Jisu Nam
Repurposing Video Diffusion Transformers for Robust Point Tracking
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Point tracking aims to localize corresponding points across video frames, serving as a fundamental task for 4D reconstruction, robotics, and video editing. Existing methods commonly rely on shallow convolutional backbones such as ResNet that process frames independently, lacking temporal coherence and producing unreliable matching costs under challenging conditions. Through systematic analysis, we find that video Diffusion Transformers (DiTs), pre-trained on large-scale real-world videos with spatio-temporal attention, inherently exhibit strong point tracking capability and robustly handle dynamic motions and frequent occlusions. We propose DiTracker, which adapts video DiTs through: (1) query-key attention matching, (2) lightweight LoRA tuning, and (3) cost fusion with a ResNet backbone. Despite training with 8 times smaller batch size, DiTracker achieves state-of-the-art performance on challenging ITTO benchmark and matches or outperforms state-of-the-art models on TAP-Vid benchmarks. Our work validates video DiT features as an effective and efficient foundation for point tracking.
MATRIX: Mask Track Alignment for Interaction-aware Video Generation
Oct 08, 2025



Abstract:Video DiTs have advanced video generation, yet they still struggle to model multi-instance or subject-object interactions. This raises a key question: How do these models internally represent interactions? To answer this, we curate MATRIX-11K, a video dataset with interaction-aware captions and multi-instance mask tracks. Using this dataset, we conduct a systematic analysis that formalizes two perspectives of video DiTs: semantic grounding, via video-to-text attention, which evaluates whether noun and verb tokens capture instances and their relations; and semantic propagation, via video-to-video attention, which assesses whether instance bindings persist across frames. We find both effects concentrate in a small subset of interaction-dominant layers. Motivated by this, we introduce MATRIX, a simple and effective regularization that aligns attention in specific layers of video DiTs with multi-instance mask tracks from the MATRIX-11K dataset, enhancing both grounding and propagation. We further propose InterGenEval, an evaluation protocol for interaction-aware video generation. In experiments, MATRIX improves both interaction fidelity and semantic alignment while reducing drift and hallucination. Extensive ablations validate our design choices. Codes and weights will be released.
Visual Persona: Foundation Model for Full-Body Human Customization
Mar 19, 2025

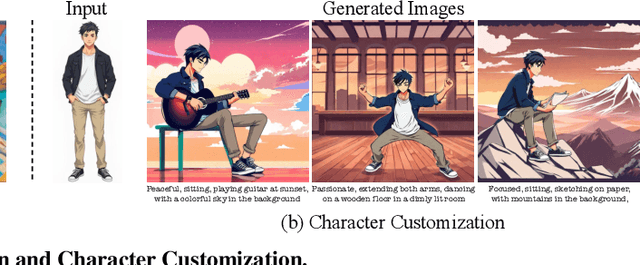
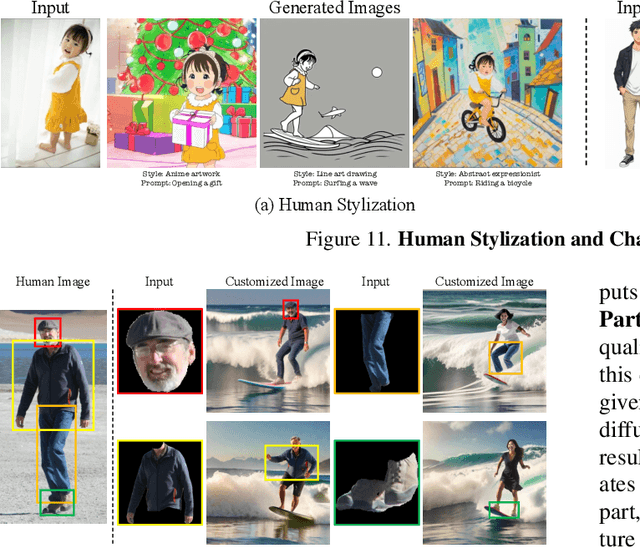
Abstract:We introduce Visual Persona, a foundation model for text-to-image full-body human customization that, given a single in-the-wild human image, generates diverse images of the individual guided by text descriptions. Unlike prior methods that focus solely on preserving facial identity, our approach captures detailed full-body appearance, aligning with text descriptions for body structure and scene variations. Training this model requires large-scale paired human data, consisting of multiple images per individual with consistent full-body identities, which is notoriously difficult to obtain. To address this, we propose a data curation pipeline leveraging vision-language models to evaluate full-body appearance consistency, resulting in Visual Persona-500K, a dataset of 580k paired human images across 100k unique identities. For precise appearance transfer, we introduce a transformer encoder-decoder architecture adapted to a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model, which augments the input image into distinct body regions, encodes these regions as local appearance features, and projects them into dense identity embeddings independently to condition the diffusion model for synthesizing customized images. Visual Persona consistently surpasses existing approaches, generating high-quality, customized images from in-the-wild inputs. Extensive ablation studies validate design choices, and we demonstrate the versatility of Visual Persona across various downstream tasks.
Appearance Matching Adapter for Exemplar-based Semantic Image Synthesis
Dec 04, 2024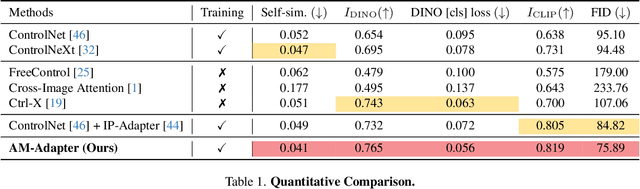
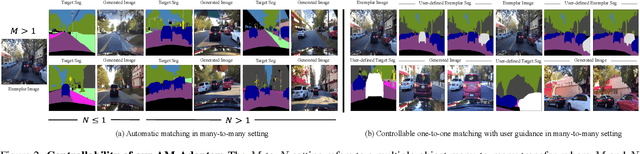
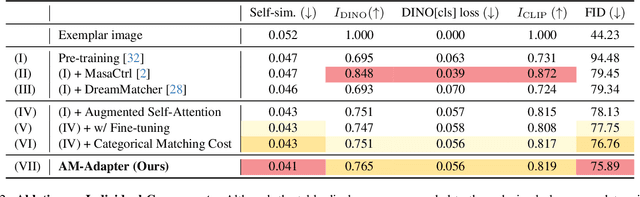
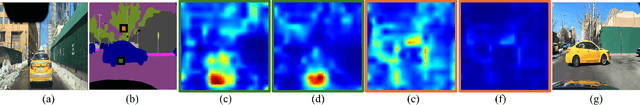
Abstract:Exemplar-based semantic image synthesis aims to generate images aligned with given semantic content while preserving the appearance of an exemplar image. Conventional structure-guidance models, such as ControlNet, are limited in that they cannot directly utilize exemplar images as input, relying instead solely on text prompts to control appearance. Recent tuning-free approaches address this limitation by transferring local appearance from the exemplar image to the synthesized image through implicit cross-image matching in the augmented self-attention mechanism of pre-trained diffusion models. However, these methods face challenges when applied to content-rich scenes with significant geometric deformations, such as driving scenes. In this paper, we propose the Appearance Matching Adapter (AM-Adapter), a learnable framework that enhances cross-image matching within augmented self-attention by incorporating semantic information from segmentation maps. To effectively disentangle generation and matching processes, we adopt a stage-wise training approach. Initially, we train the structure-guidance and generation networks, followed by training the AM-Adapter while keeping the other networks frozen. During inference, we introduce an automated exemplar retrieval method to efficiently select exemplar image-segmentation pairs. Despite utilizing a limited number of learnable parameters, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, excelling in both semantic alignment preservation and local appearance fidelity. Extensive ablation studies further validate our design choices. Code and pre-trained weights will be publicly available.: https://cvlab-kaist.github.io/AM-Adapter/
Local All-Pair Correspondence for Point Tracking
Jul 22, 2024Abstract:We introduce LocoTrack, a highly accurate and efficient model designed for the task of tracking any point (TAP) across video sequences. Previous approaches in this task often rely on local 2D correlation maps to establish correspondences from a point in the query image to a local region in the target image, which often struggle with homogeneous regions or repetitive features, leading to matching ambiguities. LocoTrack overcomes this challenge with a novel approach that utilizes all-pair correspondences across regions, i.e., local 4D correlation, to establish precise correspondences, with bidirectional correspondence and matching smoothness significantly enhancing robustness against ambiguities. We also incorporate a lightweight correlation encoder to enhance computational efficiency, and a compact Transformer architecture to integrate long-term temporal information. LocoTrack achieves unmatched accuracy on all TAP-Vid benchmarks and operates at a speed almost 6 times faster than the current state-of-the-art.
MoDiTalker: Motion-Disentangled Diffusion Model for High-Fidelity Talking Head Generation
Mar 28, 2024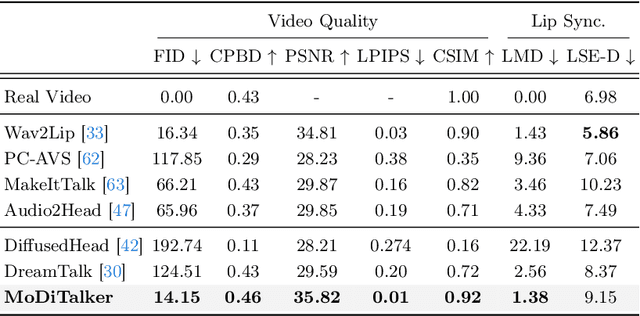
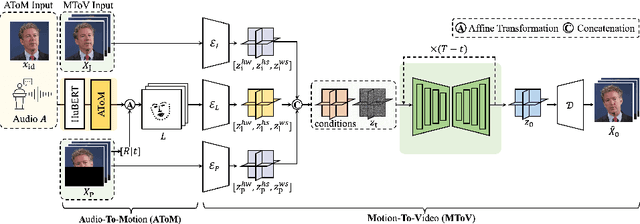
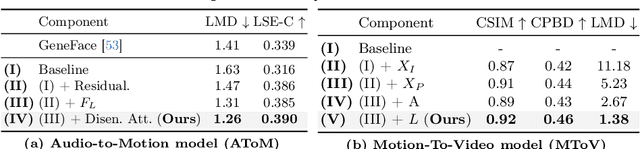
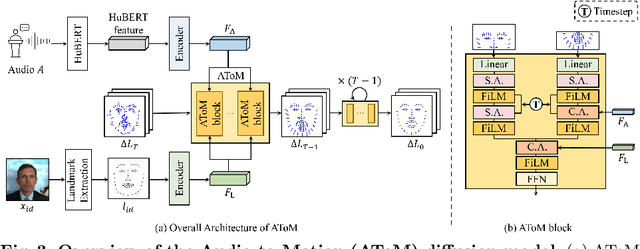
Abstract:Conventional GAN-based models for talking head generation often suffer from limited quality and unstable training. Recent approaches based on diffusion models aimed to address these limitations and improve fidelity. However, they still face challenges, including extensive sampling times and difficulties in maintaining temporal consistency due to the high stochasticity of diffusion models. To overcome these challenges, we propose a novel motion-disentangled diffusion model for high-quality talking head generation, dubbed MoDiTalker. We introduce the two modules: audio-to-motion (AToM), designed to generate a synchronized lip motion from audio, and motion-to-video (MToV), designed to produce high-quality head video following the generated motion. AToM excels in capturing subtle lip movements by leveraging an audio attention mechanism. In addition, MToV enhances temporal consistency by leveraging an efficient tri-plane representation. Our experiments conducted on standard benchmarks demonstrate that our model achieves superior performance compared to existing models. We also provide comprehensive ablation studies and user study results.
DreamMatcher: Appearance Matching Self-Attention for Semantically-Consistent Text-to-Image Personalization
Feb 15, 2024
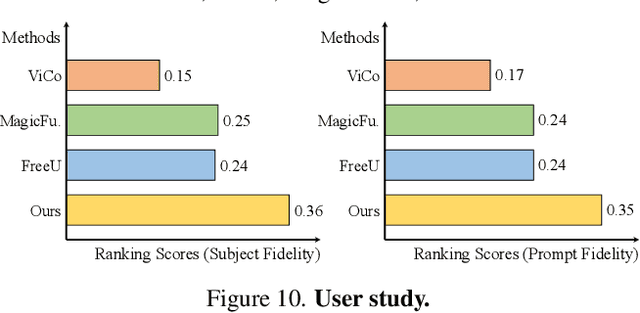
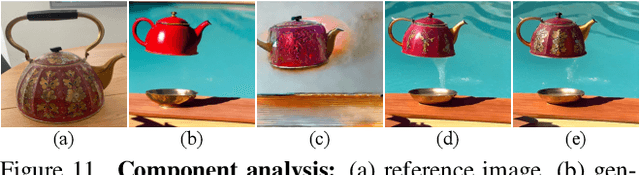

Abstract:The objective of text-to-image (T2I) personalization is to customize a diffusion model to a user-provided reference concept, generating diverse images of the concept aligned with the target prompts. Conventional methods representing the reference concepts using unique text embeddings often fail to accurately mimic the appearance of the reference. To address this, one solution may be explicitly conditioning the reference images into the target denoising process, known as key-value replacement. However, prior works are constrained to local editing since they disrupt the structure path of the pre-trained T2I model. To overcome this, we propose a novel plug-in method, called DreamMatcher, which reformulates T2I personalization as semantic matching. Specifically, DreamMatcher replaces the target values with reference values aligned by semantic matching, while leaving the structure path unchanged to preserve the versatile capability of pre-trained T2I models for generating diverse structures. We also introduce a semantic-consistent masking strategy to isolate the personalized concept from irrelevant regions introduced by the target prompts. Compatible with existing T2I models, DreamMatcher shows significant improvements in complex scenarios. Intensive analyses demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
DiffMatch: Diffusion Model for Dense Matching
May 30, 2023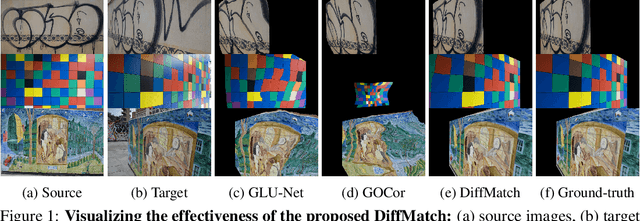
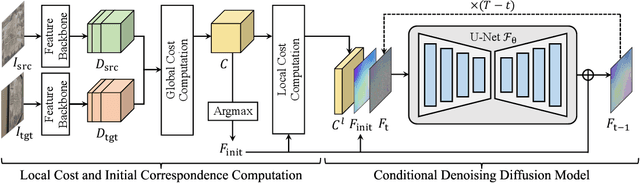

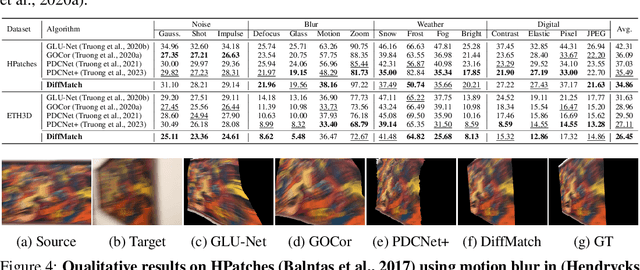
Abstract:The objective for establishing dense correspondence between paired images consists of two terms: a data term and a prior term. While conventional techniques focused on defining hand-designed prior terms, which are difficult to formulate, recent approaches have focused on learning the data term with deep neural networks without explicitly modeling the prior, assuming that the model itself has the capacity to learn an optimal prior from a large-scale dataset. The performance improvement was obvious, however, they often fail to address inherent ambiguities of matching, such as textureless regions, repetitive patterns, and large displacements. To address this, we propose DiffMatch, a novel conditional diffusion-based framework designed to explicitly model both the data and prior terms. Unlike previous approaches, this is accomplished by leveraging a conditional denoising diffusion model. DiffMatch consists of two main components: conditional denoising diffusion module and cost injection module. We stabilize the training process and reduce memory usage with a stage-wise training strategy. Furthermore, to boost performance, we introduce an inference technique that finds a better path to the accurate matching field. Our experimental results demonstrate significant performance improvements of our method over existing approaches, and the ablation studies validate our design choices along with the effectiveness of each component. Project page is available at https://ku-cvlab.github.io/DiffMatch/.
DiffFace: Diffusion-based Face Swapping with Facial Guidance
Dec 27, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a diffusion-based face swapping framework for the first time, called DiffFace, composed of training ID conditional DDPM, sampling with facial guidance, and a target-preserving blending. In specific, in the training process, the ID conditional DDPM is trained to generate face images with the desired identity. In the sampling process, we use the off-the-shelf facial expert models to make the model transfer source identity while preserving target attributes faithfully. During this process, to preserve the background of the target image and obtain the desired face swapping result, we additionally propose a target-preserving blending strategy. It helps our model to keep the attributes of the target face from noise while transferring the source facial identity. In addition, without any re-training, our model can flexibly apply additional facial guidance and adaptively control the ID-attributes trade-off to achieve the desired results. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first approach that applies the diffusion model in face swapping task. Compared with previous GAN-based approaches, by taking advantage of the diffusion model for the face swapping task, DiffFace achieves better benefits such as training stability, high fidelity, diversity of the samples, and controllability. Extensive experiments show that our DiffFace is comparable or superior to the state-of-the-art methods on several standard face swapping benchmarks.
Neural Matching Fields: Implicit Representation of Matching Fields for Visual Correspondence
Oct 06, 2022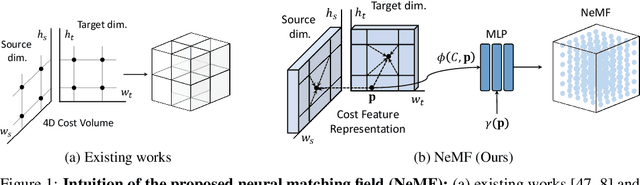
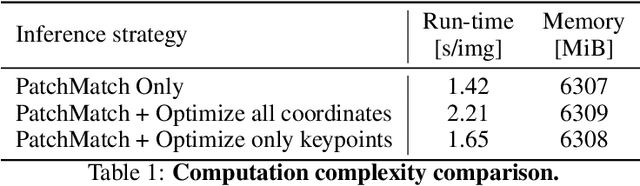
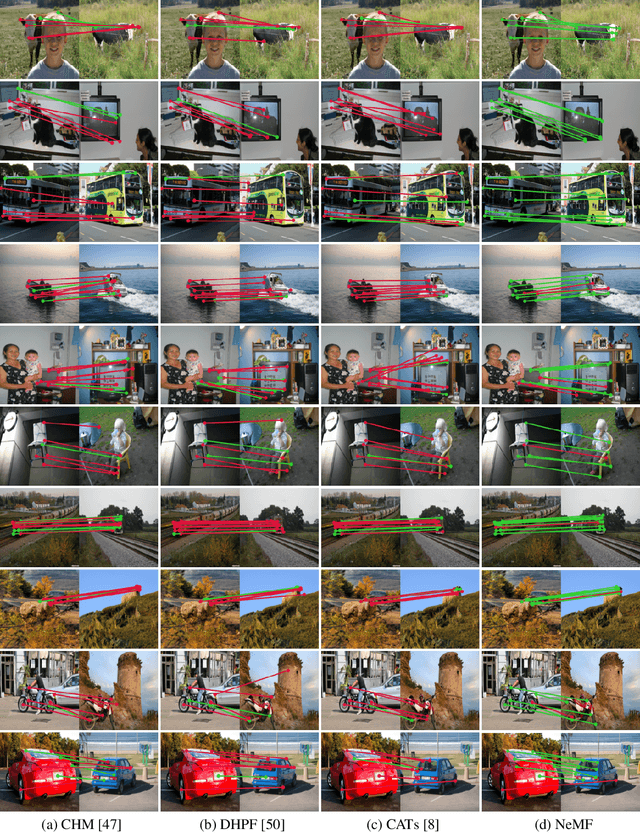

Abstract:Existing pipelines of semantic correspondence commonly include extracting high-level semantic features for the invariance against intra-class variations and background clutters. This architecture, however, inevitably results in a low-resolution matching field that additionally requires an ad-hoc interpolation process as a post-processing for converting it into a high-resolution one, certainly limiting the overall performance of matching results. To overcome this, inspired by recent success of implicit neural representation, we present a novel method for semantic correspondence, called Neural Matching Field (NeMF). However, complicacy and high-dimensionality of a 4D matching field are the major hindrances, which we propose a cost embedding network to process a coarse cost volume to use as a guidance for establishing high-precision matching field through the following fully-connected network. Nevertheless, learning a high-dimensional matching field remains challenging mainly due to computational complexity, since a naive exhaustive inference would require querying from all pixels in the 4D space to infer pixel-wise correspondences. To overcome this, we propose adequate training and inference procedures, which in the training phase, we randomly sample matching candidates and in the inference phase, we iteratively performs PatchMatch-based inference and coordinate optimization at test time. With these combined, competitive results are attained on several standard benchmarks for semantic correspondence. Code and pre-trained weights are available at https://ku-cvlab.github.io/NeMF/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge