Removing Distortion Effects in Music Using Deep Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Feb 03, 2022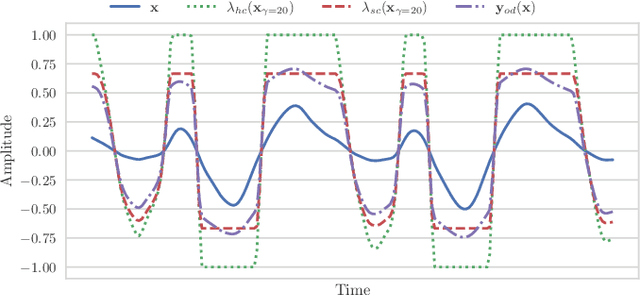
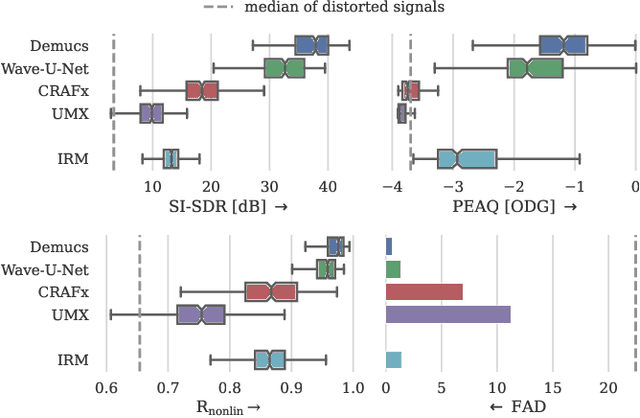
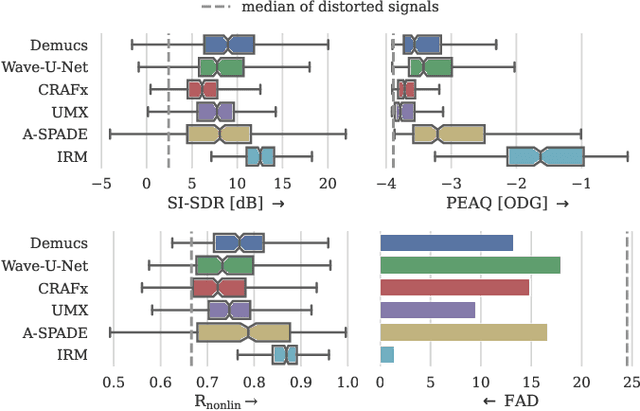
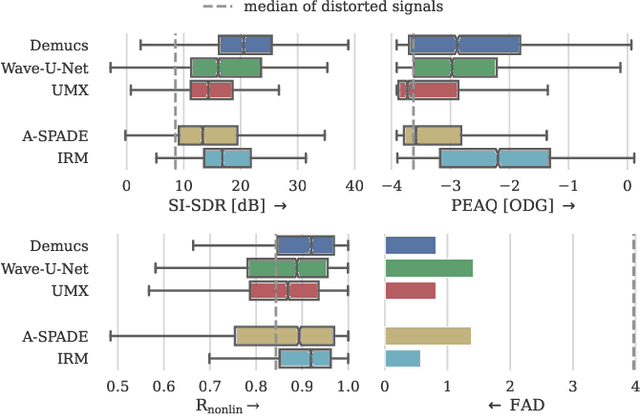
Audio effects are an essential element in the context of music production, and therefore, modeling analog audio effects has been extensively researched for decades using system-identification methods, circuit simulation, and recently, deep learning. However, only few works tackled the reconstruction of signals that were processed using an audio effect unit. Given the recent advances in music source separation and automatic mixing, the removal of audio effects could facilitate an automatic remixing system. This paper focuses on removing distortion and clipping applied to guitar tracks for music production while presenting a comparative investigation of different deep neural network (DNN) architectures on this task. We achieve exceptionally good results in distortion removal using DNNs for effects that superimpose the clean signal to the distorted signal, while the task is more challenging if the clean signal is not superimposed. Nevertheless, in the latter case, the neural models under evaluation surpass one state-of-the-art declipping system in terms of source-to-distortion ratio, leading to better quality and faster inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge