Junyoung Seo
Vid-CamEdit: Video Camera Trajectory Editing with Generative Rendering from Estimated Geometry
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:We introduce Vid-CamEdit, a novel framework for video camera trajectory editing, enabling the re-synthesis of monocular videos along user-defined camera paths. This task is challenging due to its ill-posed nature and the limited multi-view video data for training. Traditional reconstruction methods struggle with extreme trajectory changes, and existing generative models for dynamic novel view synthesis cannot handle in-the-wild videos. Our approach consists of two steps: estimating temporally consistent geometry, and generative rendering guided by this geometry. By integrating geometric priors, the generative model focuses on synthesizing realistic details where the estimated geometry is uncertain. We eliminate the need for extensive 4D training data through a factorized fine-tuning framework that separately trains spatial and temporal components using multi-view image and video data. Our method outperforms baselines in producing plausible videos from novel camera trajectories, especially in extreme extrapolation scenarios on real-world footage.
D^2USt3R: Enhancing 3D Reconstruction with 4D Pointmaps for Dynamic Scenes
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:We address the task of 3D reconstruction in dynamic scenes, where object motions degrade the quality of previous 3D pointmap regression methods, such as DUSt3R, originally designed for static 3D scene reconstruction. Although these methods provide an elegant and powerful solution in static settings, they struggle in the presence of dynamic motions that disrupt alignment based solely on camera poses. To overcome this, we propose D^2USt3R that regresses 4D pointmaps that simultaneiously capture both static and dynamic 3D scene geometry in a feed-forward manner. By explicitly incorporating both spatial and temporal aspects, our approach successfully encapsulates spatio-temporal dense correspondence to the proposed 4D pointmaps, enhancing downstream tasks. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate that our proposed approach consistently achieves superior reconstruction performance across various datasets featuring complex motions.
Pose-Diversified Augmentation with Diffusion Model for Person Re-Identification
Jun 23, 2024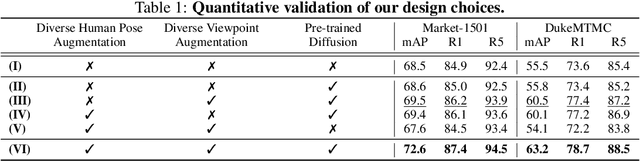
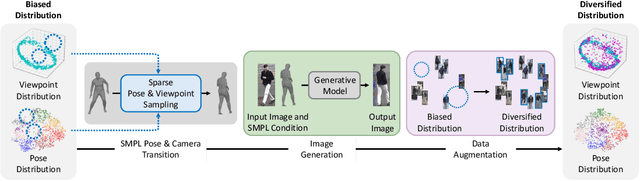
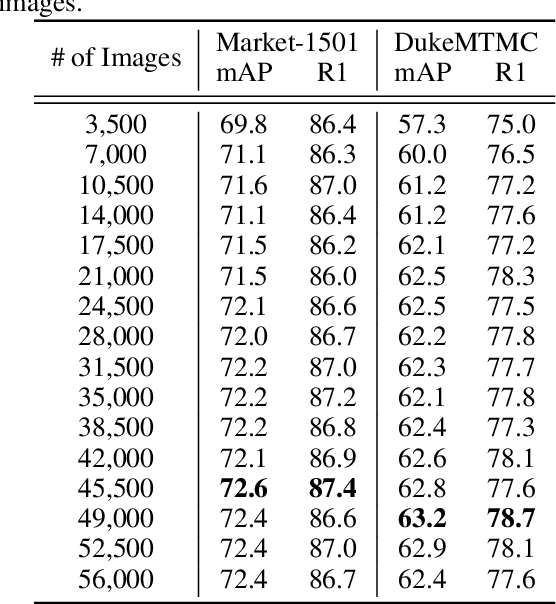
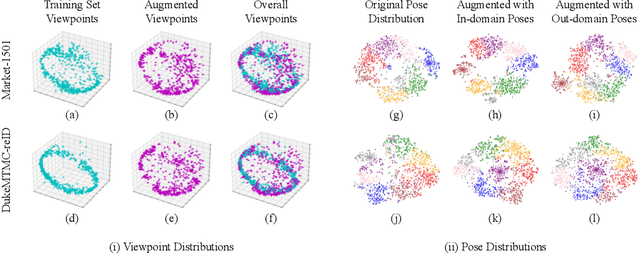
Abstract:Person re-identification (Re-ID) often faces challenges due to variations in human poses and camera viewpoints, which significantly affect the appearance of individuals across images. Existing datasets frequently lack diversity and scalability in these aspects, hindering the generalization of Re-ID models to new camera systems. Previous methods have attempted to address these issues through data augmentation; however, they rely on human poses already present in the training dataset, failing to effectively reduce the human pose bias in the dataset. We propose Diff-ID, a novel data augmentation approach that incorporates sparse and underrepresented human pose and camera viewpoint examples into the training data, addressing the limited diversity in the original training data distribution. Our objective is to augment a training dataset that enables existing Re-ID models to learn features unbiased by human pose and camera viewpoint variations. To achieve this, we leverage the knowledge of pre-trained large-scale diffusion models. Using the SMPL model, we simultaneously capture both the desired human poses and camera viewpoints, enabling realistic human rendering. The depth information provided by the SMPL model indirectly conveys the camera viewpoints. By conditioning the diffusion model on both the human pose and camera viewpoint concurrently through the SMPL model, we generate realistic images with diverse human poses and camera viewpoints. Qualitative results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in addressing human pose bias and enhancing the generalizability of Re-ID models compared to other data augmentation-based Re-ID approaches. The performance gains achieved by training Re-ID models on our offline augmented dataset highlight the potential of our proposed framework in improving the scalability and generalizability of person Re-ID models.
GenWarp: Single Image to Novel Views with Semantic-Preserving Generative Warping
May 27, 2024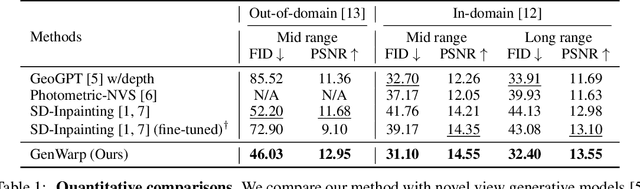
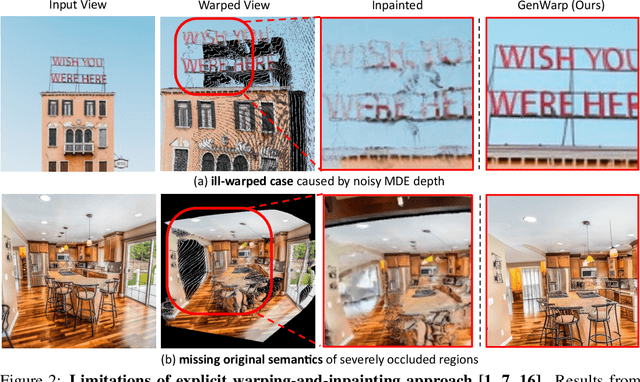
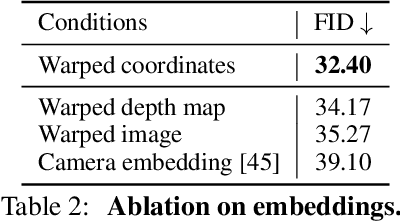
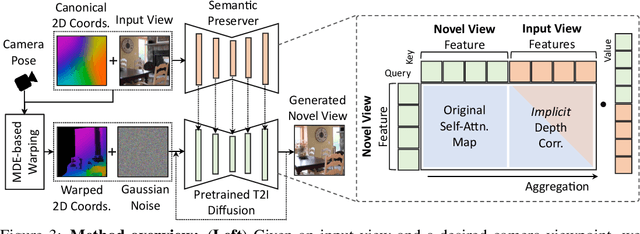
Abstract:Generating novel views from a single image remains a challenging task due to the complexity of 3D scenes and the limited diversity in the existing multi-view datasets to train a model on. Recent research combining large-scale text-to-image (T2I) models with monocular depth estimation (MDE) has shown promise in handling in-the-wild images. In these methods, an input view is geometrically warped to novel views with estimated depth maps, then the warped image is inpainted by T2I models. However, they struggle with noisy depth maps and loss of semantic details when warping an input view to novel viewpoints. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for single-shot novel view synthesis, a semantic-preserving generative warping framework that enables T2I generative models to learn where to warp and where to generate, through augmenting cross-view attention with self-attention. Our approach addresses the limitations of existing methods by conditioning the generative model on source view images and incorporating geometric warping signals. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate that our model outperforms existing methods in both in-domain and out-of-domain scenarios. Project page is available at https://GenWarp-NVS.github.io/.
Retrieval-Augmented Score Distillation for Text-to-3D Generation
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Text-to-3D generation has achieved significant success by incorporating powerful 2D diffusion models, but insufficient 3D prior knowledge also leads to the inconsistency of 3D geometry. Recently, since large-scale multi-view datasets have been released, fine-tuning the diffusion model on the multi-view datasets becomes a mainstream to solve the 3D inconsistency problem. However, it has confronted with fundamental difficulties regarding the limited quality and diversity of 3D data, compared with 2D data. To sidestep these trade-offs, we explore a retrieval-augmented approach tailored for score distillation, dubbed RetDream. We postulate that both expressiveness of 2D diffusion models and geometric consistency of 3D assets can be fully leveraged by employing the semantically relevant assets directly within the optimization process. To this end, we introduce novel framework for retrieval-based quality enhancement in text-to-3D generation. We leverage the retrieved asset to incorporate its geometric prior in the variational objective and adapt the diffusion model's 2D prior toward view consistency, achieving drastic improvements in both geometry and fidelity of generated scenes. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate that RetDream exhibits superior quality with increased geometric consistency. Project page is available at https://ku-cvlab.github.io/RetDream/.
Large Language Models are Frame-level Directors for Zero-shot Text-to-Video Generation
May 23, 2023
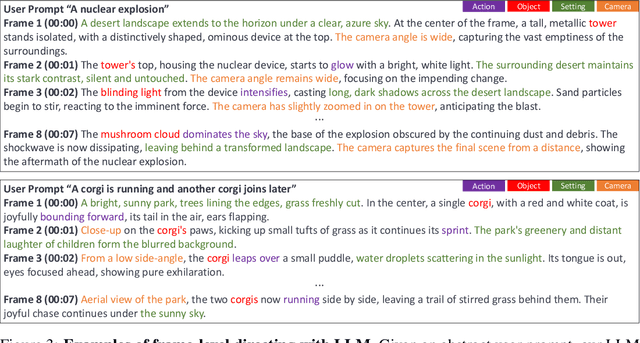
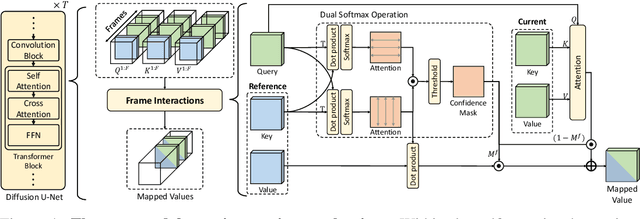
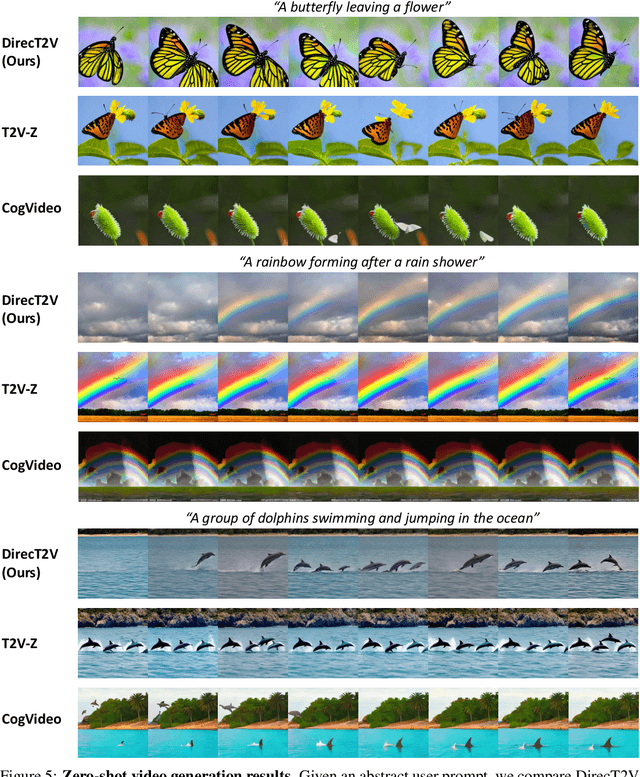
Abstract:In the paradigm of AI-generated content (AIGC), there has been increasing attention in extending pre-trained text-to-image (T2I) models to text-to-video (T2V) generation. Despite their effectiveness, these frameworks face challenges in maintaining consistent narratives and handling rapid shifts in scene composition or object placement from a single user prompt. This paper introduces a new framework, dubbed DirecT2V, which leverages instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs) to generate frame-by-frame descriptions from a single abstract user prompt. DirecT2V utilizes LLM directors to divide user inputs into separate prompts for each frame, enabling the inclusion of time-varying content and facilitating consistent video generation. To maintain temporal consistency and prevent object collapse, we propose a novel value mapping method and dual-softmax filtering. Extensive experimental results validate the effectiveness of the DirecT2V framework in producing visually coherent and consistent videos from abstract user prompts, addressing the challenges of zero-shot video generation.
Let 2D Diffusion Model Know 3D-Consistency for Robust Text-to-3D Generation
Mar 16, 2023
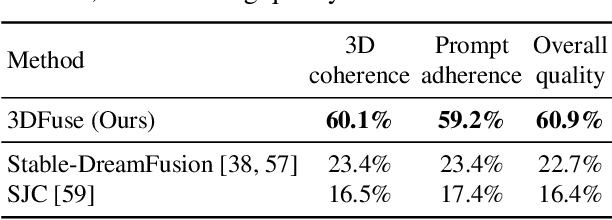

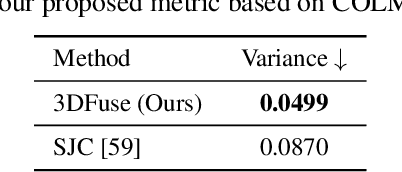
Abstract:Text-to-3D generation has shown rapid progress in recent days with the advent of score distillation, a methodology of using pretrained text-to-2D diffusion models to optimize neural radiance field (NeRF) in the zero-shot setting. However, the lack of 3D awareness in the 2D diffusion models destabilizes score distillation-based methods from reconstructing a plausible 3D scene. To address this issue, we propose 3DFuse, a novel framework that incorporates 3D awareness into pretrained 2D diffusion models, enhancing the robustness and 3D consistency of score distillation-based methods. We realize this by first constructing a coarse 3D structure of a given text prompt and then utilizing projected, view-specific depth map as a condition for the diffusion model. Additionally, we introduce a training strategy that enables the 2D diffusion model learns to handle the errors and sparsity within the coarse 3D structure for robust generation, as well as a method for ensuring semantic consistency throughout all viewpoints of the scene. Our framework surpasses the limitations of prior arts, and has significant implications for 3D consistent generation of 2D diffusion models.
DiffFace: Diffusion-based Face Swapping with Facial Guidance
Dec 27, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a diffusion-based face swapping framework for the first time, called DiffFace, composed of training ID conditional DDPM, sampling with facial guidance, and a target-preserving blending. In specific, in the training process, the ID conditional DDPM is trained to generate face images with the desired identity. In the sampling process, we use the off-the-shelf facial expert models to make the model transfer source identity while preserving target attributes faithfully. During this process, to preserve the background of the target image and obtain the desired face swapping result, we additionally propose a target-preserving blending strategy. It helps our model to keep the attributes of the target face from noise while transferring the source facial identity. In addition, without any re-training, our model can flexibly apply additional facial guidance and adaptively control the ID-attributes trade-off to achieve the desired results. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first approach that applies the diffusion model in face swapping task. Compared with previous GAN-based approaches, by taking advantage of the diffusion model for the face swapping task, DiffFace achieves better benefits such as training stability, high fidelity, diversity of the samples, and controllability. Extensive experiments show that our DiffFace is comparable or superior to the state-of-the-art methods on several standard face swapping benchmarks.
DAG: Depth-Aware Guidance with Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
Dec 17, 2022



Abstract:In recent years, generative models have undergone significant advancement due to the success of diffusion models. The success of these models is often attributed to their use of guidance techniques, such as classifier and classifier-free methods, which provides effective mechanisms to trade-off between fidelity and diversity. However, these methods are not capable of guiding a generated image to be aware of its geometric configuration, e.g., depth, which hinders the application of diffusion models to areas that require a certain level of depth awareness. To address this limitation, we propose a novel guidance approach for diffusion models that uses estimated depth information derived from the rich intermediate representations of diffusion models. To do this, we first present a label-efficient depth estimation framework using the internal representations of diffusion models. At the sampling phase, we utilize two guidance techniques to self-condition the generated image using the estimated depth map, the first of which uses pseudo-labeling, and the subsequent one uses a depth-domain diffusion prior. Experiments and extensive ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in guiding the diffusion models toward geometrically plausible image generation. Project page is available at https://ku-cvlab.github.io/DAG/.
MIDMs: Matching Interleaved Diffusion Models for Exemplar-based Image Translation
Sep 23, 2022
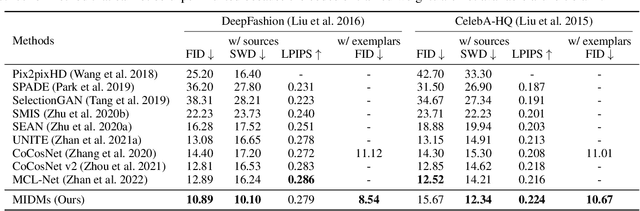
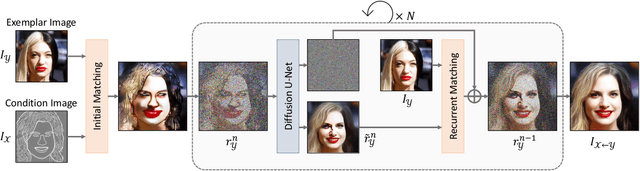
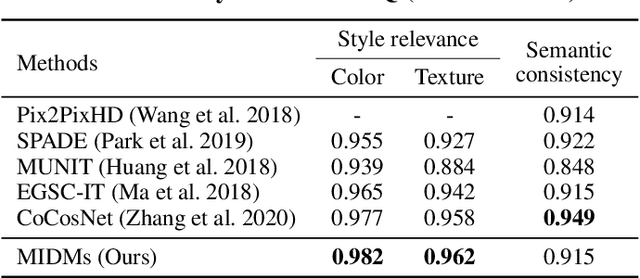
Abstract:We present a novel method for exemplar-based image translation, called matching interleaved diffusion models (MIDMs). Most existing methods for this task were formulated as GAN-based matching-then-generation framework. However, in this framework, matching errors induced by the difficulty of semantic matching across cross-domain, e.g., sketch and photo, can be easily propagated to the generation step, which in turn leads to degenerated results. Motivated by the recent success of diffusion models overcoming the shortcomings of GANs, we incorporate the diffusion models to overcome these limitations. Specifically, we formulate a diffusion-based matching-and-generation framework that interleaves cross-domain matching and diffusion steps in the latent space by iteratively feeding the intermediate warp into the noising process and denoising it to generate a translated image. In addition, to improve the reliability of the diffusion process, we design a confidence-aware process using cycle-consistency to consider only confident regions during translation. Experimental results show that our MIDMs generate more plausible images than state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge