Ivan Shchekotov
FINALLY: fast and universal speech enhancement with studio-like quality
Oct 08, 2024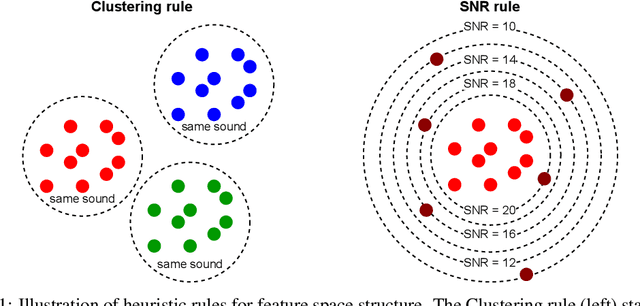
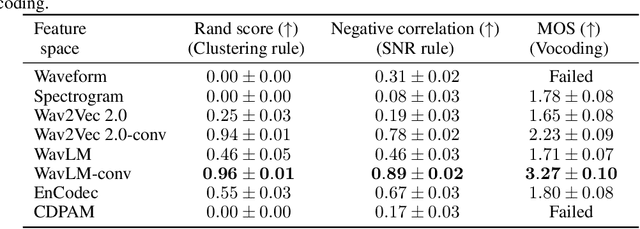
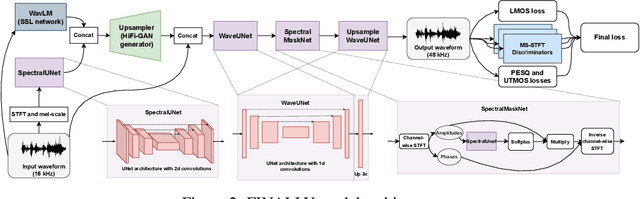
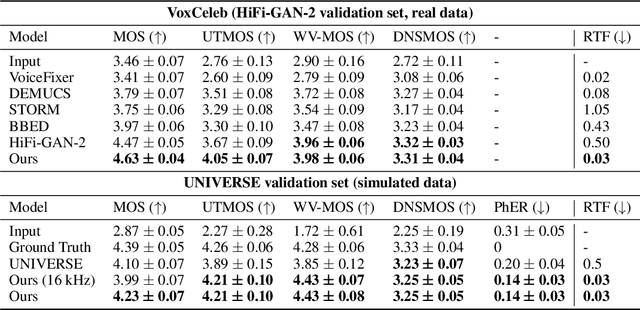
Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenge of speech enhancement in real-world recordings, which often contain various forms of distortion, such as background noise, reverberation, and microphone artifacts. We revisit the use of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for speech enhancement and theoretically show that GANs are naturally inclined to seek the point of maximum density within the conditional clean speech distribution, which, as we argue, is essential for the speech enhancement task. We study various feature extractors for perceptual loss to facilitate the stability of adversarial training, developing a methodology for probing the structure of the feature space. This leads us to integrate WavLM-based perceptual loss into MS-STFT adversarial training pipeline, creating an effective and stable training procedure for the speech enhancement model. The resulting speech enhancement model, which we refer to as FINALLY, builds upon the HiFi++ architecture, augmented with a WavLM encoder and a novel training pipeline. Empirical results on various datasets confirm our model's ability to produce clear, high-quality speech at 48 kHz, achieving state-of-the-art performance in the field of speech enhancement.
Regularized Distribution Matching Distillation for One-step Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation
Jun 20, 2024
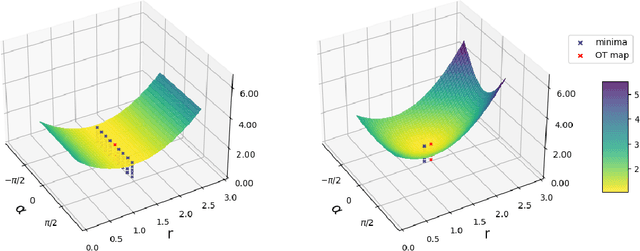
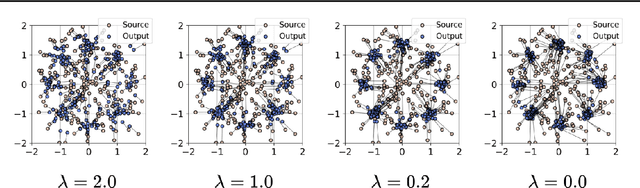
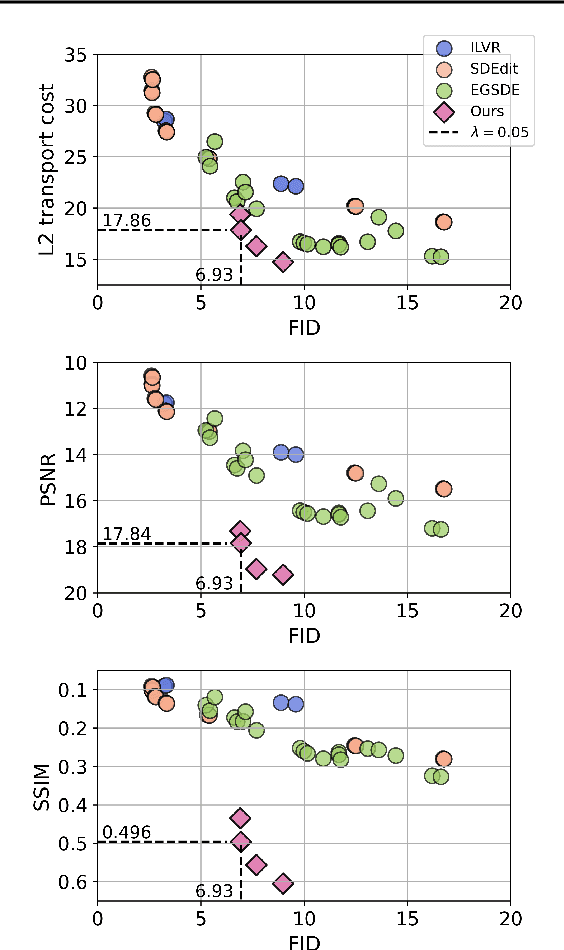
Abstract:Diffusion distillation methods aim to compress the diffusion models into efficient one-step generators while trying to preserve quality. Among them, Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD) offers a suitable framework for training general-form one-step generators, applicable beyond unconditional generation. In this work, we introduce its modification, called Regularized Distribution Matching Distillation, applicable to unpaired image-to-image (I2I) problems. We demonstrate its empirical performance in application to several translation tasks, including 2D examples and I2I between different image datasets, where it performs on par or better than multi-step diffusion baselines.
UnDiff: Unsupervised Voice Restoration with Unconditional Diffusion Model
Jun 01, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces UnDiff, a diffusion probabilistic model capable of solving various speech inverse tasks. Being once trained for speech waveform generation in an unconditional manner, it can be adapted to different tasks including degradation inversion, neural vocoding, and source separation. In this paper, we, first, tackle the challenging problem of unconditional waveform generation by comparing different neural architectures and preconditioning domains. After that, we demonstrate how the trained unconditional diffusion could be adapted to different tasks of speech processing by the means of recent developments in post-training conditioning of diffusion models. Finally, we demonstrate the performance of the proposed technique on the tasks of bandwidth extension, declipping, vocoding, and speech source separation and compare it to the baselines. The codes will be released soon.
Iterative autoregression: a novel trick to improve your low-latency speech enhancement model
Nov 03, 2022Abstract:Streaming models are an essential component of real-time speech enhancement tools. The streaming regime constrains speech enhancement models to use only a tiny context of future information, thus, the low-latency streaming setup is generally assumed to be challenging and has a significant negative effect on the model quality. However, due to the sequential nature of streaming generation, it provides a natural possibility for autoregression, i.e., using previous predictions when making current ones. In this paper, we present a simple, yet effective trick for training of autoregressive low-latency speech enhancement models. We demonstrate that the proposed technique leads to stable improvement across different architectures and training scenarios.
FFC-SE: Fast Fourier Convolution for Speech Enhancement
Apr 06, 2022
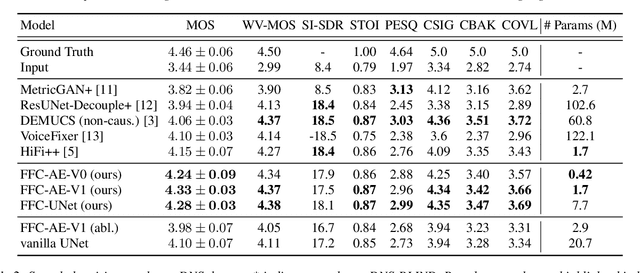
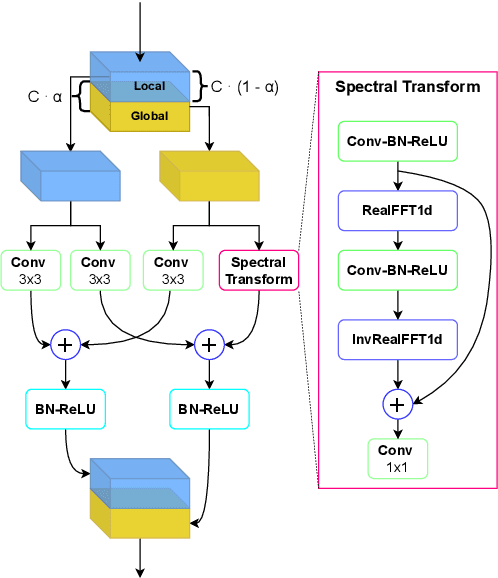
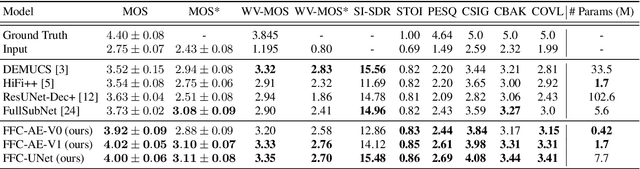
Abstract:Fast Fourier convolution (FFC) is the recently proposed neural operator showing promising performance in several computer vision problems. The FFC operator allows employing large receptive field operations within early layers of the neural network. It was shown to be especially helpful for inpainting of periodic structures which are common in audio processing. In this work, we design neural network architectures which adapt FFC for speech enhancement. We hypothesize that a large receptive field allows these networks to produce more coherent phases than vanilla convolutional models, and validate this hypothesis experimentally. We found that neural networks based on Fast Fourier convolution outperform analogous convolutional models and show better or comparable results with other speech enhancement baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge