JoungBin Lee
APPLE: Attribute-Preserving Pseudo-Labeling for Diffusion-Based Face Swapping
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Face swapping aims to transfer the identity of a source face onto a target face while preserving target-specific attributes such as pose, expression, lighting, skin tone, and makeup. However, since real ground truth for face swapping is unavailable, achieving both accurate identity transfer and high-quality attribute preservation remains challenging. In addition, recent diffusion-based approaches attempt to improve visual fidelity through conditional inpainting on masked target images, but the masked condition removes crucial appearance cues of target, resulting in plausible yet misaligned attributes. To address these limitations, we propose APPLE (Attribute-Preserving Pseudo-Labeling), a diffusion-based teacher-student framework that enhances attribute fidelity through attribute-aware pseudo-label supervision. We reformulate face swapping as a conditional deblurring task to more faithfully preserve target-specific attributes such as lighting, skin tone, and makeup. In addition, we introduce an attribute-aware inversion scheme to further improve detailed attribute preservation. Through an elaborate attribute-preserving design for teacher learning, APPLE produces high-quality pseudo triplets that explicitly provide the student with direct face-swapping supervision. Overall, APPLE achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of attribute preservation and identity transfer, producing more photorealistic and target-faithful results.
Pose-Diversified Augmentation with Diffusion Model for Person Re-Identification
Jun 23, 2024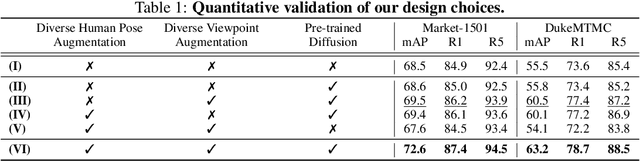
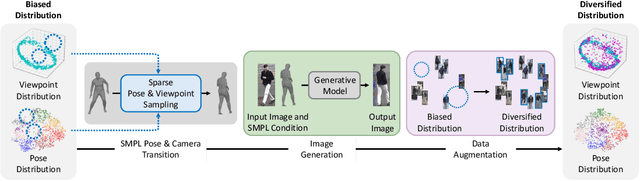
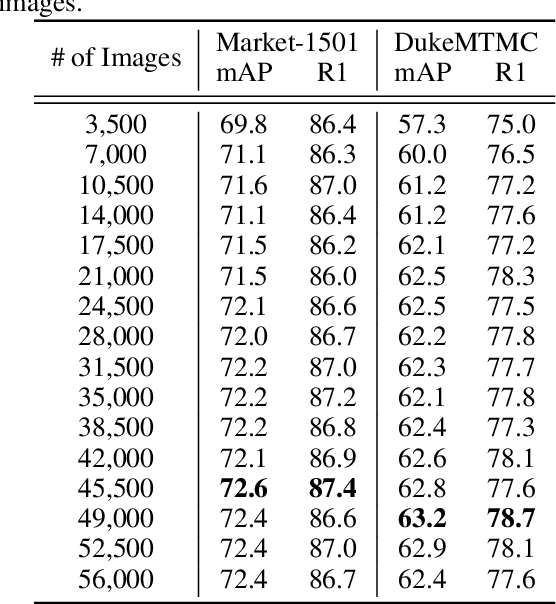
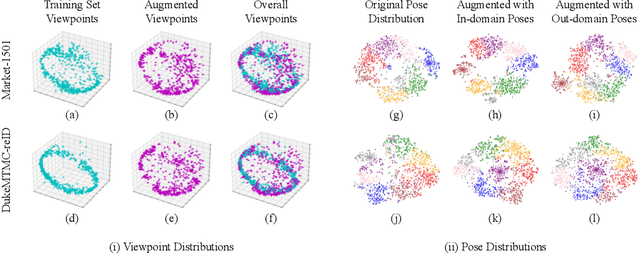
Abstract:Person re-identification (Re-ID) often faces challenges due to variations in human poses and camera viewpoints, which significantly affect the appearance of individuals across images. Existing datasets frequently lack diversity and scalability in these aspects, hindering the generalization of Re-ID models to new camera systems. Previous methods have attempted to address these issues through data augmentation; however, they rely on human poses already present in the training dataset, failing to effectively reduce the human pose bias in the dataset. We propose Diff-ID, a novel data augmentation approach that incorporates sparse and underrepresented human pose and camera viewpoint examples into the training data, addressing the limited diversity in the original training data distribution. Our objective is to augment a training dataset that enables existing Re-ID models to learn features unbiased by human pose and camera viewpoint variations. To achieve this, we leverage the knowledge of pre-trained large-scale diffusion models. Using the SMPL model, we simultaneously capture both the desired human poses and camera viewpoints, enabling realistic human rendering. The depth information provided by the SMPL model indirectly conveys the camera viewpoints. By conditioning the diffusion model on both the human pose and camera viewpoint concurrently through the SMPL model, we generate realistic images with diverse human poses and camera viewpoints. Qualitative results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in addressing human pose bias and enhancing the generalizability of Re-ID models compared to other data augmentation-based Re-ID approaches. The performance gains achieved by training Re-ID models on our offline augmented dataset highlight the potential of our proposed framework in improving the scalability and generalizability of person Re-ID models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge