Chieh-Hsin Lai
GUDA: Counterfactual Group-wise Training Data Attribution for Diffusion Models via Unlearning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Training-data attribution for vision generative models aims to identify which training data influenced a given output. While most methods score individual examples, practitioners often need group-level answers (e.g., artistic styles or object classes). Group-wise attribution is counterfactual: how would a model's behavior on a generated sample change if a group were absent from training? A natural realization of this counterfactual is Leave-One-Group-Out (LOGO) retraining, which retrains the model with each group removed; however, it becomes computationally prohibitive as the number of groups grows. We propose GUDA (Group Unlearning-based Data Attribution) for diffusion models, which approximates each counterfactual model by applying machine unlearning to a shared full-data model instead of training from scratch. GUDA quantifies group influence using differences in a likelihood-based scoring rule (ELBO) between the full model and each unlearned counterfactual. Experiments on CIFAR-10 and artistic style attribution with Stable Diffusion show that GUDA identifies primary contributing groups more reliably than semantic similarity, gradient-based attribution, and instance-level unlearning approaches, while achieving x100 speedup on CIFAR-10 over LOGO retraining.
TINNs: Time-Induced Neural Networks for Solving Time-Dependent PDEs
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) solve time-dependent partial differential equations (PDEs) by learning a mesh-free, differentiable solution that can be evaluated anywhere in space and time. However, standard space--time PINNs take time as an input but reuse a single network with shared weights across all times, forcing the same features to represent markedly different dynamics. This coupling degrades accuracy and can destabilize training when enforcing PDE, boundary, and initial constraints jointly. We propose Time-Induced Neural Networks (TINNs), a novel architecture that parameterizes the network weights as a learned function of time, allowing the effective spatial representation to evolve over time while maintaining shared structure. The resulting formulation naturally yields a nonlinear least-squares problem, which we optimize efficiently using a Levenberg--Marquardt method. Experiments on various time-dependent PDEs show up to $4\times$ improved accuracy and $10\times$ faster convergence compared to PINNs and strong baselines.
Improved Object-Centric Diffusion Learning with Registers and Contrastive Alignment
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Slot Attention (SA) with pretrained diffusion models has recently shown promise for object-centric learning (OCL), but suffers from slot entanglement and weak alignment between object slots and image content. We propose Contrastive Object-centric Diffusion Alignment (CODA), a simple extension that (i) employs register slots to absorb residual attention and reduce interference between object slots, and (ii) applies a contrastive alignment loss to explicitly encourage slot-image correspondence. The resulting training objective serves as a tractable surrogate for maximizing mutual information (MI) between slots and inputs, strengthening slot representation quality. On both synthetic (MOVi-C/E) and real-world datasets (VOC, COCO), CODA improves object discovery (e.g., +6.1% FG-ARI on COCO), property prediction, and compositional image generation over strong baselines. Register slots add negligible overhead, keeping CODA efficient and scalable. These results indicate potential applications of CODA as an effective framework for robust OCL in complex, real-world scenes.
MeanFlow Transformers with Representation Autoencoders
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:MeanFlow (MF) is a diffusion-motivated generative model that enables efficient few-step generation by learning long jumps directly from noise to data. In practice, it is often used as a latent MF by leveraging the pre-trained Stable Diffusion variational autoencoder (SD-VAE) for high-dimensional data modeling. However, MF training remains computationally demanding and is often unstable. During inference, the SD-VAE decoder dominates the generation cost, and MF depends on complex guidance hyperparameters for class-conditional generation. In this work, we develop an efficient training and sampling scheme for MF in the latent space of a Representation Autoencoder (RAE), where a pre-trained vision encoder (e.g., DINO) provides semantically rich latents paired with a lightweight decoder. We observe that naive MF training in the RAE latent space suffers from severe gradient explosion. To stabilize and accelerate training, we adopt Consistency Mid-Training for trajectory-aware initialization and use a two-stage scheme: distillation from a pre-trained flow matching teacher to speed convergence and reduce variance, followed by an optional bootstrapping stage with a one-point velocity estimator to further reduce deviation from the oracle mean flow. This design removes the need for guidance, simplifies training configurations, and reduces computation in both training and sampling. Empirically, our method achieves a 1-step FID of 2.03, outperforming vanilla MF's 3.43, while reducing sampling GFLOPS by 38% and total training cost by 83% on ImageNet 256. We further scale our approach to ImageNet 512, achieving a competitive 1-step FID of 3.23 with the lowest GFLOPS among all baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/sony/mf-rae.
SONA: Learning Conditional, Unconditional, and Mismatching-Aware Discriminator
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Deep generative models have made significant advances in generating complex content, yet conditional generation remains a fundamental challenge. Existing conditional generative adversarial networks often struggle to balance the dual objectives of assessing authenticity and conditional alignment of input samples within their conditional discriminators. To address this, we propose a novel discriminator design that integrates three key capabilities: unconditional discrimination, matching-aware supervision to enhance alignment sensitivity, and adaptive weighting to dynamically balance all objectives. Specifically, we introduce Sum of Naturalness and Alignment (SONA), which employs separate projections for naturalness (authenticity) and alignment in the final layer with an inductive bias, supported by dedicated objective functions and an adaptive weighting mechanism. Extensive experiments on class-conditional generation tasks show that \ours achieves superior sample quality and conditional alignment compared to state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, we demonstrate its effectiveness in text-to-image generation, confirming the versatility and robustness of our approach.
Concept-TRAK: Understanding how diffusion models learn concepts through concept-level attribution
Jul 09, 2025



Abstract:While diffusion models excel at image generation, their growing adoption raises critical concerns around copyright issues and model transparency. Existing attribution methods identify training examples influencing an entire image, but fall short in isolating contributions to specific elements, such as styles or objects, that matter most to stakeholders. To bridge this gap, we introduce \emph{concept-level attribution} via a novel method called \emph{Concept-TRAK}. Concept-TRAK extends influence functions with two key innovations: (1) a reformulated diffusion training loss based on diffusion posterior sampling, enabling robust, sample-specific attribution; and (2) a concept-aware reward function that emphasizes semantic relevance. We evaluate Concept-TRAK on the AbC benchmark, showing substantial improvements over prior methods. Through diverse case studies--ranging from identifying IP-protected and unsafe content to analyzing prompt engineering and compositional learning--we demonstrate how concept-level attribution yields actionable insights for responsible generative AI development and governance.
Denoising Multi-Beta VAE: Representation Learning for Disentanglement and Generation
Jul 09, 2025



Abstract:Disentangled and interpretable latent representations in generative models typically come at the cost of generation quality. The $\beta$-VAE framework introduces a hyperparameter $\beta$ to balance disentanglement and reconstruction quality, where setting $\beta > 1$ introduces an information bottleneck that favors disentanglement over sharp, accurate reconstructions. To address this trade-off, we propose a novel generative modeling framework that leverages a range of $\beta$ values to learn multiple corresponding latent representations. First, we obtain a slew of representations by training a single variational autoencoder (VAE), with a new loss function that controls the information retained in each latent representation such that the higher $\beta$ value prioritize disentanglement over reconstruction fidelity. We then, introduce a non-linear diffusion model that smoothly transitions latent representations corresponding to different $\beta$ values. This model denoises towards less disentangled and more informative representations, ultimately leading to (almost) lossless representations, enabling sharp reconstructions. Furthermore, our model supports sample generation without input images, functioning as a standalone generative model. We evaluate our framework in terms of both disentanglement and generation quality. Additionally, we observe smooth transitions in the latent spaces with respect to changes in $\beta$, facilitating consistent manipulation of generated outputs.
SteerMusic: Enhanced Musical Consistency for Zero-shot Text-Guided and Personalized Music Editing
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Music editing is an important step in music production, which has broad applications, including game development and film production. Most existing zero-shot text-guided methods rely on pretrained diffusion models by involving forward-backward diffusion processes for editing. However, these methods often struggle to maintain the music content consistency. Additionally, text instructions alone usually fail to accurately describe the desired music. In this paper, we propose two music editing methods that enhance the consistency between the original and edited music by leveraging score distillation. The first method, SteerMusic, is a coarse-grained zero-shot editing approach using delta denoising score. The second method, SteerMusic+, enables fine-grained personalized music editing by manipulating a concept token that represents a user-defined musical style. SteerMusic+ allows for the editing of music into any user-defined musical styles that cannot be achieved by the text instructions alone. Experimental results show that our methods outperform existing approaches in preserving both music content consistency and editing fidelity. User studies further validate that our methods achieve superior music editing quality. Audio examples are available on https://steermusic.pages.dev/.
Training Consistency Models with Variational Noise Coupling
Feb 25, 2025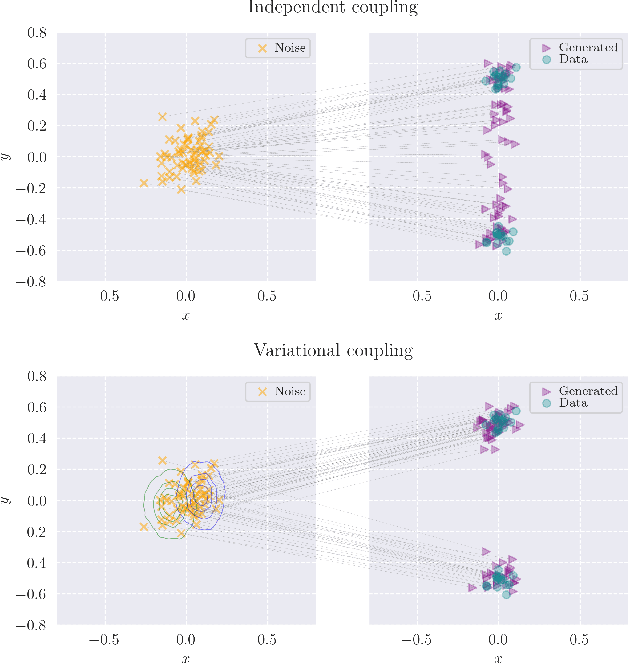
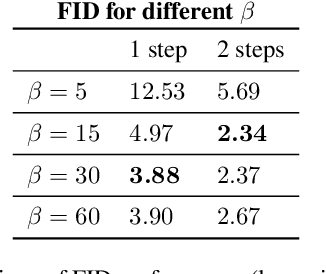

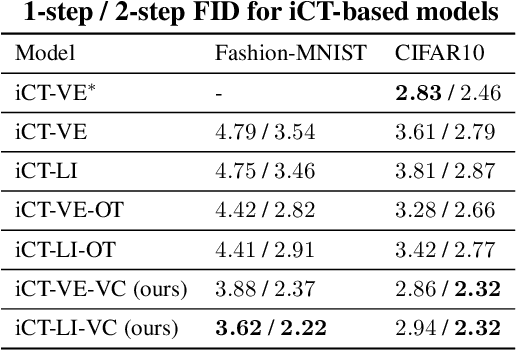
Abstract:Consistency Training (CT) has recently emerged as a promising alternative to diffusion models, achieving competitive performance in image generation tasks. However, non-distillation consistency training often suffers from high variance and instability, and analyzing and improving its training dynamics is an active area of research. In this work, we propose a novel CT training approach based on the Flow Matching framework. Our main contribution is a trained noise-coupling scheme inspired by the architecture of Variational Autoencoders (VAE). By training a data-dependent noise emission model implemented as an encoder architecture, our method can indirectly learn the geometry of the noise-to-data mapping, which is instead fixed by the choice of the forward process in classical CT. Empirical results across diverse image datasets show significant generative improvements, with our model outperforming baselines and achieving the state-of-the-art (SoTA) non-distillation CT FID on CIFAR-10, and attaining FID on par with SoTA on ImageNet at $64 \times 64$ resolution in 2-step generation. Our code is available at https://github.com/sony/vct .
Consistency Training with Physical Constraints
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:We propose a physics-aware Consistency Training (CT) method that accelerates sampling in Diffusion Models with physical constraints. Our approach leverages a two-stage strategy: (1) learning the noise-to-data mapping via CT, and (2) incorporating physics constraints as a regularizer. Experiments on toy examples show that our method generates samples in a single step while adhering to the imposed constraints. This approach has the potential to efficiently solve partial differential equations (PDEs) using deep generative modeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge