Charles Patrick Martin
Beyond Video-to-SFX: Video to Audio Synthesis with Environmentally Aware Speech
Sep 19, 2025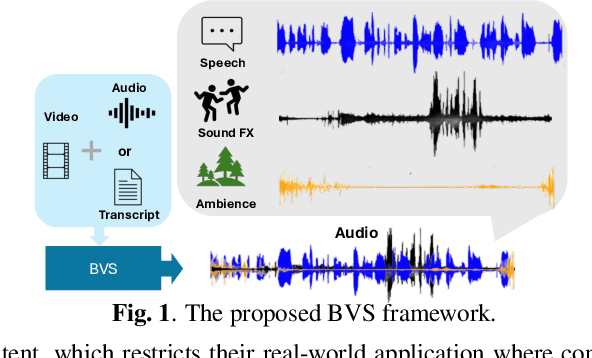



Abstract:The generation of realistic, context-aware audio is important in real-world applications such as video game development. While existing video-to-audio (V2A) methods mainly focus on Foley sound generation, they struggle to produce intelligible speech. Meanwhile, current environmental speech synthesis approaches remain text-driven and fail to temporally align with dynamic video content. In this paper, we propose Beyond Video-to-SFX (BVS), a method to generate synchronized audio with environmentally aware intelligible speech for given videos. We introduce a two-stage modeling method: (1) stage one is a video-guided audio semantic (V2AS) model to predict unified audio semantic tokens conditioned on phonetic cues; (2) stage two is a video-conditioned semantic-to-acoustic (VS2A) model that refines semantic tokens into detailed acoustic tokens. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of BVS in scenarios such as video-to-context-aware speech synthesis and immersive audio background conversion, with ablation studies further validating our design. Our demonstration is available at~\href{https://xinleiniu.github.io/BVS-demo/}{BVS-Demo}.
SteerMusic: Enhanced Musical Consistency for Zero-shot Text-Guided and Personalized Music Editing
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Music editing is an important step in music production, which has broad applications, including game development and film production. Most existing zero-shot text-guided methods rely on pretrained diffusion models by involving forward-backward diffusion processes for editing. However, these methods often struggle to maintain the music content consistency. Additionally, text instructions alone usually fail to accurately describe the desired music. In this paper, we propose two music editing methods that enhance the consistency between the original and edited music by leveraging score distillation. The first method, SteerMusic, is a coarse-grained zero-shot editing approach using delta denoising score. The second method, SteerMusic+, enables fine-grained personalized music editing by manipulating a concept token that represents a user-defined musical style. SteerMusic+ allows for the editing of music into any user-defined musical styles that cannot be achieved by the text instructions alone. Experimental results show that our methods outperform existing approaches in preserving both music content consistency and editing fidelity. User studies further validate that our methods achieve superior music editing quality. Audio examples are available on https://steermusic.pages.dev/.
SoundMorpher: Perceptually-Uniform Sound Morphing with Diffusion Model
Oct 03, 2024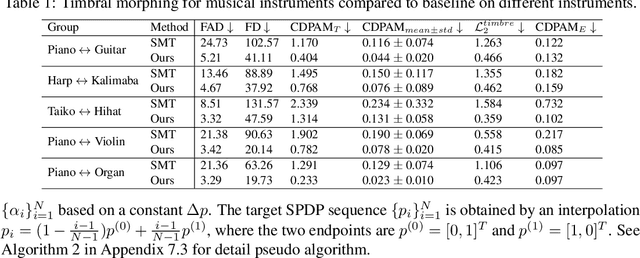
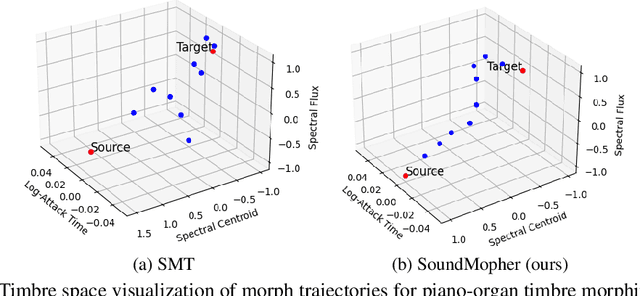


Abstract:We present SoundMorpher, a sound morphing method that generates perceptually uniform morphing trajectories using a diffusion model. Traditional sound morphing methods models the intractable relationship between morph factor and perception of the stimuli for resulting sounds under a linear assumption, which oversimplifies the complex nature of sound perception and limits their morph quality. In contrast, SoundMorpher explores an explicit proportional mapping between the morph factor and the perceptual stimuli of morphed sounds based on Mel-spectrogram. This approach enables smoother transitions between intermediate sounds and ensures perceptually consistent transformations, which can be easily extended to diverse sound morphing tasks. Furthermore, we present a set of quantitative metrics to comprehensively assess sound morphing systems based on three objective criteria, namely, correspondence, perceptual intermediateness, and smoothness. We provide extensive experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness and versatility of SoundMorpher in real-world scenarios, highlighting its potential impact on various applications such as creative music composition, film post-production and interactive audio technologies.
SoundLoCD: An Efficient Conditional Discrete Contrastive Latent Diffusion Model for Text-to-Sound Generation
May 24, 2024
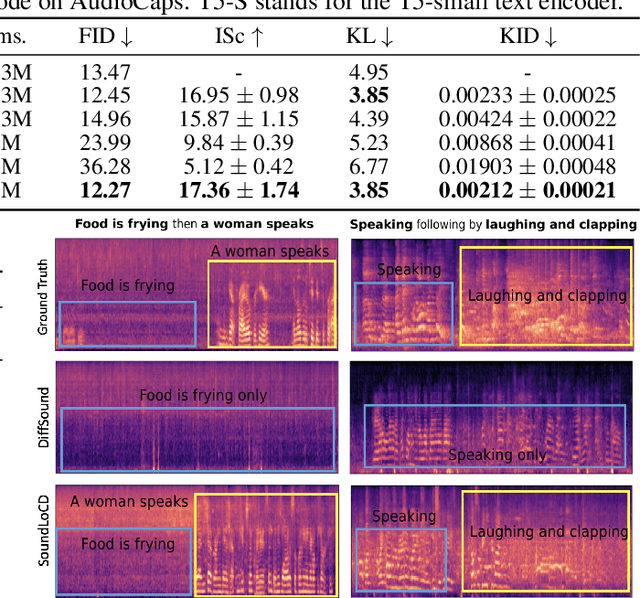

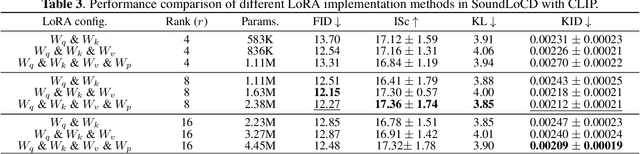
Abstract:We present SoundLoCD, a novel text-to-sound generation framework, which incorporates a LoRA-based conditional discrete contrastive latent diffusion model. Unlike recent large-scale sound generation models, our model can be efficiently trained under limited computational resources. The integration of a contrastive learning strategy further enhances the connection between text conditions and the generated outputs, resulting in coherent and high-fidelity performance. Our experiments demonstrate that SoundLoCD outperforms the baseline with greatly reduced computational resources. A comprehensive ablation study further validates the contribution of each component within SoundLoCD. Demo page: \url{https://XinleiNIU.github.io/demo-SoundLoCD/}.
HybridVC: Efficient Voice Style Conversion with Text and Audio Prompts
Apr 24, 2024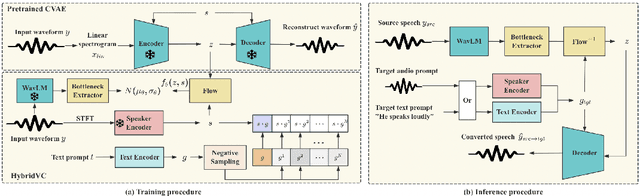
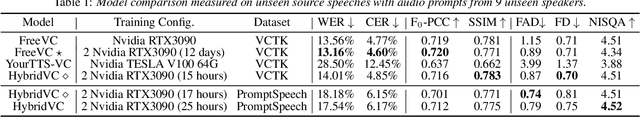
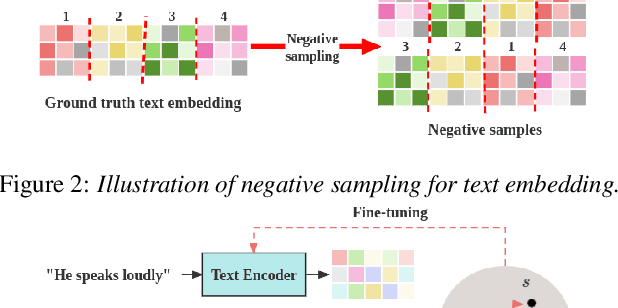
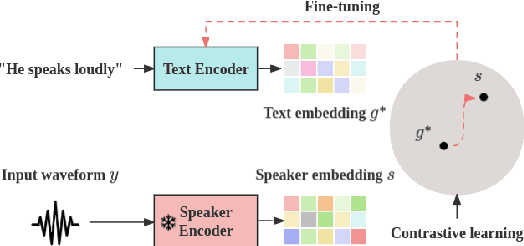
Abstract:We introduce HybridVC, a voice conversion (VC) framework built upon a pre-trained conditional variational autoencoder (CVAE) that combines the strengths of a latent model with contrastive learning. HybridVC supports text and audio prompts, enabling more flexible voice style conversion. HybridVC models a latent distribution conditioned on speaker embeddings acquired by a pretrained speaker encoder and optimises style text embeddings to align with the speaker style information through contrastive learning in parallel. Therefore, HybridVC can be efficiently trained under limited computational resources. Our experiments demonstrate HybridVC's superior training efficiency and its capability for advanced multi-modal voice style conversion. This underscores its potential for widespread applications such as user-defined personalised voice in various social media platforms. A comprehensive ablation study further validates the effectiveness of our method.
Latent Optimal Paths by Gumbel Propagation for Variational Bayesian Dynamic Programming
Jun 05, 2023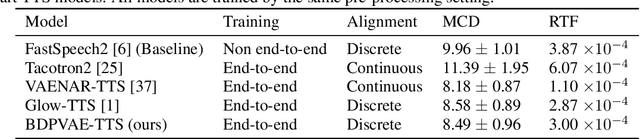
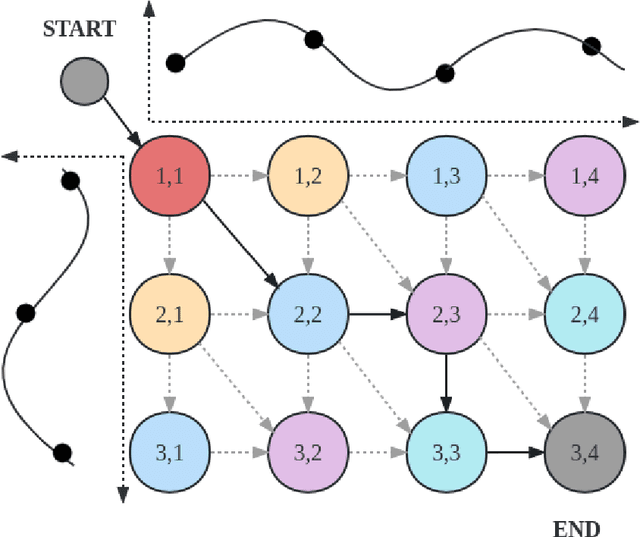


Abstract:We propose a unified approach to obtain structured sparse optimal paths in the latent space of a variational autoencoder (VAE) using dynamic programming and Gumbel propagation. We solve the classical optimal path problem by a probability softening solution, called the stochastic optimal path, and transform a wide range of DP problems into directed acyclic graphs in which all possible paths follow a Gibbs distribution. We show the equivalence of the Gibbs distribution to a message-passing algorithm by the properties of the Gumbel distribution and give all the ingredients required for variational Bayesian inference. Our approach obtaining latent optimal paths enables end-to-end training for generative tasks in which models rely on the information of unobserved structural features. We validate the behavior of our approach and showcase its applicability in two real-world applications: text-to-speech and singing voice synthesis.
Evolving Robots on Easy Mode: Towards a Variable Complexity Controller for Quadrupeds
Feb 12, 2019



Abstract:The complexity of a legged robot's environment or task can inform how specialised its gait must be to ensure success. Evolving specialised robotic gaits demands many evaluations - acceptable for computer simulations, but not for physical robots. For some tasks, a more general gait, with lower optimization costs, could be satisfactory. In this paper, we introduce a new type of gait controller where complexity can be set by a single parameter, using a dynamic genotype-phenotype mapping. Low controller complexity leads to conservative gaits, while higher complexity allows more sophistication and high performance for demanding tasks, at the cost of optimization effort. We investigate the new controller on a virtual robot in simulations and do preliminary testing on a real-world robot. We show that having variable complexity allows us to adapt to different optimization budgets. With a high evaluation budget in simulation, a complex controller performs best. Moreover, real-world evolution with a limited evaluation budget indicates that a lower gait complexity is preferable for a relatively simple environment.
How do Mixture Density RNNs Predict the Future?
Jan 23, 2019



Abstract:Gaining a better understanding of how and what machine learning systems learn is important to increase confidence in their decisions and catalyze further research. In this paper, we analyze the predictions made by a specific type of recurrent neural network, mixture density RNNs (MD-RNNs). These networks learn to model predictions as a combination of multiple Gaussian distributions, making them particularly interesting for problems where a sequence of inputs may lead to several distinct future possibilities. An example is learning internal models of an environment, where different events may or may not occur, but where the average over different events is not meaningful. By analyzing the predictions made by trained MD-RNNs, we find that their different Gaussian components have two complementary roles: 1) Separately modeling different stochastic events and 2) Separately modeling scenarios governed by different rules. These findings increase our understanding of what is learned by predictive MD-RNNs, and open up new research directions for further understanding how we can benefit from their self-organizing model decomposition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge