Giorgio Fabbro
Reverse Engineering of Music Mixing Graphs with Differentiable Processors and Iterative Pruning
Sep 19, 2025



Abstract:Reverse engineering of music mixes aims to uncover how dry source signals are processed and combined to produce a final mix. We extend the prior works to reflect the compositional nature of mixing and search for a graph of audio processors. First, we construct a mixing console, applying all available processors to every track and subgroup. With differentiable processor implementations, we optimize their parameters with gradient descent. Then, we repeat the process of removing negligible processors and fine-tuning the remaining ones. This way, the quality of the full mixing console can be preserved while removing approximately two-thirds of the processors. The proposed method can be used not only to analyze individual music mixes but also to collect large-scale graph data that can be used for downstream tasks, e.g., automatic mixing. Especially for the latter purpose, efficient implementation of the search is crucial. To this end, we present an efficient batch-processing method that computes multiple processors in parallel. We also exploit the "dry/wet" parameter of the processors to accelerate the search. Extensive quantitative and qualitative analyses are conducted to evaluate the proposed method's performance, behavior, and computational cost.
SteerMusic: Enhanced Musical Consistency for Zero-shot Text-Guided and Personalized Music Editing
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Music editing is an important step in music production, which has broad applications, including game development and film production. Most existing zero-shot text-guided methods rely on pretrained diffusion models by involving forward-backward diffusion processes for editing. However, these methods often struggle to maintain the music content consistency. Additionally, text instructions alone usually fail to accurately describe the desired music. In this paper, we propose two music editing methods that enhance the consistency between the original and edited music by leveraging score distillation. The first method, SteerMusic, is a coarse-grained zero-shot editing approach using delta denoising score. The second method, SteerMusic+, enables fine-grained personalized music editing by manipulating a concept token that represents a user-defined musical style. SteerMusic+ allows for the editing of music into any user-defined musical styles that cannot be achieved by the text instructions alone. Experimental results show that our methods outperform existing approaches in preserving both music content consistency and editing fidelity. User studies further validate that our methods achieve superior music editing quality. Audio examples are available on https://steermusic.pages.dev/.
Music Foundation Model as Generic Booster for Music Downstream Tasks
Nov 05, 2024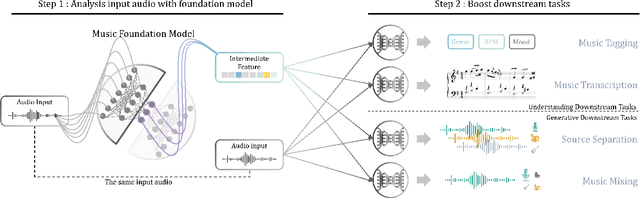

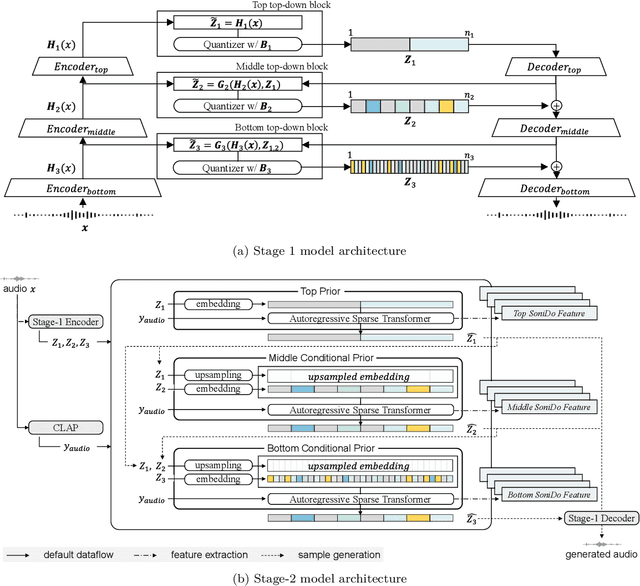

Abstract:We demonstrate the efficacy of using intermediate representations from a single foundation model to enhance various music downstream tasks. We introduce SoniDo, a music foundation model (MFM) designed to extract hierarchical features from target music samples. By leveraging hierarchical intermediate features, SoniDo constrains the information granularity, leading to improved performance across various downstream tasks including both understanding and generative tasks. We specifically evaluated this approach on representative tasks such as music tagging, music transcription, music source separation, and music mixing. Our results reveal that the features extracted from foundation models provide valuable enhancements in training downstream task models. This highlights the capability of using features extracted from music foundation models as a booster for downstream tasks. Our approach not only benefits existing task-specific models but also supports music downstream tasks constrained by data scarcity. This paves the way for more effective and accessible music processing solutions.
High-Resolution Speech Restoration with Latent Diffusion Model
Sep 17, 2024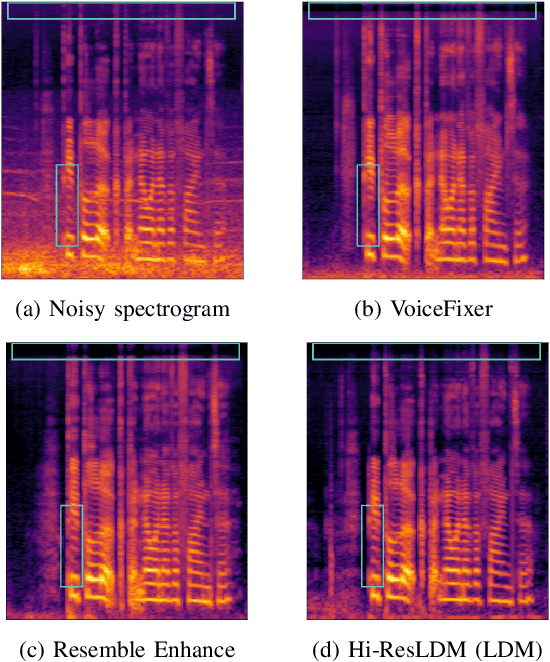
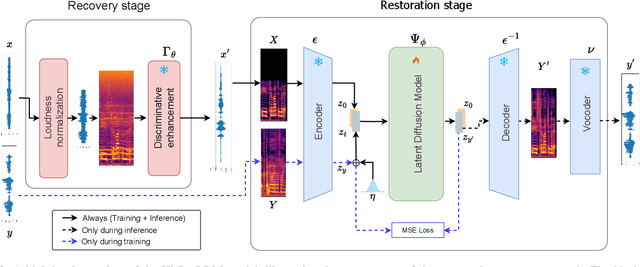
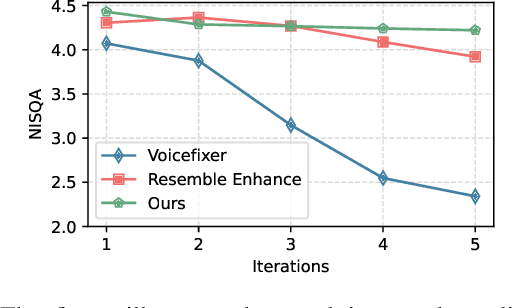
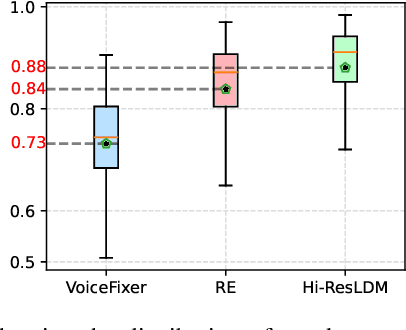
Abstract:Traditional speech enhancement methods often oversimplify the task of restoration by focusing on a single type of distortion. Generative models that handle multiple distortions frequently struggle with phone reconstruction and high-frequency harmonics, leading to breathing and gasping artifacts that reduce the intelligibility of reconstructed speech. These models are also computationally demanding, and many solutions are restricted to producing outputs in the wide-band frequency range, which limits their suitability for professional applications. To address these challenges, we propose Hi-ResLDM, a novel generative model based on latent diffusion designed to remove multiple distortions and restore speech recordings to studio quality, sampled at 48kHz. We benchmark Hi-ResLDM against state-of-the-art methods that leverage GAN and Conditional Flow Matching (CFM) components, demonstrating superior performance in regenerating high-frequency-band details. Hi-ResLDM not only excels in non-instrusive metrics but is also consistently preferred in human evaluation and performs competitively on intrusive evaluations, making it ideal for high-resolution speech restoration.
Latent Diffusion Bridges for Unsupervised Musical Audio Timbre Transfer
Sep 09, 2024Abstract:Music timbre transfer is a challenging task that involves modifying the timbral characteristics of an audio signal while preserving its melodic structure. In this paper, we propose a novel method based on dual diffusion bridges, trained using the CocoChorales Dataset, which consists of unpaired monophonic single-instrument audio data. Each diffusion model is trained on a specific instrument with a Gaussian prior. During inference, a model is designated as the source model to map the input audio to its corresponding Gaussian prior, and another model is designated as the target model to reconstruct the target audio from this Gaussian prior, thereby facilitating timbre transfer. We compare our approach against existing unsupervised timbre transfer models such as VAEGAN and Gaussian Flow Bridges (GFB). Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves both better Fr\'echet Audio Distance (FAD) and melody preservation, as reflected by lower pitch distances (DPD) compared to VAEGAN and GFB. Additionally, we discover that the noise level from the Gaussian prior, $\sigma$, can be adjusted to control the degree of melody preservation and amount of timbre transferred.
GRAFX: An Open-Source Library for Audio Processing Graphs in PyTorch
Aug 06, 2024


Abstract:We present GRAFX, an open-source library designed for handling audio processing graphs in PyTorch. Along with various library functionalities, we describe technical details on the efficient parallel computation of input graphs, signals, and processor parameters in GPU. Then, we show its example use under a music mixing scenario, where parameters of every differentiable processor in a large graph are optimized via gradient descent. The code is available at https://github.com/sh-lee97/grafx.
The Sound Demixing Challenge 2023 $\unicode{x2013}$ Music Demixing Track
Aug 14, 2023
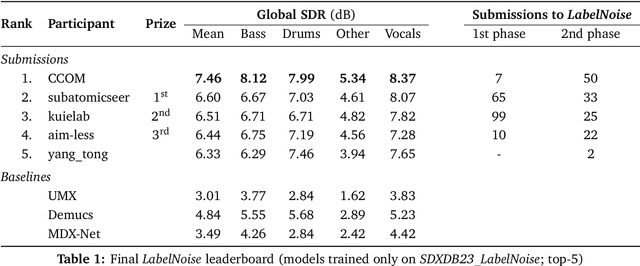

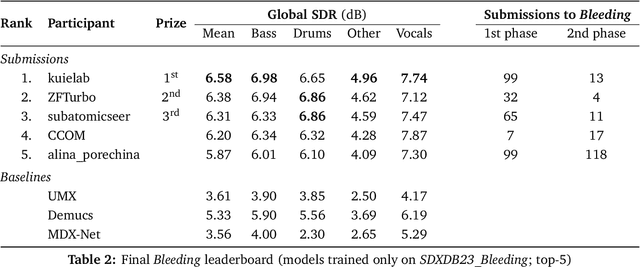
Abstract:This paper summarizes the music demixing (MDX) track of the Sound Demixing Challenge (SDX'23). We provide a summary of the challenge setup and introduce the task of robust music source separation (MSS), i.e., training MSS models in the presence of errors in the training data. We propose a formalization of the errors that can occur in the design of a training dataset for MSS systems and introduce two new datasets that simulate such errors: SDXDB23_LabelNoise and SDXDB23_Bleeding1. We describe the methods that achieved the highest scores in the competition. Moreover, we present a direct comparison with the previous edition of the challenge (the Music Demixing Challenge 2021): the best performing system under the standard MSS formulation achieved an improvement of over 1.6dB in signal-to-distortion ratio over the winner of the previous competition, when evaluated on MDXDB21. Besides relying on the signal-to-distortion ratio as objective metric, we also performed a listening test with renowned producers/musicians to study the perceptual quality of the systems and report here the results. Finally, we provide our insights into the organization of the competition and our prospects for future editions.
The Sound Demixing Challenge 2023 $\unicode{x2013}$ Cinematic Demixing Track
Aug 14, 2023
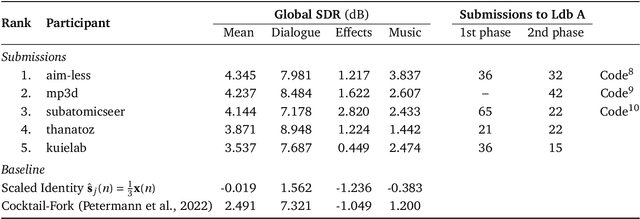


Abstract:This paper summarizes the cinematic demixing (CDX) track of the Sound Demixing Challenge 2023 (SDX'23). We provide a comprehensive summary of the challenge setup, detailing the structure of the competition and the datasets used. Especially, we detail CDXDB23, a new hidden dataset constructed from real movies that was used to rank the submissions. The paper also offers insights into the most successful approaches employed by participants. Compared to the cocktail-fork baseline, the best-performing system trained exclusively on the simulated Divide and Remaster (DnR) dataset achieved an improvement of 1.8dB in SDR whereas the top performing system on the open leaderboard, where any data could be used for training, saw a significant improvement of 5.7dB.
Automatic music mixing with deep learning and out-of-domain data
Aug 29, 2022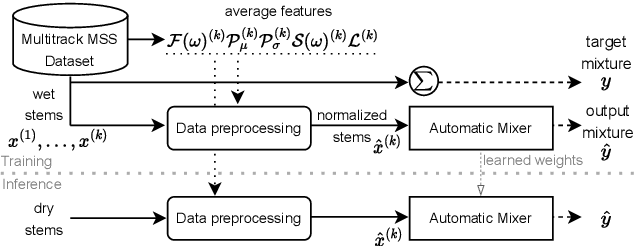
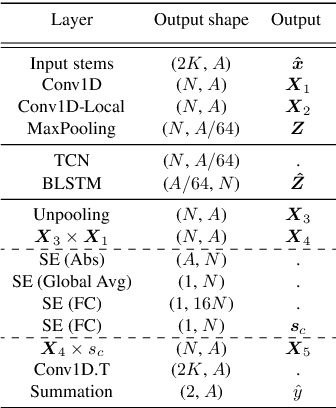
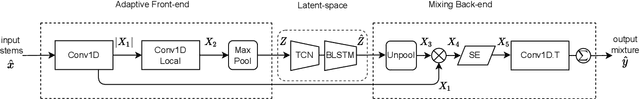
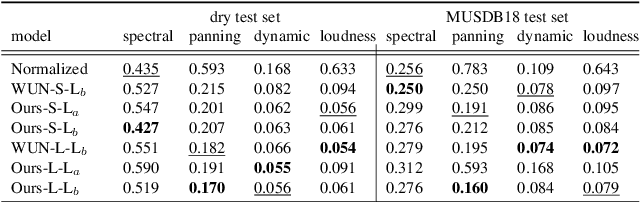
Abstract:Music mixing traditionally involves recording instruments in the form of clean, individual tracks and blending them into a final mixture using audio effects and expert knowledge (e.g., a mixing engineer). The automation of music production tasks has become an emerging field in recent years, where rule-based methods and machine learning approaches have been explored. Nevertheless, the lack of dry or clean instrument recordings limits the performance of such models, which is still far from professional human-made mixes. We explore whether we can use out-of-domain data such as wet or processed multitrack music recordings and repurpose it to train supervised deep learning models that can bridge the current gap in automatic mixing quality. To achieve this we propose a novel data preprocessing method that allows the models to perform automatic music mixing. We also redesigned a listening test method for evaluating music mixing systems. We validate our results through such subjective tests using highly experienced mixing engineers as participants.
Removing Distortion Effects in Music Using Deep Neural Networks
Feb 03, 2022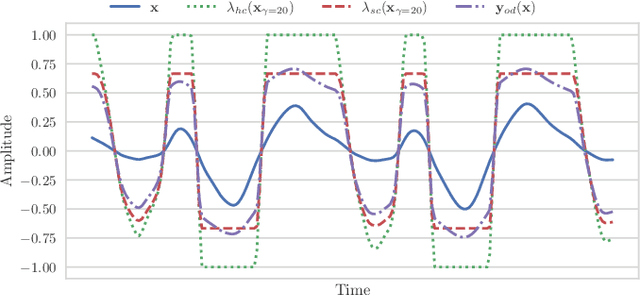
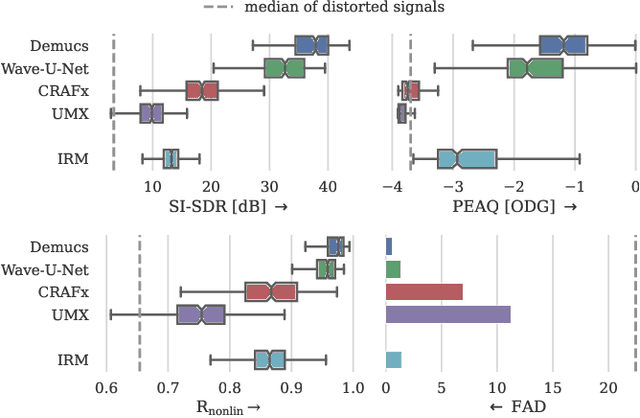
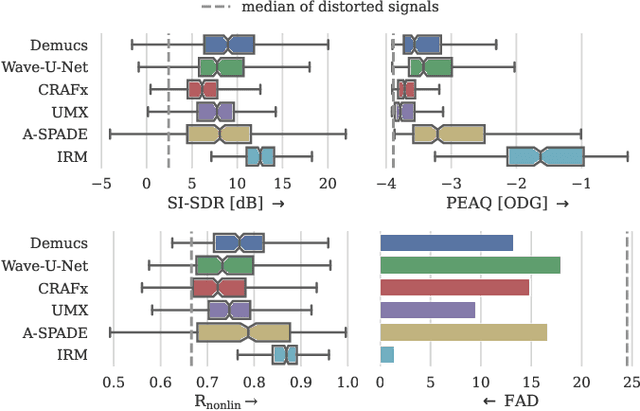
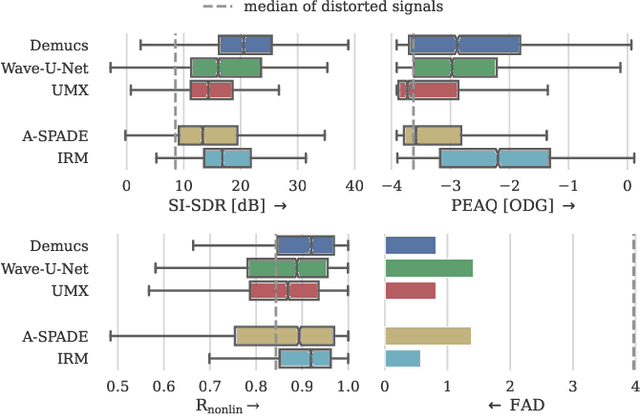
Abstract:Audio effects are an essential element in the context of music production, and therefore, modeling analog audio effects has been extensively researched for decades using system-identification methods, circuit simulation, and recently, deep learning. However, only few works tackled the reconstruction of signals that were processed using an audio effect unit. Given the recent advances in music source separation and automatic mixing, the removal of audio effects could facilitate an automatic remixing system. This paper focuses on removing distortion and clipping applied to guitar tracks for music production while presenting a comparative investigation of different deep neural network (DNN) architectures on this task. We achieve exceptionally good results in distortion removal using DNNs for effects that superimpose the clean signal to the distorted signal, while the task is more challenging if the clean signal is not superimposed. Nevertheless, in the latter case, the neural models under evaluation surpass one state-of-the-art declipping system in terms of source-to-distortion ratio, leading to better quality and faster inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge