John Collomosse
MultiNeRF: Multiple Watermark Embedding for Neural Radiance Fields
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:We present MultiNeRF, a 3D watermarking method that embeds multiple uniquely keyed watermarks within images rendered by a single Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) model, whilst maintaining high visual quality. Our approach extends the TensoRF NeRF model by incorporating a dedicated watermark grid alongside the existing geometry and appearance grids. This extension ensures higher watermark capacity without entangling watermark signals with scene content. We propose a FiLM-based conditional modulation mechanism that dynamically activates watermarks based on input identifiers, allowing multiple independent watermarks to be embedded and extracted without requiring model retraining. MultiNeRF is validated on the NeRF-Synthetic and LLFF datasets, with statistically significant improvements in robust capacity without compromising rendering quality. By generalizing single-watermark NeRF methods into a flexible multi-watermarking framework, MultiNeRF provides a scalable solution for 3D content. attribution.
Multitwine: Multi-Object Compositing with Text and Layout Control
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:We introduce the first generative model capable of simultaneous multi-object compositing, guided by both text and layout. Our model allows for the addition of multiple objects within a scene, capturing a range of interactions from simple positional relations (e.g., next to, in front of) to complex actions requiring reposing (e.g., hugging, playing guitar). When an interaction implies additional props, like `taking a selfie', our model autonomously generates these supporting objects. By jointly training for compositing and subject-driven generation, also known as customization, we achieve a more balanced integration of textual and visual inputs for text-driven object compositing. As a result, we obtain a versatile model with state-of-the-art performance in both tasks. We further present a data generation pipeline leveraging visual and language models to effortlessly synthesize multimodal, aligned training data.
On the Coexistence and Ensembling of Watermarks
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:Watermarking, the practice of embedding imperceptible information into media such as images, videos, audio, and text, is essential for intellectual property protection, content provenance and attribution. The growing complexity of digital ecosystems necessitates watermarks for different uses to be embedded in the same media. However, to detect and decode all watermarks, they need to coexist well with one another. We perform the first study of coexistence of deep image watermarking methods and, contrary to intuition, we find that various open-source watermarks can coexist with only minor impacts on image quality and decoding robustness. The coexistence of watermarks also opens the avenue for ensembling watermarking methods. We show how ensembling can increase the overall message capacity and enable new trade-offs between capacity, accuracy, robustness and image quality, without needing to retrain the base models.
MAGNET: Augmenting Generative Decoders with Representation Learning and Infilling Capabilities
Jan 15, 2025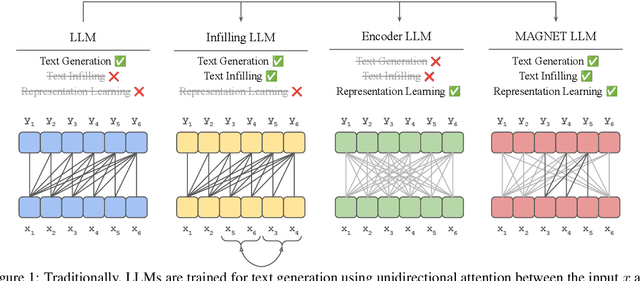
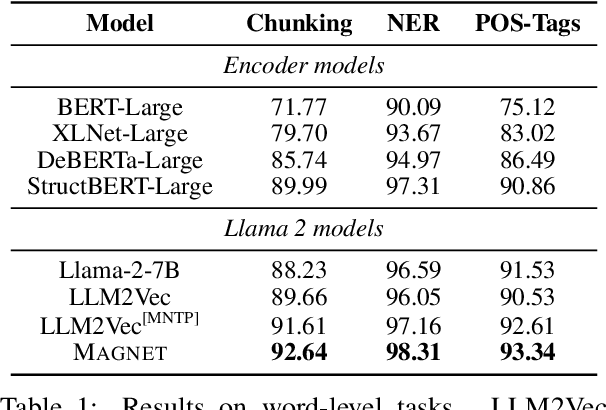
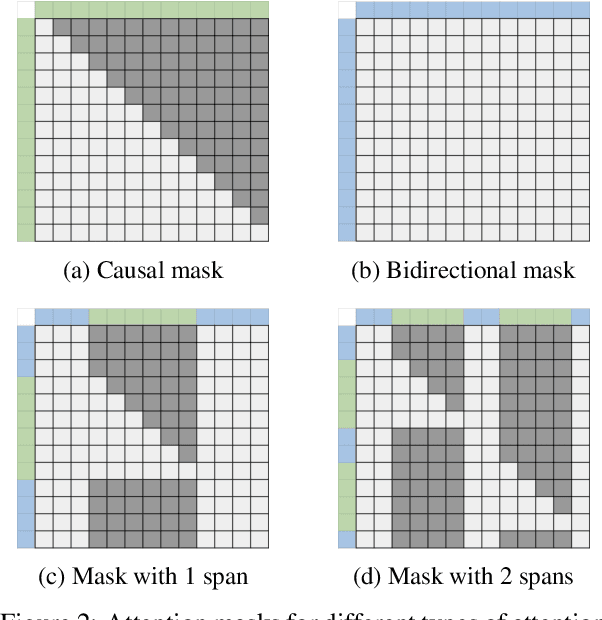
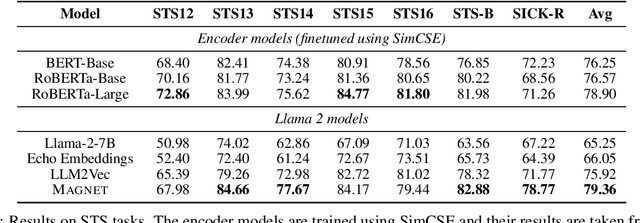
Abstract:While originally designed for unidirectional generative modeling, decoder-only large language models (LLMs) are increasingly being adapted for bidirectional modeling. However, unidirectional and bidirectional models are typically trained separately with distinct objectives (generation and representation learning, respectively). This separation overlooks the opportunity for developing a more versatile language model and for these objectives to complement each other. In this work, we introduce MAGNET, an adaptation of decoder-only LLMs that enhances their ability to generate robust representations and infill missing text spans, while preserving their knowledge and text generation capabilities. MAGNET employs three self-supervised training objectives and introduces an attention mechanism that combines bidirectional and causal attention, enabling unified training across all objectives. Our results demonstrate that LLMs adapted with MAGNET (1) surpass strong text encoders on token-level and sentence-level representation learning tasks, (2) generate contextually appropriate text infills by leveraging future context, (3) retain the ability for open-ended text generation without exhibiting repetition problem, and (4) preserve the knowledge gained by the LLM during pretraining.
MAD-Sherlock: Multi-Agent Debates for Out-of-Context Misinformation Detection
Oct 26, 2024



Abstract:One of the most challenging forms of misinformation involves the out-of-context (OOC) use of images paired with misleading text, creating false narratives. Existing AI-driven detection systems lack explainability and require expensive fine-tuning. We address these issues with MAD-Sherlock: a Multi-Agent Debate system for OOC Misinformation Detection. MAD-Sherlock introduces a novel multi-agent debate framework where multimodal agents collaborate to assess contextual consistency and request external information to enhance cross-context reasoning and decision-making. Our framework enables explainable detection with state-of-the-art accuracy even without domain-specific fine-tuning. Extensive ablation studies confirm that external retrieval significantly improves detection accuracy, and user studies demonstrate that MAD-Sherlock boosts performance for both experts and non-experts. These results position MAD-Sherlock as a powerful tool for autonomous and citizen intelligence applications.
PDFed: Privacy-Preserving and Decentralized Asynchronous Federated Learning for Diffusion Models
Sep 26, 2024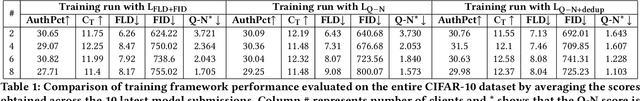
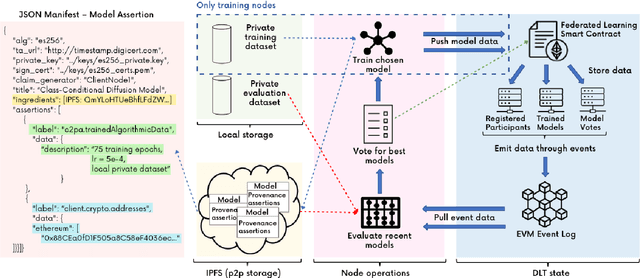
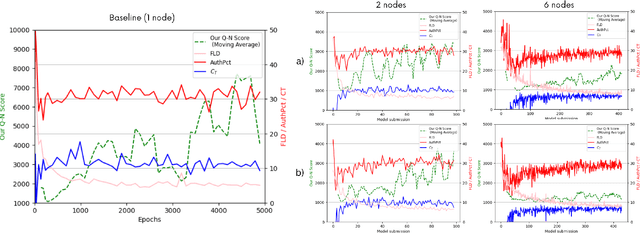
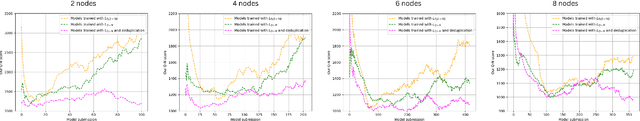
Abstract:We present PDFed, a decentralized, aggregator-free, and asynchronous federated learning protocol for training image diffusion models using a public blockchain. In general, diffusion models are prone to memorization of training data, raising privacy and ethical concerns (e.g., regurgitation of private training data in generated images). Federated learning (FL) offers a partial solution via collaborative model training across distributed nodes that safeguard local data privacy. PDFed proposes a novel sample-based score that measures the novelty and quality of generated samples, incorporating these into a blockchain-based federated learning protocol that we show reduces private data memorization in the collaboratively trained model. In addition, PDFed enables asynchronous collaboration among participants with varying hardware capabilities, facilitating broader participation. The protocol records the provenance of AI models, improving transparency and auditability, while also considering automated incentive and reward mechanisms for participants. PDFed aims to empower artists and creators by protecting the privacy of creative works and enabling decentralized, peer-to-peer collaboration. The protocol positively impacts the creative economy by opening up novel revenue streams and fostering innovative ways for artists to benefit from their contributions to the AI space.
Thinking Outside the BBox: Unconstrained Generative Object Compositing
Sep 11, 2024Abstract:Compositing an object into an image involves multiple non-trivial sub-tasks such as object placement and scaling, color/lighting harmonization, viewpoint/geometry adjustment, and shadow/reflection generation. Recent generative image compositing methods leverage diffusion models to handle multiple sub-tasks at once. However, existing models face limitations due to their reliance on masking the original object during training, which constrains their generation to the input mask. Furthermore, obtaining an accurate input mask specifying the location and scale of the object in a new image can be highly challenging. To overcome such limitations, we define a novel problem of unconstrained generative object compositing, i.e., the generation is not bounded by the mask, and train a diffusion-based model on a synthesized paired dataset. Our first-of-its-kind model is able to generate object effects such as shadows and reflections that go beyond the mask, enhancing image realism. Additionally, if an empty mask is provided, our model automatically places the object in diverse natural locations and scales, accelerating the compositing workflow. Our model outperforms existing object placement and compositing models in various quality metrics and user studies.
Self-Improving Diffusion Models with Synthetic Data
Aug 29, 2024
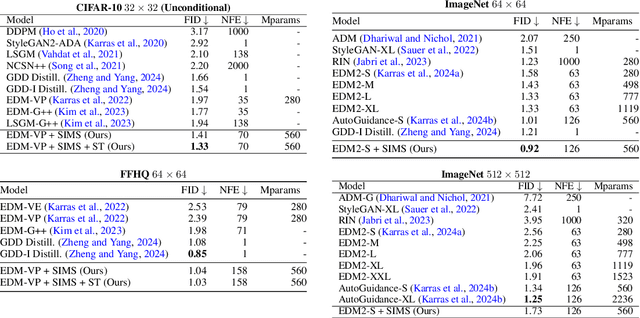
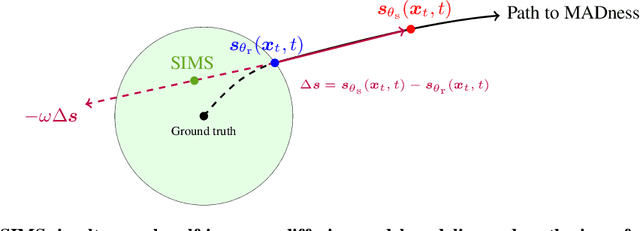
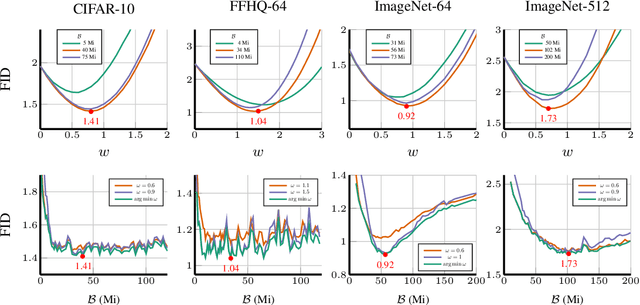
Abstract:The artificial intelligence (AI) world is running out of real data for training increasingly large generative models, resulting in accelerating pressure to train on synthetic data. Unfortunately, training new generative models with synthetic data from current or past generation models creates an autophagous (self-consuming) loop that degrades the quality and/or diversity of the synthetic data in what has been termed model autophagy disorder (MAD) and model collapse. Current thinking around model autophagy recommends that synthetic data is to be avoided for model training lest the system deteriorate into MADness. In this paper, we take a different tack that treats synthetic data differently from real data. Self-IMproving diffusion models with Synthetic data (SIMS) is a new training concept for diffusion models that uses self-synthesized data to provide negative guidance during the generation process to steer a model's generative process away from the non-ideal synthetic data manifold and towards the real data distribution. We demonstrate that SIMS is capable of self-improvement; it establishes new records based on the Fr\'echet inception distance (FID) metric for CIFAR-10 and ImageNet-64 generation and achieves competitive results on FFHQ-64 and ImageNet-512. Moreover, SIMS is, to the best of our knowledge, the first prophylactic generative AI algorithm that can be iteratively trained on self-generated synthetic data without going MAD. As a bonus, SIMS can adjust a diffusion model's synthetic data distribution to match any desired in-domain target distribution to help mitigate biases and ensure fairness.
FINEMATCH: Aspect-based Fine-grained Image and Text Mismatch Detection and Correction
Apr 23, 2024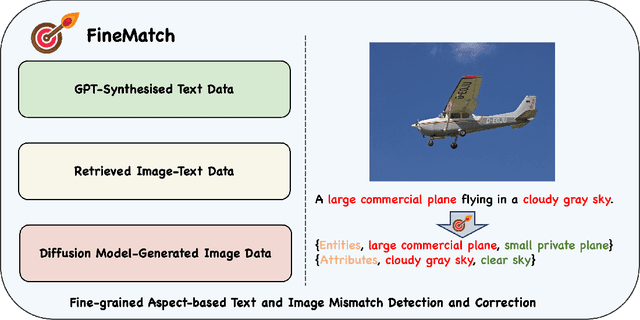
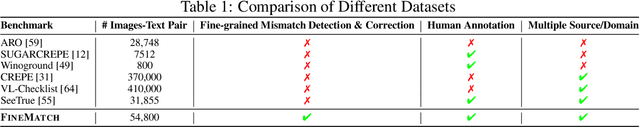
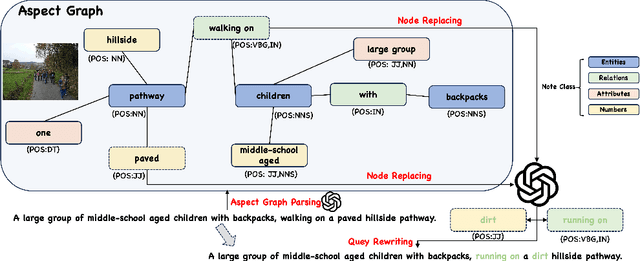
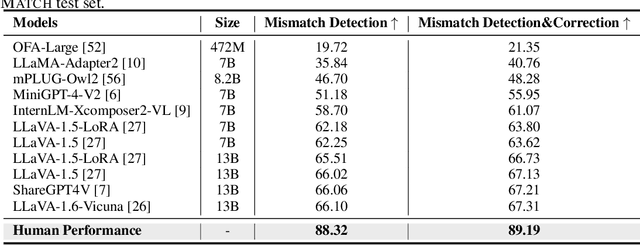
Abstract:Recent progress in large-scale pre-training has led to the development of advanced vision-language models (VLMs) with remarkable proficiency in comprehending and generating multimodal content. Despite the impressive ability to perform complex reasoning for VLMs, current models often struggle to effectively and precisely capture the compositional information on both the image and text sides. To address this, we propose FineMatch, a new aspect-based fine-grained text and image matching benchmark, focusing on text and image mismatch detection and correction. This benchmark introduces a novel task for boosting and evaluating the VLMs' compositionality for aspect-based fine-grained text and image matching. In this task, models are required to identify mismatched aspect phrases within a caption, determine the aspect's class, and propose corrections for an image-text pair that may contain between 0 and 3 mismatches. To evaluate the models' performance on this new task, we propose a new evaluation metric named ITM-IoU for which our experiments show a high correlation to human evaluation. In addition, we also provide a comprehensive experimental analysis of existing mainstream VLMs, including fully supervised learning and in-context learning settings. We have found that models trained on FineMatch demonstrate enhanced proficiency in detecting fine-grained text and image mismatches. Moreover, models (e.g., GPT-4V, Gemini Pro Vision) with strong abilities to perform multimodal in-context learning are not as skilled at fine-grained compositional image and text matching analysis. With FineMatch, we are able to build a system for text-to-image generation hallucination detection and correction.
VIXEN: Visual Text Comparison Network for Image Difference Captioning
Mar 14, 2024
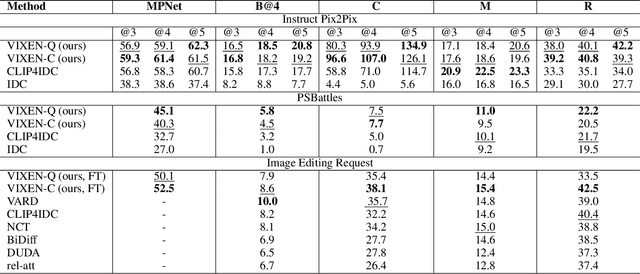
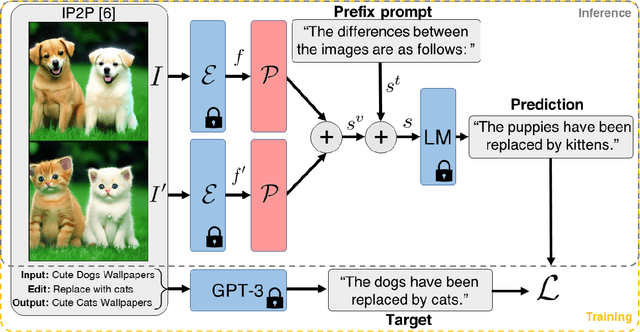
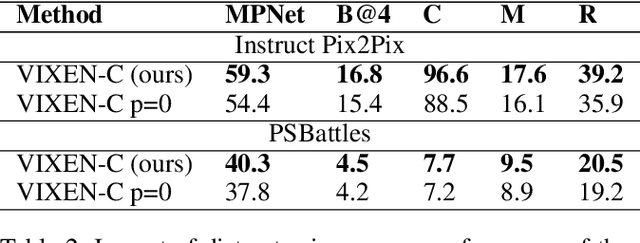
Abstract:We present VIXEN - a technique that succinctly summarizes in text the visual differences between a pair of images in order to highlight any content manipulation present. Our proposed network linearly maps image features in a pairwise manner, constructing a soft prompt for a pretrained large language model. We address the challenge of low volume of training data and lack of manipulation variety in existing image difference captioning (IDC) datasets by training on synthetically manipulated images from the recent InstructPix2Pix dataset generated via prompt-to-prompt editing framework. We augment this dataset with change summaries produced via GPT-3. We show that VIXEN produces state-of-the-art, comprehensible difference captions for diverse image contents and edit types, offering a potential mitigation against misinformation disseminated via manipulated image content. Code and data are available at http://github.com/alexblck/vixen
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge