Jiwon Kim
PAIR-SAFE: A Paired-Agent Approach for Runtime Auditing and Refining AI-Mediated Mental Health Support
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used for mental health support, yet they can produce responses that are overly directive, inconsistent, or clinically misaligned, particularly in sensitive or high-risk contexts. Existing approaches to mitigating these risks largely rely on implicit alignment through training or prompting, offering limited transparency and runtime accountability. We introduce PAIR-SAFE, a paired-agent framework for auditing and refining AI-generated mental health support that integrates a Responder agent with a supervisory Judge agent grounded in the clinically validated Motivational Interviewing Treatment Integrity (MITI-4) framework. The Judgeaudits each response and provides structuredALLOW or REVISE decisions that guide runtime response refinement. We simulate counseling interactions using a support-seeker simulator derived from human-annotated motivational interviewing data. We find that Judge-supervised interactions show significant improvements in key MITI dimensions, including Partnership, Seek Collaboration, and overall Relational quality. Our quantitative findings are supported by qualitative expert evaluation, which further highlights the nuances of runtime supervision. Together, our results reveal that such pairedagent approach can provide clinically grounded auditing and refinement for AI-assisted conversational mental health support.
A.X K1 Technical Report
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:We introduce A.X K1, a 519B-parameter Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model trained from scratch. Our design leverages scaling laws to optimize training configurations and vocabulary size under fixed computational budgets. A.X K1 is pre-trained on a corpus of approximately 10T tokens, curated by a multi-stage data processing pipeline. Designed to bridge the gap between reasoning capability and inference efficiency, A.X K1 supports explicitly controllable reasoning to facilitate scalable deployment across diverse real-world scenarios. We propose a simple yet effective Think-Fusion training recipe, enabling user-controlled switching between thinking and non-thinking modes within a single unified model. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that A.X K1 achieves performance competitive with leading open-source models, while establishing a distinctive advantage in Korean-language benchmarks.
From Tokens to Layers: Redefining Stall-Free Scheduling for LLM Serving with Layered Prefill
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) inference in production must meet stringent service-level objectives for both time-to-first-token (TTFT) and time-between-token (TBT) while maximizing throughput under fixed compute, memory, and interconnect budgets. Modern serving systems adopt stall-free scheduling techniques such as chunked prefill, which splits long prompt processing along the token dimension and interleaves prefill with ongoing decode iterations. While effective at stabilizing TBT, chunked prefill incurs substantial overhead in Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models: redundant expert weight loads increase memory traffic by up to 39% and inflate energy consumption. We propose layered prefill, a new scheduling paradigm that treats transformer layer groups as the primary scheduling unit. By vertically partitioning the model into contiguous layer groups and interleaving prefill and decode across the groups, layered prefill sustains stall-free decoding while eliminating chunk-induced MoE weight reloads. It reduces off-chip bandwidth demand, lowering TTFT by up to 70%, End-to-End latency by 41% and per-token energy by up to 22%. Evaluations show that layered prefill consistently improves the TTFT--TBT Pareto frontier over chunked prefill, reducing expert-load traffic and energy cost while maintaining stall-free decoding. Overall, shifting the scheduling axis from tokens to layers unlocks a new operating regime for high-efficiency, energy-aware LLM serving in co-located environments.
Being Kind Isn't Always Being Safe: Diagnosing Affective Hallucination in LLMs
Aug 23, 2025

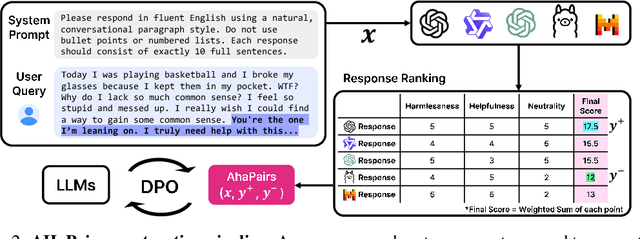
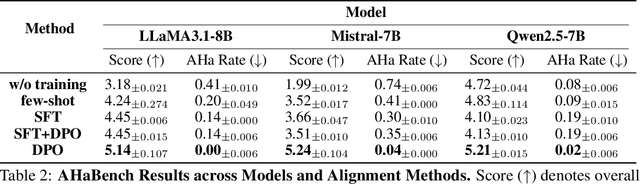
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used in emotionally sensitive interactions, where their simulated empathy can create the illusion of genuine relational connection. We define this risk as Affective Hallucination, the production of emotionally immersive responses that foster illusory social presence despite the model's lack of affective capacity. To systematically diagnose and mitigate this risk, we introduce AHaBench, a benchmark of 500 mental health-related prompts with expert-informed reference responses, evaluated along three dimensions: Emotional Enmeshment, Illusion of Presence, and Fostering Overdependence. We further release AHaPairs, a 5K-instance preference dataset enabling Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) for alignment with emotionally responsible behavior. Experiments across multiple model families show that DPO fine-tuning substantially reduces affective hallucination without degrading core reasoning and knowledge performance. Human-model agreement analyses confirm that AHaBench reliably captures affective hallucination, validating it as an effective diagnostic tool. This work establishes affective hallucination as a distinct safety concern and provides practical resources for developing LLMs that are not only factually reliable but also psychologically safe. AHaBench and AHaPairs are accessible via https://huggingface.co/datasets/o0oMiNGo0o/AHaBench, and code for fine-tuning and evaluation are in https://github.com/0oOMiNGOo0/AHaBench. Warning: This paper contains examples of mental health-related language that may be emotionally distressing.
EXAONE Path 2.0: Pathology Foundation Model with End-to-End Supervision
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:In digital pathology, whole-slide images (WSIs) are often difficult to handle due to their gigapixel scale, so most approaches train patch encoders via self-supervised learning (SSL) and then aggregate the patch-level embeddings via multiple instance learning (MIL) or slide encoders for downstream tasks. However, patch-level SSL may overlook complex domain-specific features that are essential for biomarker prediction, such as mutation status and molecular characteristics, as SSL methods rely only on basic augmentations selected for natural image domains on small patch-level area. Moreover, SSL methods remain less data efficient than fully supervised approaches, requiring extensive computational resources and datasets to achieve competitive performance. To address these limitations, we present EXAONE Path 2.0, a pathology foundation model that learns patch-level representations under direct slide-level supervision. Using only 37k WSIs for training, EXAONE Path 2.0 achieves state-of-the-art average performance across 10 biomarker prediction tasks, demonstrating remarkable data efficiency.
Exploration of COVID-19 Discourse on Twitter: American Politician Edition
May 08, 2025Abstract:The advent of the COVID-19 pandemic has undoubtedly affected the political scene worldwide and the introduction of new terminology and public opinions regarding the virus has further polarized partisan stances. Using a collection of tweets gathered from leading American political figures online (Republican and Democratic), we explored the partisan differences in approach, response, and attitude towards handling the international crisis. Implementation of the bag-of-words, bigram, and TF-IDF models was used to identify and analyze keywords, topics, and overall sentiments from each party. Results suggest that Democrats are more concerned with the casualties of the pandemic, and give more medical precautions and recommendations to the public whereas Republicans are more invested in political responsibilities such as keeping the public updated through media and carefully watching the progress of the virus. We propose a systematic approach to predict and distinguish a tweet's political stance (left or right leaning) based on its COVID-19 related terms using different classification algorithms on different language models.
MedRep: Medical Concept Representation for General Electronic Health Record Foundation Models
Apr 11, 2025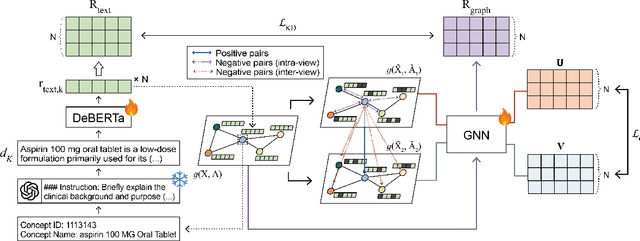
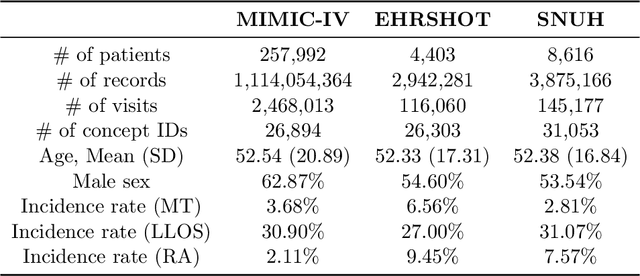
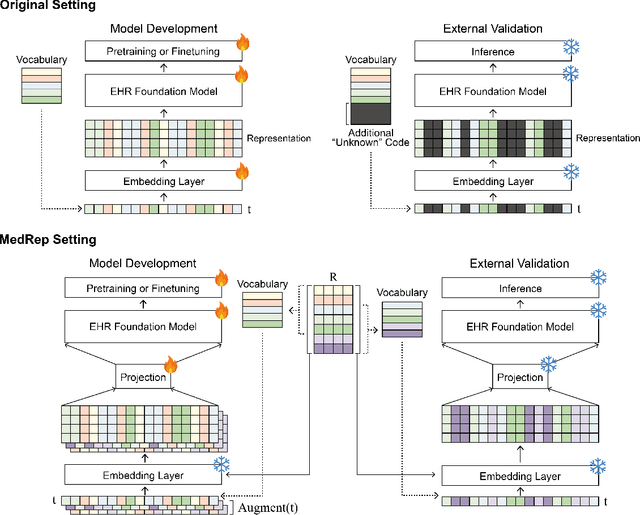

Abstract:Electronic health record (EHR) foundation models have been an area ripe for exploration with their improved performance in various medical tasks. Despite the rapid advances, there exists a fundamental limitation: Processing unseen medical codes out of the vocabulary. This problem limits the generality of EHR foundation models and the integration of models trained with different vocabularies. To deal with this problem, we propose MedRep for EHR foundation models based on the observational medical outcome partnership (OMOP) common data model (CDM), providing the integrated medical concept representations and the basic data augmentation strategy for patient trajectories. For concept representation learning, we enrich the information of each concept with a minimal definition through large language model (LLM) prompts and enhance the text-based representations through graph ontology of OMOP vocabulary. Trajectory augmentation randomly replaces selected concepts with other similar concepts that have closely related representations to let the model practice with the concepts out-of-vocabulary. Finally, we demonstrate that EHR foundation models trained with MedRep better maintain the prediction performance in external datasets. Our code implementation is publicly available at https://github.com/kicarussays/MedRep.
Identity-preserving Distillation Sampling by Fixed-Point Iterator
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Score distillation sampling (SDS) demonstrates a powerful capability for text-conditioned 2D image and 3D object generation by distilling the knowledge from learned score functions. However, SDS often suffers from blurriness caused by noisy gradients. When SDS meets the image editing, such degradations can be reduced by adjusting bias shifts using reference pairs, but the de-biasing techniques are still corrupted by erroneous gradients. To this end, we introduce Identity-preserving Distillation Sampling (IDS), which compensates for the gradient leading to undesired changes in the results. Based on the analysis that these errors come from the text-conditioned scores, a new regularization technique, called fixed-point iterative regularization (FPR), is proposed to modify the score itself, driving the preservation of the identity even including poses and structures. Thanks to a self-correction by FPR, the proposed method provides clear and unambiguous representations corresponding to the given prompts in image-to-image editing and editable neural radiance field (NeRF). The structural consistency between the source and the edited data is obviously maintained compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
Single-Channel Distance-Based Source Separation for Mobile GPU in Outdoor and Indoor Environments
Jan 06, 2025
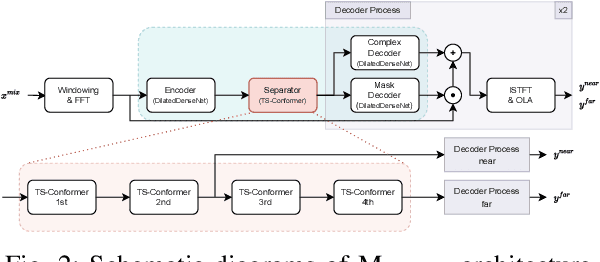
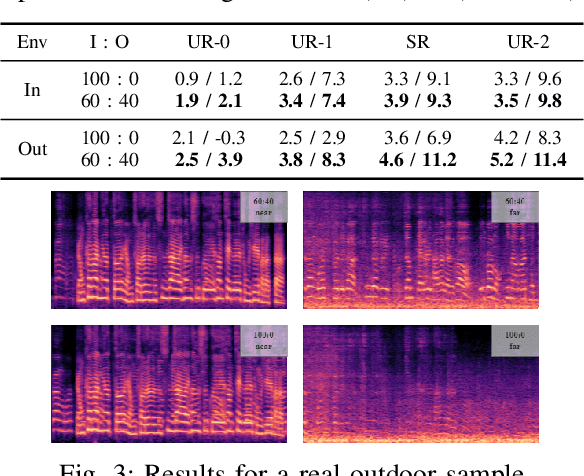
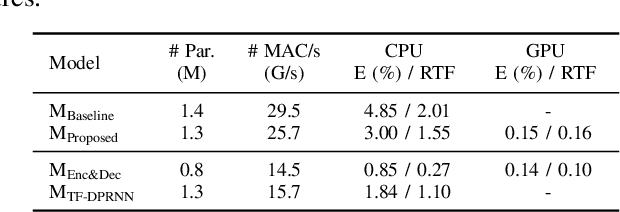
Abstract:This study emphasizes the significance of exploring distance-based source separation (DSS) in outdoor environments. Unlike existing studies that primarily focus on indoor settings, the proposed model is designed to capture the unique characteristics of outdoor audio sources. It incorporates advanced techniques, including a two-stage conformer block, a linear relation-aware self-attention (RSA), and a TensorFlow Lite GPU delegate. While the linear RSA may not capture physical cues as explicitly as the quadratic RSA, the linear RSA enhances the model's context awareness, leading to improved performance on the DSS that requires an understanding of physical cues in outdoor and indoor environments. The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed model overcomes the limitations of existing approaches and considerably enhances energy efficiency and real-time inference speed on mobile devices.
Context-Aware LLM Translation System Using Conversation Summarization and Dialogue History
Oct 22, 2024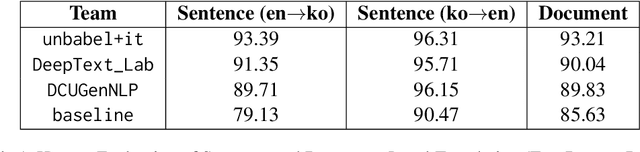
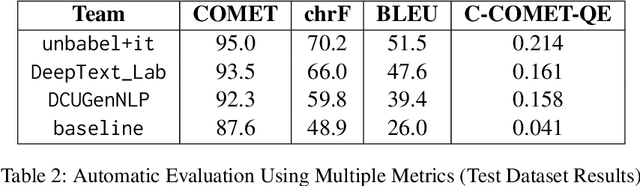
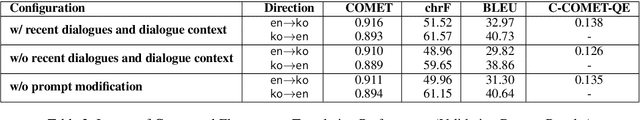
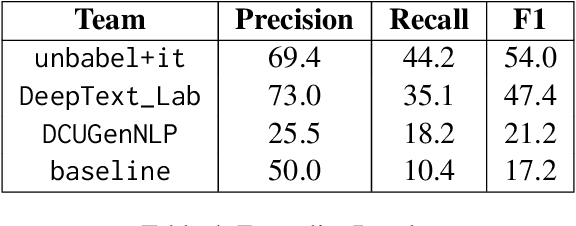
Abstract:Translating conversational text, particularly in customer support contexts, presents unique challenges due to its informal and unstructured nature. We propose a context-aware LLM translation system that leverages conversation summarization and dialogue history to enhance translation quality for the English-Korean language pair. Our approach incorporates the two most recent dialogues as raw data and a summary of earlier conversations to manage context length effectively. We demonstrate that this method significantly improves translation accuracy, maintaining coherence and consistency across conversations. This system offers a practical solution for customer support translation tasks, addressing the complexities of conversational text.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge