Heeseong Shin
Visual Representation Alignment for Multimodal Large Language Models
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) trained with visual instruction tuning have achieved strong performance across diverse tasks, yet they remain limited in vision-centric tasks such as object counting or spatial reasoning. We attribute this gap to the prevailing text-only supervision paradigm, which provides only indirect guidance for the visual pathway and often leads MLLMs to discard fine-grained visual details during training. In this paper, we present VIsual Representation ALignment (VIRAL), a simple yet effective regularization strategy that aligns the internal visual representations of MLLMs with those of pre-trained vision foundation models (VFMs). By explicitly enforcing this alignment, VIRAL enables the model not only to retain critical visual details from the input vision encoder but also to complement additional visual knowledge from VFMs, thereby enhancing its ability to reason over complex visual inputs. Our experiments demonstrate consistent improvements across all tasks on widely adopted multimodal benchmarks. Furthermore, we conduct comprehensive ablation studies to validate the key design choices underlying our framework. We believe this simple finding opens up an important direction for the effective integration of visual information in training MLLMs.
S^4M: Boosting Semi-Supervised Instance Segmentation with SAM
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Semi-supervised instance segmentation poses challenges due to limited labeled data, causing difficulties in accurately localizing distinct object instances. Current teacher-student frameworks still suffer from performance constraints due to unreliable pseudo-label quality stemming from limited labeled data. While the Segment Anything Model (SAM) offers robust segmentation capabilities at various granularities, directly applying SAM to this task introduces challenges such as class-agnostic predictions and potential over-segmentation. To address these complexities, we carefully integrate SAM into the semi-supervised instance segmentation framework, developing a novel distillation method that effectively captures the precise localization capabilities of SAM without compromising semantic recognition. Furthermore, we incorporate pseudo-label refinement as well as a specialized data augmentation with the refined pseudo-labels, resulting in superior performance. We establish state-of-the-art performance, and provide comprehensive experiments and ablation studies to validate the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
PF3plat: Pose-Free Feed-Forward 3D Gaussian Splatting
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:We consider the problem of novel view synthesis from unposed images in a single feed-forward. Our framework capitalizes on fast speed, scalability, and high-quality 3D reconstruction and view synthesis capabilities of 3DGS, where we further extend it to offer a practical solution that relaxes common assumptions such as dense image views, accurate camera poses, and substantial image overlaps. We achieve this through identifying and addressing unique challenges arising from the use of pixel-aligned 3DGS: misaligned 3D Gaussians across different views induce noisy or sparse gradients that destabilize training and hinder convergence, especially when above assumptions are not met. To mitigate this, we employ pre-trained monocular depth estimation and visual correspondence models to achieve coarse alignments of 3D Gaussians. We then introduce lightweight, learnable modules to refine depth and pose estimates from the coarse alignments, improving the quality of 3D reconstruction and novel view synthesis. Furthermore, the refined estimates are leveraged to estimate geometry confidence scores, which assess the reliability of 3D Gaussian centers and condition the prediction of Gaussian parameters accordingly. Extensive evaluations on large-scale real-world datasets demonstrate that PF3plat sets a new state-of-the-art across all benchmarks, supported by comprehensive ablation studies validating our design choices.
Towards Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation Without Semantic Labels
Sep 30, 2024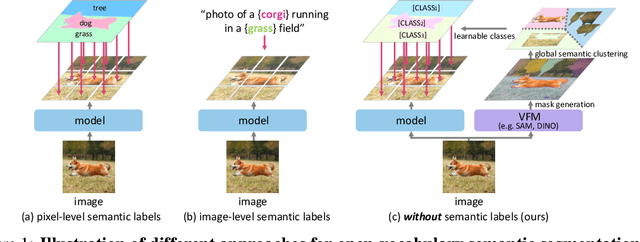
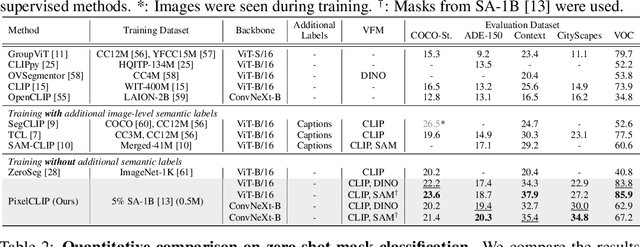

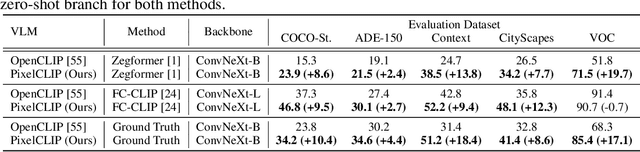
Abstract:Large-scale vision-language models like CLIP have demonstrated impressive open-vocabulary capabilities for image-level tasks, excelling in recognizing what objects are present. However, they struggle with pixel-level recognition tasks like semantic segmentation, which additionally require understanding where the objects are located. In this work, we propose a novel method, PixelCLIP, to adapt the CLIP image encoder for pixel-level understanding by guiding the model on where, which is achieved using unlabeled images and masks generated from vision foundation models such as SAM and DINO. To address the challenges of leveraging masks without semantic labels, we devise an online clustering algorithm using learnable class names to acquire general semantic concepts. PixelCLIP shows significant performance improvements over CLIP and competitive results compared to caption-supervised methods in open-vocabulary semantic segmentation. Project page is available at https://cvlab-kaist.github.io/PixelCLIP
Unifying Correspondence, Pose and NeRF for Pose-Free Novel View Synthesis from Stereo Pairs
Dec 12, 2023Abstract:This work delves into the task of pose-free novel view synthesis from stereo pairs, a challenging and pioneering task in 3D vision. Our innovative framework, unlike any before, seamlessly integrates 2D correspondence matching, camera pose estimation, and NeRF rendering, fostering a synergistic enhancement of these tasks. We achieve this through designing an architecture that utilizes a shared representation, which serves as a foundation for enhanced 3D geometry understanding. Capitalizing on the inherent interplay between the tasks, our unified framework is trained end-to-end with the proposed training strategy to improve overall model accuracy. Through extensive evaluations across diverse indoor and outdoor scenes from two real-world datasets, we demonstrate that our approach achieves substantial improvement over previous methodologies, especially in scenarios characterized by extreme viewpoint changes and the absence of accurate camera poses.
Large Language Models are Frame-level Directors for Zero-shot Text-to-Video Generation
May 23, 2023
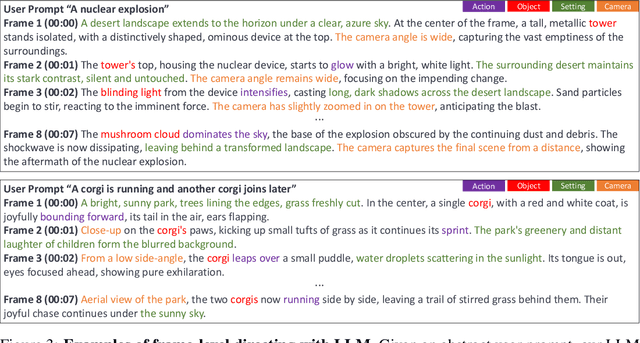
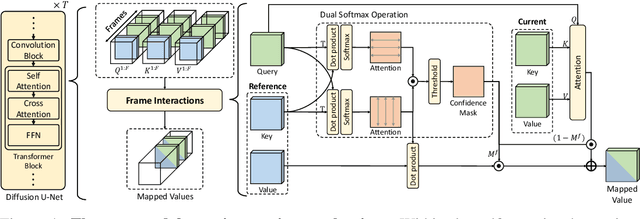
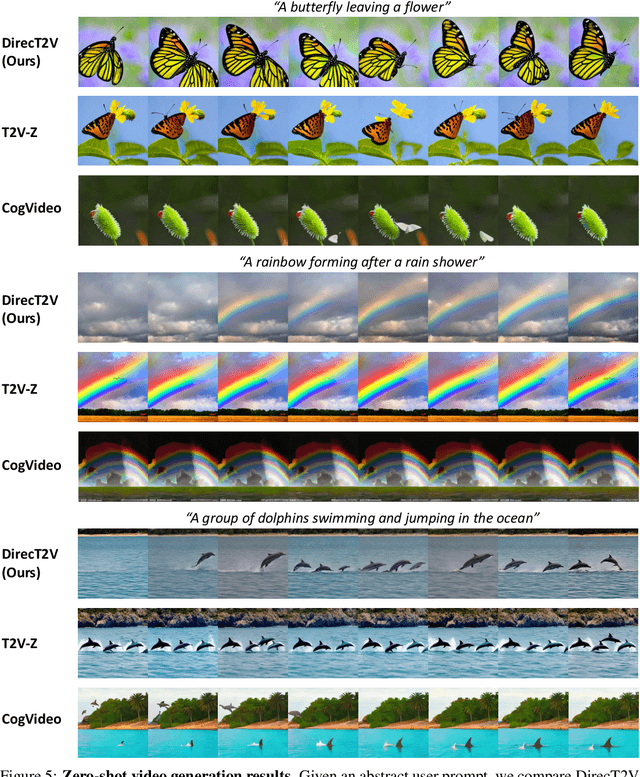
Abstract:In the paradigm of AI-generated content (AIGC), there has been increasing attention in extending pre-trained text-to-image (T2I) models to text-to-video (T2V) generation. Despite their effectiveness, these frameworks face challenges in maintaining consistent narratives and handling rapid shifts in scene composition or object placement from a single user prompt. This paper introduces a new framework, dubbed DirecT2V, which leverages instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs) to generate frame-by-frame descriptions from a single abstract user prompt. DirecT2V utilizes LLM directors to divide user inputs into separate prompts for each frame, enabling the inclusion of time-varying content and facilitating consistent video generation. To maintain temporal consistency and prevent object collapse, we propose a novel value mapping method and dual-softmax filtering. Extensive experimental results validate the effectiveness of the DirecT2V framework in producing visually coherent and consistent videos from abstract user prompts, addressing the challenges of zero-shot video generation.
CAT-Seg: Cost Aggregation for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Mar 21, 2023Abstract:Existing works on open-vocabulary semantic segmentation have utilized large-scale vision-language models, such as CLIP, to leverage their exceptional open-vocabulary recognition capabilities. However, the problem of transferring these capabilities learned from image-level supervision to the pixel-level task of segmentation and addressing arbitrary unseen categories at inference makes this task challenging. To address these issues, we aim to attentively relate objects within an image to given categories by leveraging relational information among class categories and visual semantics through aggregation, while also adapting the CLIP representations to the pixel-level task. However, we observe that direct optimization of the CLIP embeddings can harm its open-vocabulary capabilities. In this regard, we propose an alternative approach to optimize the image-text similarity map, i.e. the cost map, using a novel cost aggregation-based method. Our framework, namely CAT-Seg, achieves state-of-the-art performance across all benchmarks. We provide extensive ablation studies to validate our choices. Project page: https://ku-cvlab.github.io/CAT-Seg/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge