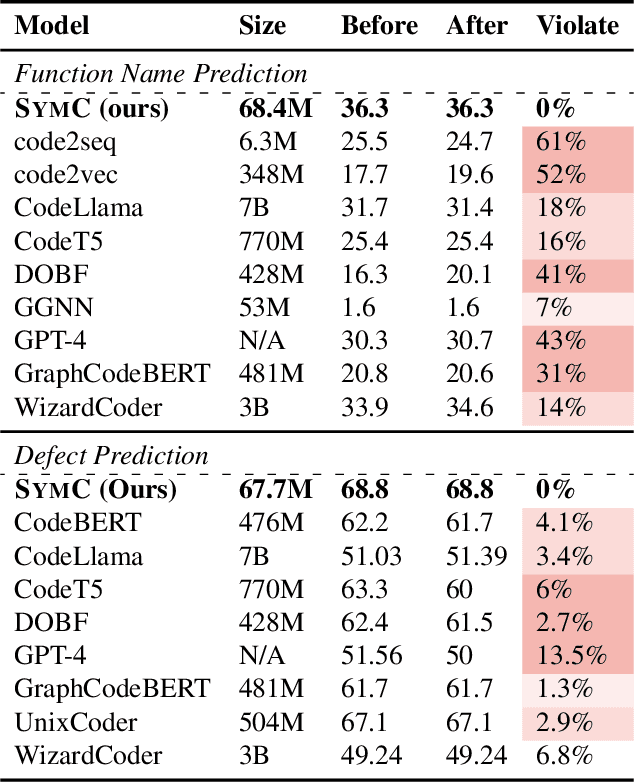
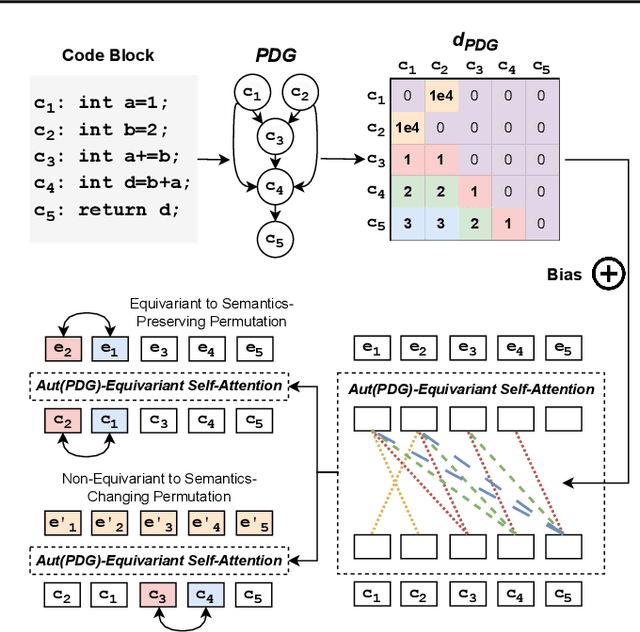
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in automated program reasoning, a crucial aspect of many security tasks. However, existing LLM architectures for code are often borrowed from other domains like natural language processing, raising concerns about their generalization and robustness to unseen code. A key generalization challenge is to incorporate the knowledge of code semantics, including control and data flow, into the LLM architectures. Drawing inspiration from examples of convolution layers exploiting translation symmetry, we explore how code symmetries can enhance LLM architectures for program analysis and modeling. We present a rigorous group-theoretic framework that formally defines code symmetries as semantics-preserving transformations and provides techniques for precisely reasoning about symmetry preservation within LLM architectures. Using this framework, we introduce a novel variant of self-attention that preserves program symmetries, demonstrating its effectiveness in generalization and robustness through detailed experimental evaluations across different binary and source code analysis tasks. Overall, our code symmetry framework offers rigorous and powerful reasoning techniques that can guide the future development of specialized LLMs for code and advance LLM-guided program reasoning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge