Seunggyu Chang
HyperCLOVA X Technical Report
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce HyperCLOVA X, a family of large language models (LLMs) tailored to the Korean language and culture, along with competitive capabilities in English, math, and coding. HyperCLOVA X was trained on a balanced mix of Korean, English, and code data, followed by instruction-tuning with high-quality human-annotated datasets while abiding by strict safety guidelines reflecting our commitment to responsible AI. The model is evaluated across various benchmarks, including comprehensive reasoning, knowledge, commonsense, factuality, coding, math, chatting, instruction-following, and harmlessness, in both Korean and English. HyperCLOVA X exhibits strong reasoning capabilities in Korean backed by a deep understanding of the language and cultural nuances. Further analysis of the inherent bilingual nature and its extension to multilingualism highlights the model's cross-lingual proficiency and strong generalization ability to untargeted languages, including machine translation between several language pairs and cross-lingual inference tasks. We believe that HyperCLOVA X can provide helpful guidance for regions or countries in developing their sovereign LLMs.
One-Shot Structure-Aware Stylized Image Synthesis
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:While GAN-based models have been successful in image stylization tasks, they often struggle with structure preservation while stylizing a wide range of input images. Recently, diffusion models have been adopted for image stylization but still lack the capability to maintain the original quality of input images. Building on this, we propose OSASIS: a novel one-shot stylization method that is robust in structure preservation. We show that OSASIS is able to effectively disentangle the semantics from the structure of an image, allowing it to control the level of content and style implemented to a given input. We apply OSASIS to various experimental settings, including stylization with out-of-domain reference images and stylization with text-driven manipulation. Results show that OSASIS outperforms other stylization methods, especially for input images that were rarely encountered during training, providing a promising solution to stylization via diffusion models.
DreamMatcher: Appearance Matching Self-Attention for Semantically-Consistent Text-to-Image Personalization
Feb 15, 2024
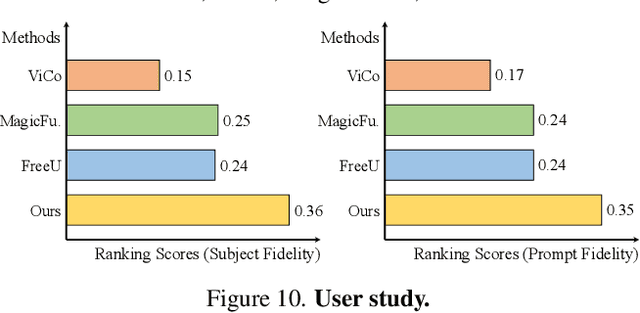
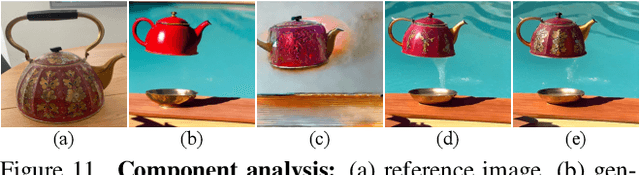

Abstract:The objective of text-to-image (T2I) personalization is to customize a diffusion model to a user-provided reference concept, generating diverse images of the concept aligned with the target prompts. Conventional methods representing the reference concepts using unique text embeddings often fail to accurately mimic the appearance of the reference. To address this, one solution may be explicitly conditioning the reference images into the target denoising process, known as key-value replacement. However, prior works are constrained to local editing since they disrupt the structure path of the pre-trained T2I model. To overcome this, we propose a novel plug-in method, called DreamMatcher, which reformulates T2I personalization as semantic matching. Specifically, DreamMatcher replaces the target values with reference values aligned by semantic matching, while leaving the structure path unchanged to preserve the versatile capability of pre-trained T2I models for generating diverse structures. We also introduce a semantic-consistent masking strategy to isolate the personalized concept from irrelevant regions introduced by the target prompts. Compatible with existing T2I models, DreamMatcher shows significant improvements in complex scenarios. Intensive analyses demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
Past as a Guide: Leveraging Retrospective Learning for Python Code Completion
Nov 13, 2023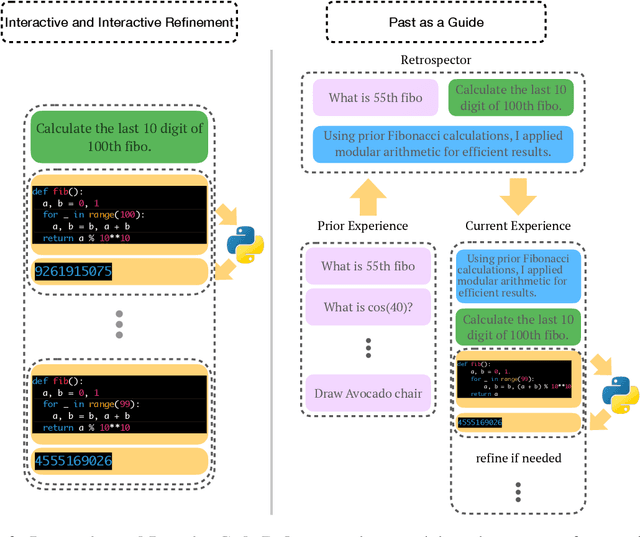


Abstract:This work presents Past as a Guide (PaG), a simple approach for Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve the coding capabilities by integrating the past history with interactive and iterative code refinements. To be specific, inspired by human cognitive processes, the proposed method enables LLMs to utilize previous programming and debugging experiences to enhance the Python code completion tasks. The framework facilitates LLMs to iteratively refine the Python code based on previous execution and debugging results and optimize learning and reasoning capabilities. The proposed methodology achieved a 92\% pass@1 on HumanEval, demonstrating the potential to advance the field by leveraging retrospection from past experiences and interactive and iterative refinement processes without external correctness indicators.
Texture Generation Using Dual-Domain Feature Flow with Multi-View Hallucinations
Mar 14, 2022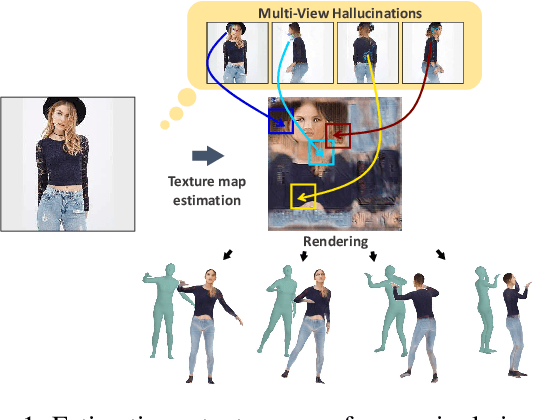
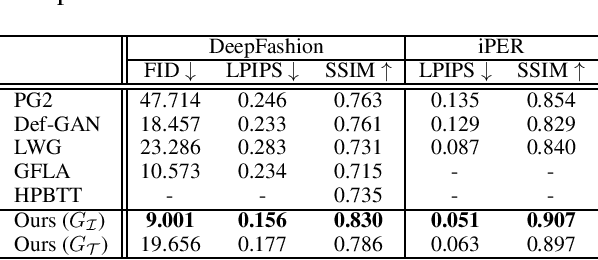
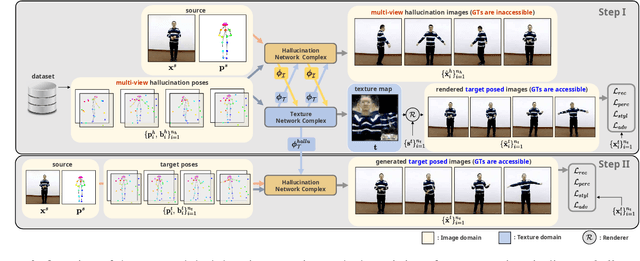
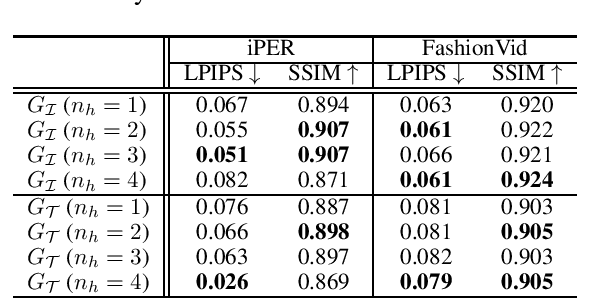
Abstract:We propose a dual-domain generative model to estimate a texture map from a single image for colorizing a 3D human model. When estimating a texture map, a single image is insufficient as it reveals only one facet of a 3D object. To provide sufficient information for estimating a complete texture map, the proposed model simultaneously generates multi-view hallucinations in the image domain and an estimated texture map in the texture domain. During the generating process, each domain generator exchanges features to the other by a flow-based local attention mechanism. In this manner, the proposed model can estimate a texture map utilizing abundant multi-view image features from which multiview hallucinations are generated. As a result, the estimated texture map contains consistent colors and patterns over the entire region. Experiments show the superiority of our model for estimating a directly render-able texture map, which is applicable to 3D animation rendering. Furthermore, our model also improves an overall generation quality in the image domain for pose and viewpoint transfer tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge