Hoon-Young Cho
Triage knowledge distillation for speaker verification
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Deploying speaker verification on resource-constrained devices remains challenging due to the computational cost of high-capacity models; knowledge distillation (KD) offers a remedy. Classical KD entangles target confidence with non-target structure in a Kullback-Leibler term, limiting the transfer of relational information. Decoupled KD separates these signals into target and non-target terms, yet treats non-targets uniformly and remains vulnerable to the long tail of low-probability classes in large-class settings. We introduce Triage KD (TRKD), a distillation scheme that operationalizes assess-prioritize-focus. TRKD introduces a cumulative-probability cutoff $τ$ to assess per-example difficulty and partition the teacher posterior into three groups: the target class, a high-probability non-target confusion-set, and a background-set. To prioritize informative signals, TRKD distills the confusion-set conditional distribution and discards the background. Concurrently, it transfers a three-mass (target/confusion/background) that capture sample difficulty and inter-class confusion. Finally, TRKD focuses learning via a curriculum on $τ$: training begins with a larger $τ$ to convey broad non-target context, then $τ$ is progressively decreased to shrink the confusion-set, concentrating supervision on the most confusable classes. In extensive experiments on VoxCeleb1 with both homogeneous and heterogeneous teacher-student pairs, TRKD was consistently superior to recent KD variants and attained the lowest EER across all protocols.
MATE: Matryoshka Audio-Text Embeddings for Open-Vocabulary Keyword Spotting
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Open-vocabulary keyword spotting (KWS) with text-based enrollment has emerged as a flexible alternative to fixed-phrase triggers. Prior utterance-level matching methods, from an embedding-learning standpoint, learn embeddings at a single fixed dimensionality. We depart from this design and propose Matryoshka Audio-Text Embeddings (MATE), a dual-encoder framework that encodes multiple embedding granularities within a single vector via nested sub-embeddings ("prefixes"). Specifically, we introduce a PCA-guided prefix alignment: PCA-compressed versions of the full text embedding for each prefix size serve as teacher targets to align both audio and text prefixes. This alignment concentrates salient keyword cues in lower-dimensional prefixes, while higher dimensions add detail. MATE is trained with standard deep metric learning objectives for audio-text KWS, and is loss-agnostic. To our knowledge, this is the first application of matryoshka-style embeddings to KWS, achieving state-of-the-art results on WSJ and LibriPhrase without any inference overhead.
DAME: Duration-Aware Matryoshka Embedding for Duration-Robust Speaker Verification
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Short-utterance speaker verification remains challenging due to limited speaker-discriminative cues in short speech segments. While existing methods focus on enhancing speaker encoders, the embedding learning strategy still forces a single fixed-dimensional representation reused for utterances of any length, leaving capacity misaligned with the information available at different durations. We propose Duration-Aware Matryoshka Embedding (DAME), a model-agnostic framework that builds a nested hierarchy of sub-embeddings aligned to utterance durations: lower-dimensional representations capture compact speaker traits from short utterances, while higher dimensions encode richer details from longer speech. DAME supports both training from scratch and fine-tuning, and serves as a direct alternative to conventional large-margin fine-tuning, consistently improving performance across durations. On the VoxCeleb1-O/E/H and VOiCES evaluation sets, DAME consistently reduces the equal error rate on 1-s and other short-duration trials, while maintaining full-length performance with no additional inference cost. These gains generalize across various speaker encoder architectures under both general training and fine-tuning setups.
Adversarial Deep Metric Learning for Cross-Modal Audio-Text Alignment in Open-Vocabulary Keyword Spotting
May 22, 2025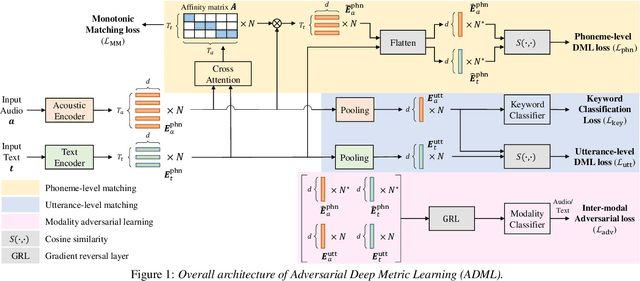



Abstract:For text enrollment-based open-vocabulary keyword spotting (KWS), acoustic and text embeddings are typically compared at either the phoneme or utterance level. To facilitate this, we optimize acoustic and text encoders using deep metric learning (DML), enabling direct comparison of multi-modal embeddings in a shared embedding space. However, the inherent heterogeneity between audio and text modalities presents a significant challenge. To address this, we propose Modality Adversarial Learning (MAL), which reduces the domain gap in heterogeneous modality representations. Specifically, we train a modality classifier adversarially to encourage both encoders to generate modality-invariant embeddings. Additionally, we apply DML to achieve phoneme-level alignment between audio and text, and conduct comprehensive comparisons across various DML objectives. Experiments on the Wall Street Journal (WSJ) and LibriPhrase datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Single-Channel Distance-Based Source Separation for Mobile GPU in Outdoor and Indoor Environments
Jan 06, 2025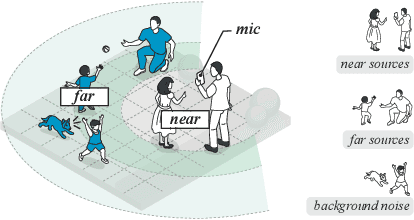
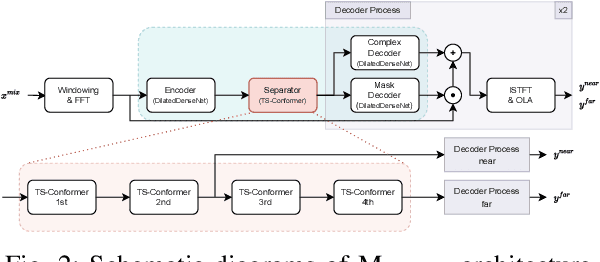
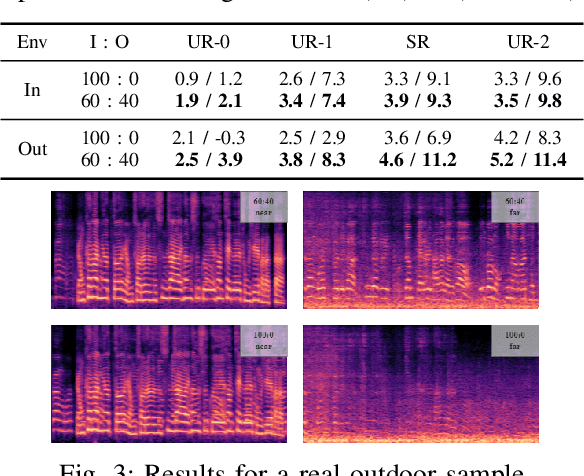
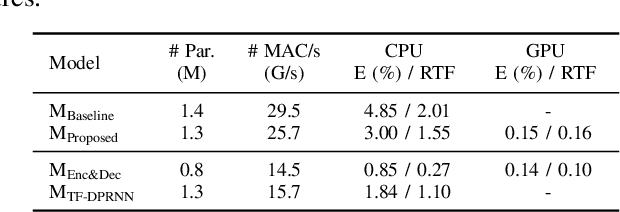
Abstract:This study emphasizes the significance of exploring distance-based source separation (DSS) in outdoor environments. Unlike existing studies that primarily focus on indoor settings, the proposed model is designed to capture the unique characteristics of outdoor audio sources. It incorporates advanced techniques, including a two-stage conformer block, a linear relation-aware self-attention (RSA), and a TensorFlow Lite GPU delegate. While the linear RSA may not capture physical cues as explicitly as the quadratic RSA, the linear RSA enhances the model's context awareness, leading to improved performance on the DSS that requires an understanding of physical cues in outdoor and indoor environments. The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed model overcomes the limitations of existing approaches and considerably enhances energy efficiency and real-time inference speed on mobile devices.
Text-Aware Adapter for Few-Shot Keyword Spotting
Dec 24, 2024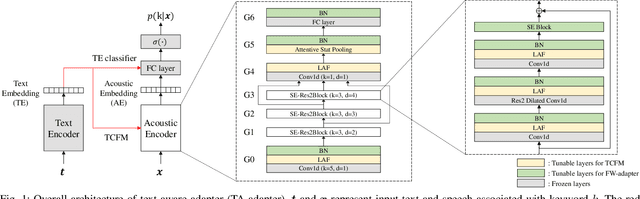
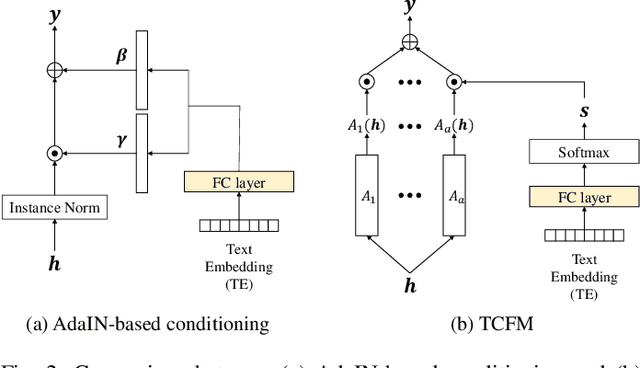
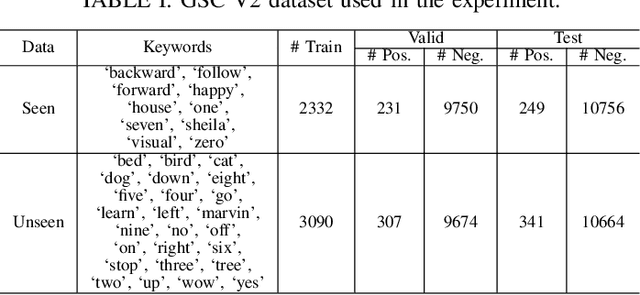
Abstract:Recent advances in flexible keyword spotting (KWS) with text enrollment allow users to personalize keywords without uttering them during enrollment. However, there is still room for improvement in target keyword performance. In this work, we propose a novel few-shot transfer learning method, called text-aware adapter (TA-adapter), designed to enhance a pre-trained flexible KWS model for specific keywords with limited speech samples. To adapt the acoustic encoder, we leverage a jointly pre-trained text encoder to generate a text embedding that acts as a representative vector for the keyword. By fine-tuning only a small portion of the network while keeping the core components' weights intact, the TA-adapter proves highly efficient for few-shot KWS, enabling a seamless return to the original pre-trained model. In our experiments, the TA-adapter demonstrated significant performance improvements across 35 distinct keywords from the Google Speech Commands V2 dataset, with only a 0.14% increase in the total number of parameters.
FINALLY: fast and universal speech enhancement with studio-like quality
Oct 08, 2024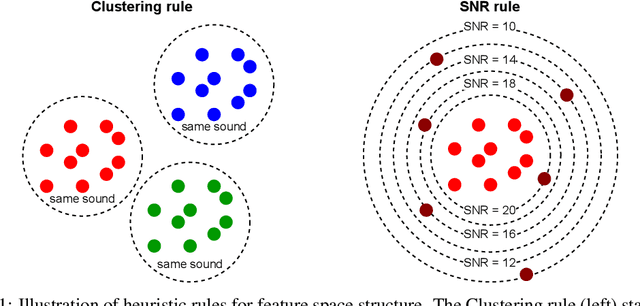
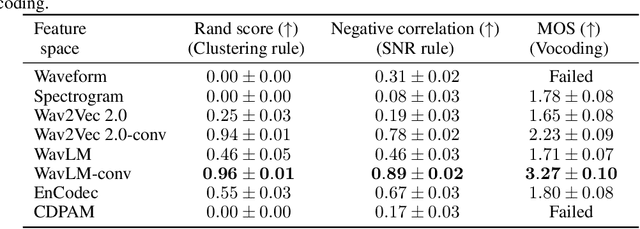
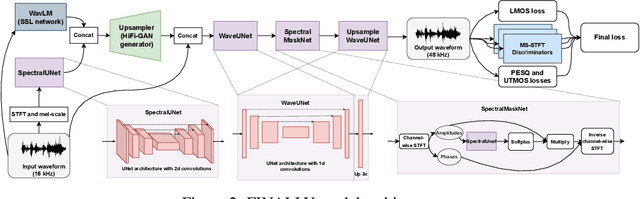
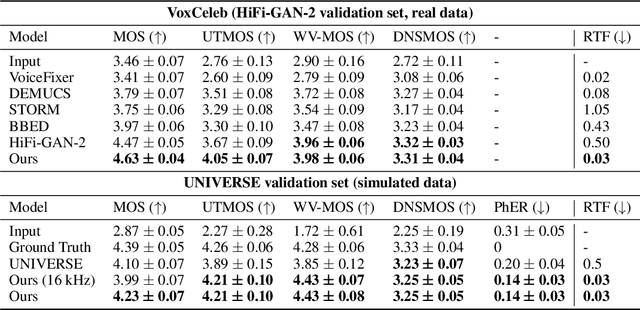
Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenge of speech enhancement in real-world recordings, which often contain various forms of distortion, such as background noise, reverberation, and microphone artifacts. We revisit the use of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for speech enhancement and theoretically show that GANs are naturally inclined to seek the point of maximum density within the conditional clean speech distribution, which, as we argue, is essential for the speech enhancement task. We study various feature extractors for perceptual loss to facilitate the stability of adversarial training, developing a methodology for probing the structure of the feature space. This leads us to integrate WavLM-based perceptual loss into MS-STFT adversarial training pipeline, creating an effective and stable training procedure for the speech enhancement model. The resulting speech enhancement model, which we refer to as FINALLY, builds upon the HiFi++ architecture, augmented with a WavLM encoder and a novel training pipeline. Empirical results on various datasets confirm our model's ability to produce clear, high-quality speech at 48 kHz, achieving state-of-the-art performance in the field of speech enhancement.
Speech Boosting: Low-Latency Live Speech Enhancement for TWS Earbuds
Sep 27, 2024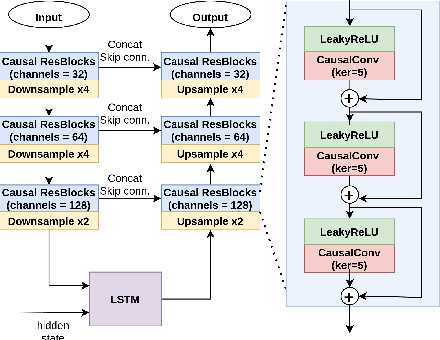


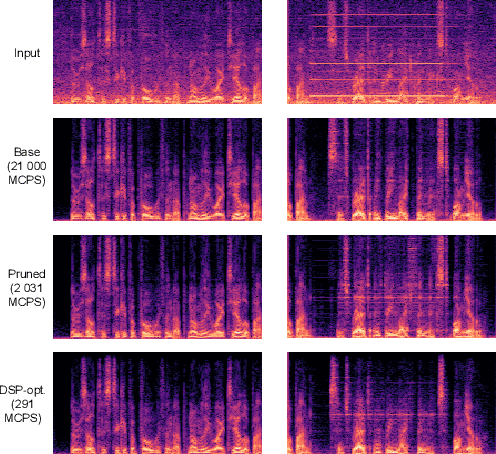
Abstract:This paper introduces a speech enhancement solution tailored for true wireless stereo (TWS) earbuds on-device usage. The solution was specifically designed to support conversations in noisy environments, with active noise cancellation (ANC) activated. The primary challenges for speech enhancement models in this context arise from computational complexity that limits on-device usage and latency that must be less than 3 ms to preserve a live conversation. To address these issues, we evaluated several crucial design elements, including the network architecture and domain, design of loss functions, pruning method, and hardware-specific optimization. Consequently, we demonstrated substantial improvements in speech enhancement quality compared with that in baseline models, while simultaneously reducing the computational complexity and algorithmic latency.
High Fidelity Text-to-Speech Via Discrete Tokens Using Token Transducer and Group Masked Language Model
Jun 25, 2024
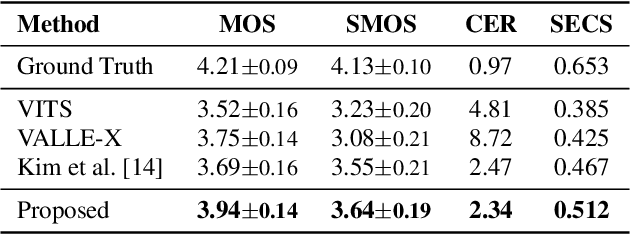
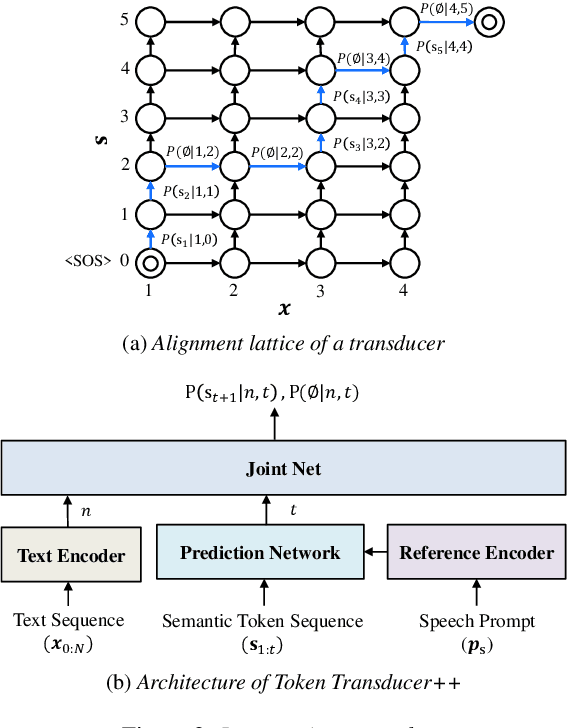
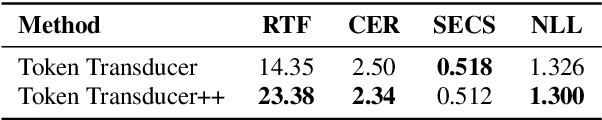
Abstract:We propose a novel two-stage text-to-speech (TTS) framework with two types of discrete tokens, i.e., semantic and acoustic tokens, for high-fidelity speech synthesis. It features two core components: the Interpreting module, which processes text and a speech prompt into semantic tokens focusing on linguistic contents and alignment, and the Speaking module, which captures the timbre of the target voice to generate acoustic tokens from semantic tokens, enriching speech reconstruction. The Interpreting stage employs a transducer for its robustness in aligning text to speech. In contrast, the Speaking stage utilizes a Conformer-based architecture integrated with a Grouped Masked Language Model (G-MLM) to boost computational efficiency. Our experiments verify that this innovative structure surpasses the conventional models in the zero-shot scenario in terms of speech quality and speaker similarity.
Relational Proxy Loss for Audio-Text based Keyword Spotting
Jun 08, 2024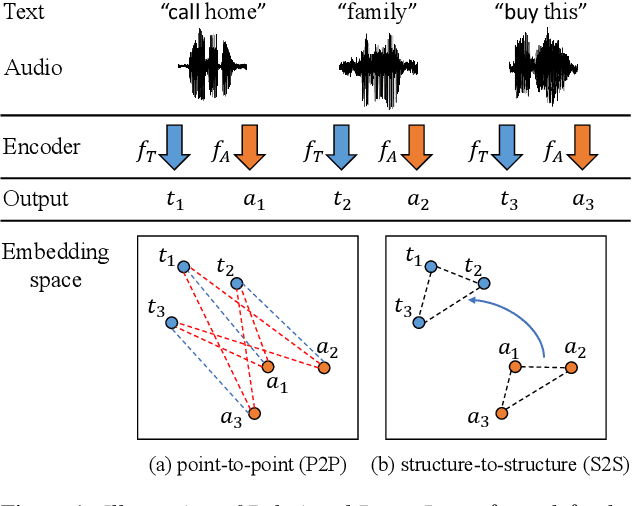
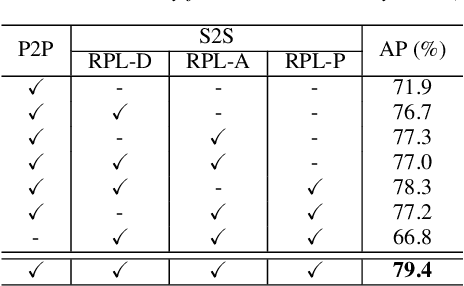
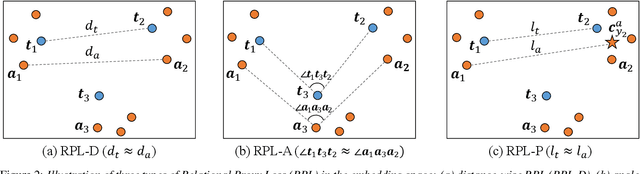

Abstract:In recent years, there has been an increasing focus on user convenience, leading to increased interest in text-based keyword enrollment systems for keyword spotting (KWS). Since the system utilizes text input during the enrollment phase and audio input during actual usage, we call this task audio-text based KWS. To enable this task, both acoustic and text encoders are typically trained using deep metric learning loss functions, such as triplet- and proxy-based losses. This study aims to improve existing methods by leveraging the structural relations within acoustic embeddings and within text embeddings. Unlike previous studies that only compare acoustic and text embeddings on a point-to-point basis, our approach focuses on the relational structures within the embedding space by introducing the concept of Relational Proxy Loss (RPL). By incorporating RPL, we demonstrated improved performance on the Wall Street Journal (WSJ) corpus.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge