Fritz Hohl
High-Resolution Speech Restoration with Latent Diffusion Model
Sep 17, 2024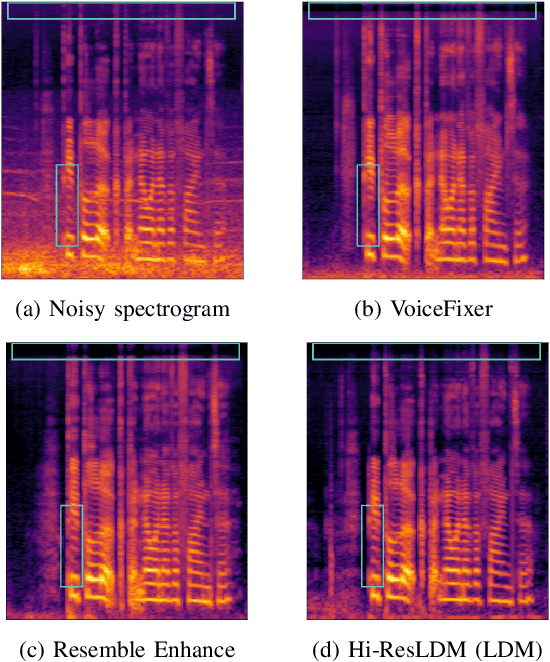
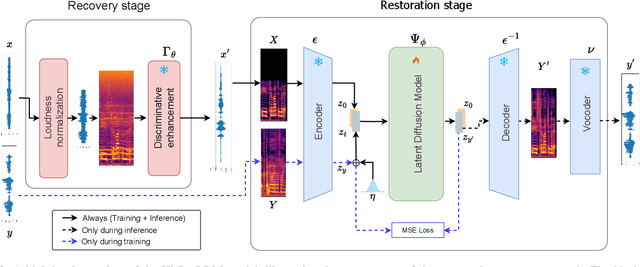
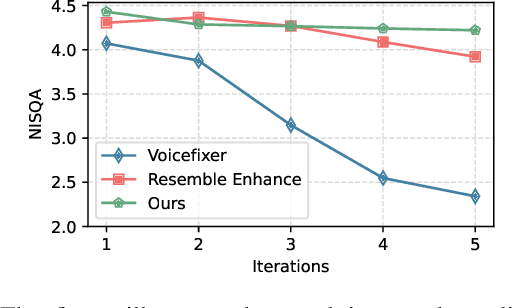
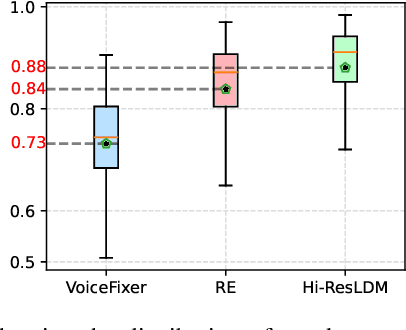
Abstract:Traditional speech enhancement methods often oversimplify the task of restoration by focusing on a single type of distortion. Generative models that handle multiple distortions frequently struggle with phone reconstruction and high-frequency harmonics, leading to breathing and gasping artifacts that reduce the intelligibility of reconstructed speech. These models are also computationally demanding, and many solutions are restricted to producing outputs in the wide-band frequency range, which limits their suitability for professional applications. To address these challenges, we propose Hi-ResLDM, a novel generative model based on latent diffusion designed to remove multiple distortions and restore speech recordings to studio quality, sampled at 48kHz. We benchmark Hi-ResLDM against state-of-the-art methods that leverage GAN and Conditional Flow Matching (CFM) components, demonstrating superior performance in regenerating high-frequency-band details. Hi-ResLDM not only excels in non-instrusive metrics but is also consistently preferred in human evaluation and performs competitively on intrusive evaluations, making it ideal for high-resolution speech restoration.
MetaSRL++: A Uniform Scheme for Modelling Deeper Semantics
May 16, 2023Abstract:Despite enormous progress in Natural Language Processing (NLP), our field is still lacking a common deep semantic representation scheme. As a result, the problem of meaning and understanding is typically sidestepped through more simple, approximative methods. This paper argues that in order to arrive at such a scheme, we also need a common modelling scheme. It therefore introduces MetaSRL++, a uniform, language- and modality-independent modelling scheme based on Semantic Graphs, as a step towards a common representation scheme; as well as a method for defining the concepts and entities that are used in these graphs. Our output is twofold. First, we illustrate MetaSRL++ through concrete examples. Secondly, we discuss how it relates to existing work in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge