Yong-Hyeok Lee
MATE: Matryoshka Audio-Text Embeddings for Open-Vocabulary Keyword Spotting
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Open-vocabulary keyword spotting (KWS) with text-based enrollment has emerged as a flexible alternative to fixed-phrase triggers. Prior utterance-level matching methods, from an embedding-learning standpoint, learn embeddings at a single fixed dimensionality. We depart from this design and propose Matryoshka Audio-Text Embeddings (MATE), a dual-encoder framework that encodes multiple embedding granularities within a single vector via nested sub-embeddings ("prefixes"). Specifically, we introduce a PCA-guided prefix alignment: PCA-compressed versions of the full text embedding for each prefix size serve as teacher targets to align both audio and text prefixes. This alignment concentrates salient keyword cues in lower-dimensional prefixes, while higher dimensions add detail. MATE is trained with standard deep metric learning objectives for audio-text KWS, and is loss-agnostic. To our knowledge, this is the first application of matryoshka-style embeddings to KWS, achieving state-of-the-art results on WSJ and LibriPhrase without any inference overhead.
Adversarial Deep Metric Learning for Cross-Modal Audio-Text Alignment in Open-Vocabulary Keyword Spotting
May 22, 2025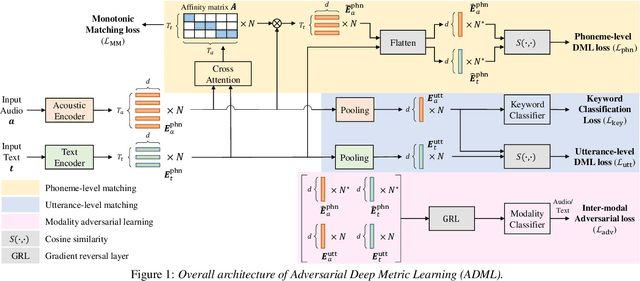



Abstract:For text enrollment-based open-vocabulary keyword spotting (KWS), acoustic and text embeddings are typically compared at either the phoneme or utterance level. To facilitate this, we optimize acoustic and text encoders using deep metric learning (DML), enabling direct comparison of multi-modal embeddings in a shared embedding space. However, the inherent heterogeneity between audio and text modalities presents a significant challenge. To address this, we propose Modality Adversarial Learning (MAL), which reduces the domain gap in heterogeneous modality representations. Specifically, we train a modality classifier adversarially to encourage both encoders to generate modality-invariant embeddings. Additionally, we apply DML to achieve phoneme-level alignment between audio and text, and conduct comprehensive comparisons across various DML objectives. Experiments on the Wall Street Journal (WSJ) and LibriPhrase datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Text-Aware Adapter for Few-Shot Keyword Spotting
Dec 24, 2024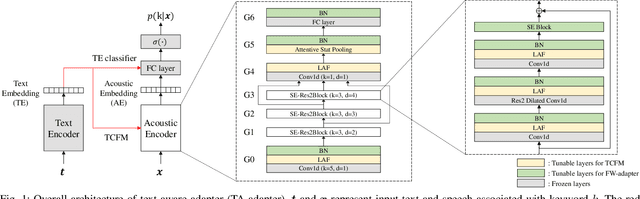
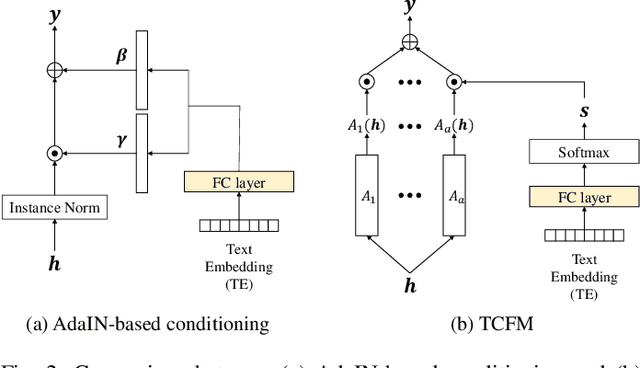
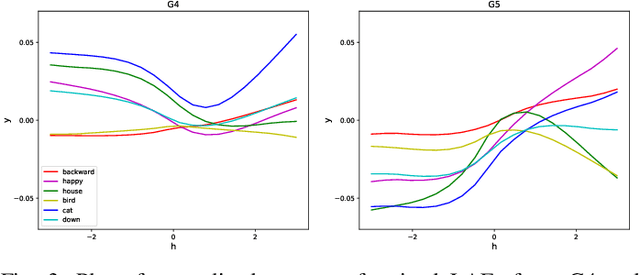
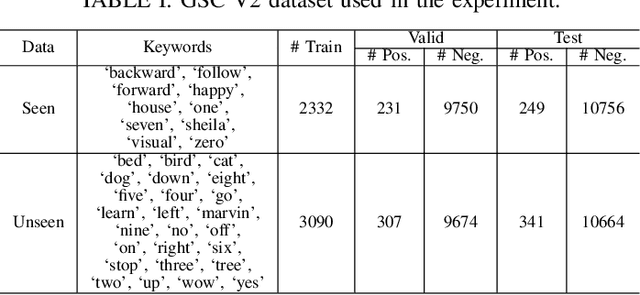
Abstract:Recent advances in flexible keyword spotting (KWS) with text enrollment allow users to personalize keywords without uttering them during enrollment. However, there is still room for improvement in target keyword performance. In this work, we propose a novel few-shot transfer learning method, called text-aware adapter (TA-adapter), designed to enhance a pre-trained flexible KWS model for specific keywords with limited speech samples. To adapt the acoustic encoder, we leverage a jointly pre-trained text encoder to generate a text embedding that acts as a representative vector for the keyword. By fine-tuning only a small portion of the network while keeping the core components' weights intact, the TA-adapter proves highly efficient for few-shot KWS, enabling a seamless return to the original pre-trained model. In our experiments, the TA-adapter demonstrated significant performance improvements across 35 distinct keywords from the Google Speech Commands V2 dataset, with only a 0.14% increase in the total number of parameters.
iPhonMatchNet: Zero-Shot User-Defined Keyword Spotting Using Implicit Acoustic Echo Cancellation
Sep 13, 2023

Abstract:In response to the increasing interest in human--machine communication across various domains, this paper introduces a novel approach called iPhonMatchNet, which addresses the challenge of barge-in scenarios, wherein user speech overlaps with device playback audio, thereby creating a self-referencing problem. The proposed model leverages implicit acoustic echo cancellation (iAEC) techniques to increase the efficiency of user-defined keyword spotting models, achieving a remarkable 95% reduction in mean absolute error with a minimal increase in model size (0.13%) compared to the baseline model, PhonMatchNet. We also present an efficient model structure and demonstrate its capability to learn iAEC functionality without requiring a clean signal. The findings of our study indicate that the proposed model achieves competitive performance in real-world deployment conditions of smart devices.
PhonMatchNet: Phoneme-Guided Zero-Shot Keyword Spotting for User-Defined Keywords
Aug 31, 2023



Abstract:This study presents a novel zero-shot user-defined keyword spotting model that utilizes the audio-phoneme relationship of the keyword to improve performance. Unlike the previous approach that estimates at utterance level, we use both utterance and phoneme level information. Our proposed method comprises a two-stream speech encoder architecture, self-attention-based pattern extractor, and phoneme-level detection loss for high performance in various pronunciation environments. Based on experimental results, our proposed model outperforms the baseline model and achieves competitive performance compared with full-shot keyword spotting models. Our proposed model significantly improves the EER and AUC across all datasets, including familiar words, proper nouns, and indistinguishable pronunciations, with an average relative improvement of 67% and 80%, respectively. The implementation code of our proposed model is available at https://github.com/ncsoft/PhonMatchNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge