Doyup Lee
LILaC: Late Interacting in Layered Component Graph for Open-domain Multimodal Multihop Retrieval
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Multimodal document retrieval aims to retrieve query-relevant components from documents composed of textual, tabular, and visual elements. An effective multimodal retriever needs to handle two main challenges: (1) mitigate the effect of irrelevant contents caused by fixed, single-granular retrieval units, and (2) support multihop reasoning by effectively capturing semantic relationships among components within and across documents. To address these challenges, we propose LILaC, a multimodal retrieval framework featuring two core innovations. First, we introduce a layered component graph, explicitly representing multimodal information at two layers - each representing coarse and fine granularity - facilitating efficient yet precise reasoning. Second, we develop a late-interaction-based subgraph retrieval method, an edge-based approach that initially identifies coarse-grained nodes for efficient candidate generation, then performs fine-grained reasoning via late interaction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LILaC achieves state-of-the-art retrieval performance on all five benchmarks, notably without additional fine-tuning. We make the artifacts publicly available at github.com/joohyung00/lilac.
Failure is Feedback: History-Aware Backtracking for Agentic Traversal in Multimodal Graphs
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Open-domain multimodal document retrieval aims to retrieve specific components (paragraphs, tables, or images) from large and interconnected document corpora. Existing graph-based retrieval approaches typically rely on a uniform similarity metric that overlooks hop-specific semantics, and their rigid pre-defined plans hinder dynamic error correction. These limitations suggest that a retriever should adapt its reasoning to the evolving context and recover intelligently from dead ends. To address these needs, we propose Failure is Feedback (FiF), which casts subgraph retrieval as a sequential decision process and introduces two key innovations. (i) We introduce a history-aware backtracking mechanism; unlike standard backtracking that simply reverts the state, our approach piggybacks on the context of failed traversals, leveraging insights from previous failures. (ii) We implement an economically-rational agentic workflow. Unlike conventional agents with static strategies, our orchestrator employs a cost-aware traversal method to dynamically manage the trade-off between retrieval accuracy and inference costs, escalating to intensive LLM-based reasoning only when the prior failure justifies the additional computational investment. Extensive experiments show that FiF achieves state-of-the-art retrieval on the benchmarks of MultimodalQA, MMCoQA and WebQA.
Retrieval-Augmented Score Distillation for Text-to-3D Generation
Feb 05, 2024Abstract:Text-to-3D generation has achieved significant success by incorporating powerful 2D diffusion models, but insufficient 3D prior knowledge also leads to the inconsistency of 3D geometry. Recently, since large-scale multi-view datasets have been released, fine-tuning the diffusion model on the multi-view datasets becomes a mainstream to solve the 3D inconsistency problem. However, it has confronted with fundamental difficulties regarding the limited quality and diversity of 3D data, compared with 2D data. To sidestep these trade-offs, we explore a retrieval-augmented approach tailored for score distillation, dubbed RetDream. We postulate that both expressiveness of 2D diffusion models and geometric consistency of 3D assets can be fully leveraged by employing the semantically relevant assets directly within the optimization process. To this end, we introduce novel framework for retrieval-based quality enhancement in text-to-3D generation. We leverage the retrieved asset to incorporate its geometric prior in the variational objective and adapt the diffusion model's 2D prior toward view consistency, achieving drastic improvements in both geometry and fidelity of generated scenes. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate that RetDream exhibits superior quality with increased geometric consistency. Project page is available at https://ku-cvlab.github.io/RetDream/.
NVS-Adapter: Plug-and-Play Novel View Synthesis from a Single Image
Dec 12, 2023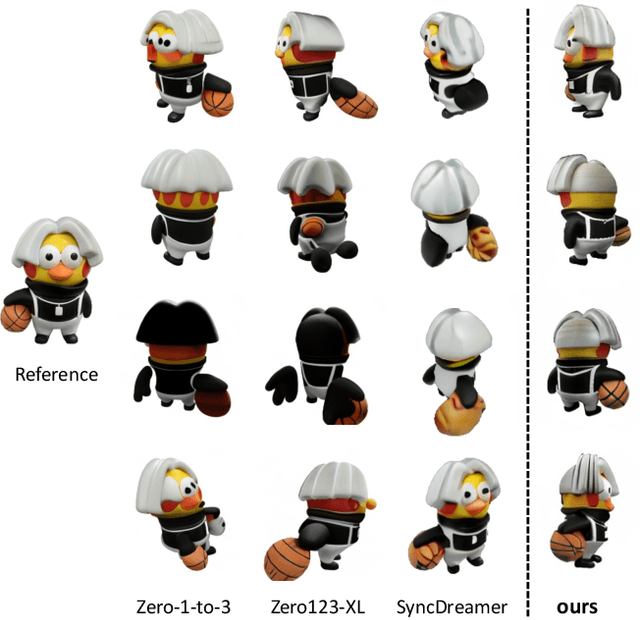
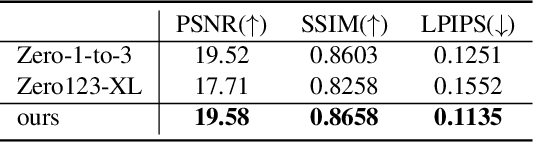
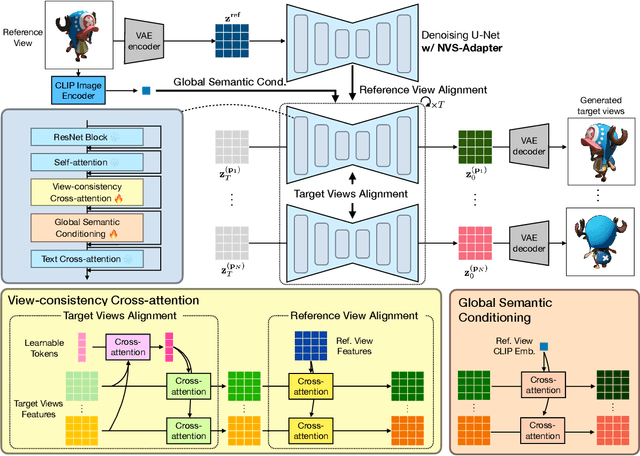
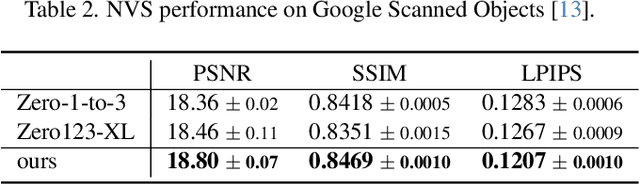
Abstract:Transfer learning of large-scale Text-to-Image (T2I) models has recently shown impressive potential for Novel View Synthesis (NVS) of diverse objects from a single image. While previous methods typically train large models on multi-view datasets for NVS, fine-tuning the whole parameters of T2I models not only demands a high cost but also reduces the generalization capacity of T2I models in generating diverse images in a new domain. In this study, we propose an effective method, dubbed NVS-Adapter, which is a plug-and-play module for a T2I model, to synthesize novel multi-views of visual objects while fully exploiting the generalization capacity of T2I models. NVS-Adapter consists of two main components; view-consistency cross-attention learns the visual correspondences to align the local details of view features, and global semantic conditioning aligns the semantic structure of generated views with the reference view. Experimental results demonstrate that the NVS-Adapter can effectively synthesize geometrically consistent multi-views and also achieve high performance on benchmarks without full fine-tuning of T2I models. The code and data are publicly available in ~\href{https://postech-cvlab.github.io/nvsadapter/}{https://postech-cvlab.github.io/nvsadapter/}.
Locality-Aware Generalizable Implicit Neural Representation
Oct 12, 2023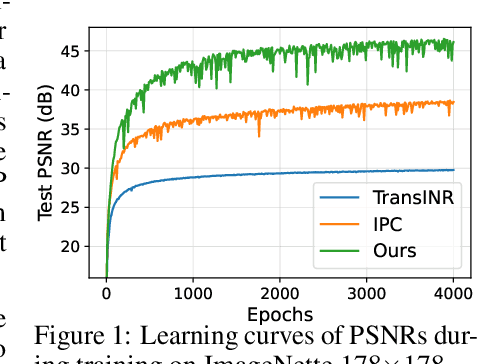
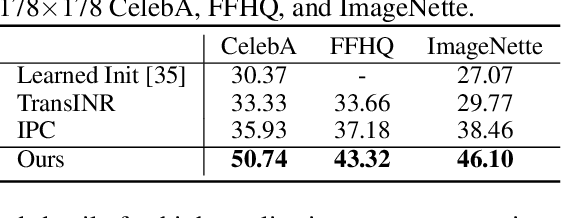
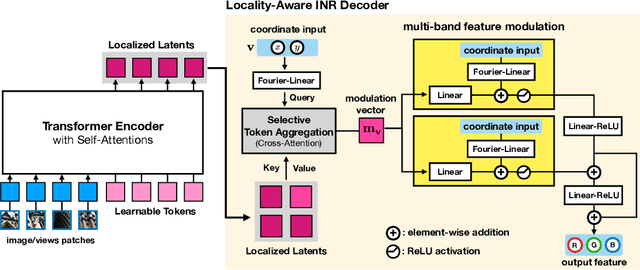

Abstract:Generalizable implicit neural representation (INR) enables a single continuous function, i.e., a coordinate-based neural network, to represent multiple data instances by modulating its weights or intermediate features using latent codes. However, the expressive power of the state-of-the-art modulation is limited due to its inability to localize and capture fine-grained details of data entities such as specific pixels and rays. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework for generalizable INR that combines a transformer encoder with a locality-aware INR decoder. The transformer encoder predicts a set of latent tokens from a data instance to encode local information into each latent token. The locality-aware INR decoder extracts a modulation vector by selectively aggregating the latent tokens via cross-attention for a coordinate input and then predicts the output by progressively decoding with coarse-to-fine modulation through multiple frequency bandwidths. The selective token aggregation and the multi-band feature modulation enable us to learn locality-aware representation in spatial and spectral aspects, respectively. Our framework significantly outperforms previous generalizable INRs and validates the usefulness of the locality-aware latents for downstream tasks such as image generation.
Variational Distribution Learning for Unsupervised Text-to-Image Generation
Mar 28, 2023



Abstract:We propose a text-to-image generation algorithm based on deep neural networks when text captions for images are unavailable during training. In this work, instead of simply generating pseudo-ground-truth sentences of training images using existing image captioning methods, we employ a pretrained CLIP model, which is capable of properly aligning embeddings of images and corresponding texts in a joint space and, consequently, works well on zero-shot recognition tasks. We optimize a text-to-image generation model by maximizing the data log-likelihood conditioned on pairs of image-text CLIP embeddings. To better align data in the two domains, we employ a principled way based on a variational inference, which efficiently estimates an approximate posterior of the hidden text embedding given an image and its CLIP feature. Experimental results validate that the proposed framework outperforms existing approaches by large margins under unsupervised and semi-supervised text-to-image generation settings.
Towards End-to-End Generative Modeling of Long Videos with Memory-Efficient Bidirectional Transformers
Mar 27, 2023Abstract:Autoregressive transformers have shown remarkable success in video generation. However, the transformers are prohibited from directly learning the long-term dependency in videos due to the quadratic complexity of self-attention, and inherently suffering from slow inference time and error propagation due to the autoregressive process. In this paper, we propose Memory-efficient Bidirectional Transformer (MeBT) for end-to-end learning of long-term dependency in videos and fast inference. Based on recent advances in bidirectional transformers, our method learns to decode the entire spatio-temporal volume of a video in parallel from partially observed patches. The proposed transformer achieves a linear time complexity in both encoding and decoding, by projecting observable context tokens into a fixed number of latent tokens and conditioning them to decode the masked tokens through the cross-attention. Empowered by linear complexity and bidirectional modeling, our method demonstrates significant improvement over the autoregressive Transformers for generating moderately long videos in both quality and speed. Videos and code are available at https://sites.google.com/view/mebt-cvpr2023 .
Generalizable Implicit Neural Representations via Instance Pattern Composers
Nov 23, 2022



Abstract:Despite recent advances in implicit neural representations (INRs), it remains challenging for a coordinate-based multi-layer perceptron (MLP) of INRs to learn a common representation across data instances and generalize it for unseen instances. In this work, we introduce a simple yet effective framework for generalizable INRs that enables a coordinate-based MLP to represent complex data instances by modulating only a small set of weights in an early MLP layer as an instance pattern composer; the remaining MLP weights learn pattern composition rules for common representations across instances. Our generalizable INR framework is fully compatible with existing meta-learning and hypernetworks in learning to predict the modulated weight for unseen instances. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves high performance on a wide range of domains such as an audio, image, and 3D object, while the ablation study validates our weight modulation.
Draft-and-Revise: Effective Image Generation with Contextual RQ-Transformer
Jun 09, 2022
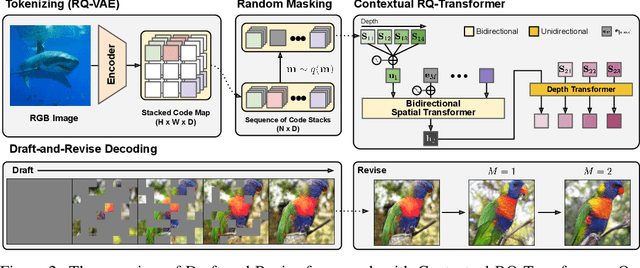
Abstract:Although autoregressive models have achieved promising results on image generation, their unidirectional generation process prevents the resultant images from fully reflecting global contexts. To address the issue, we propose an effective image generation framework of Draft-and-Revise with Contextual RQ-transformer to consider global contexts during the generation process. As a generalized VQ-VAE, RQ-VAE first represents a high-resolution image as a sequence of discrete code stacks. After code stacks in the sequence are randomly masked, Contextual RQ-Transformer is trained to infill the masked code stacks based on the unmasked contexts of the image. Then, Contextual RQ-Transformer uses our two-phase decoding, Draft-and-Revise, and generates an image, while exploiting the global contexts of the image during the generation process. Specifically. in the draft phase, our model first focuses on generating diverse images despite rather low quality. Then, in the revise phase, the model iteratively improves the quality of images, while preserving the global contexts of generated images. In experiments, our method achieves state-of-the-art results on conditional image generation. We also validate that the Draft-and-Revise decoding can achieve high performance by effectively controlling the quality-diversity trade-off in image generation.
Autoregressive Image Generation using Residual Quantization
Mar 09, 2022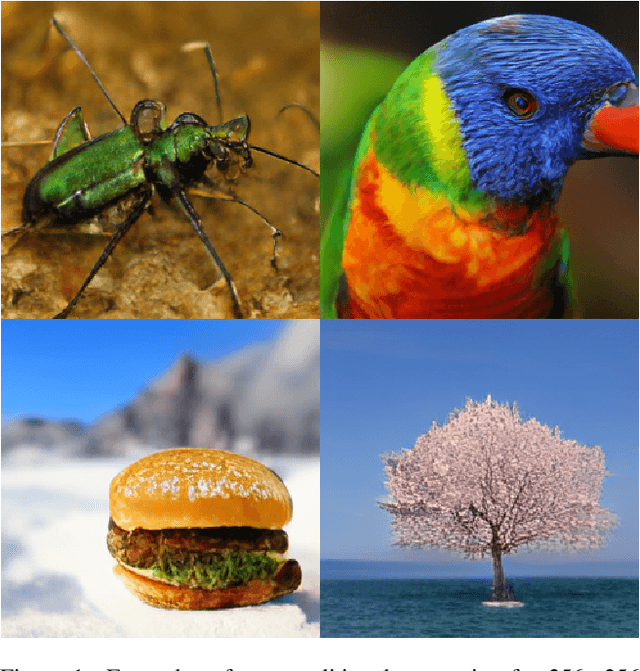
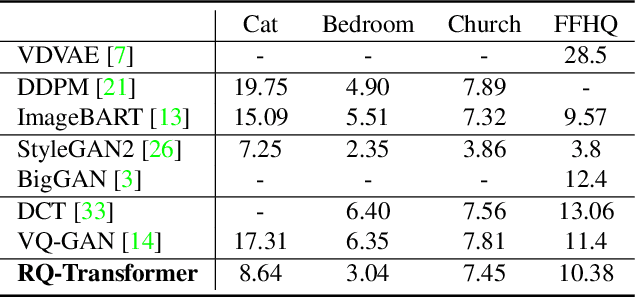
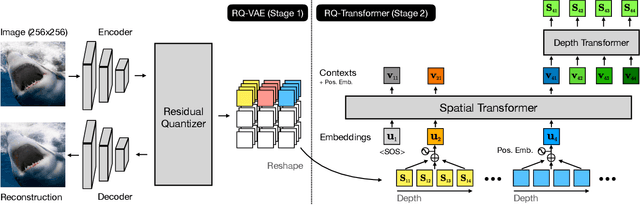
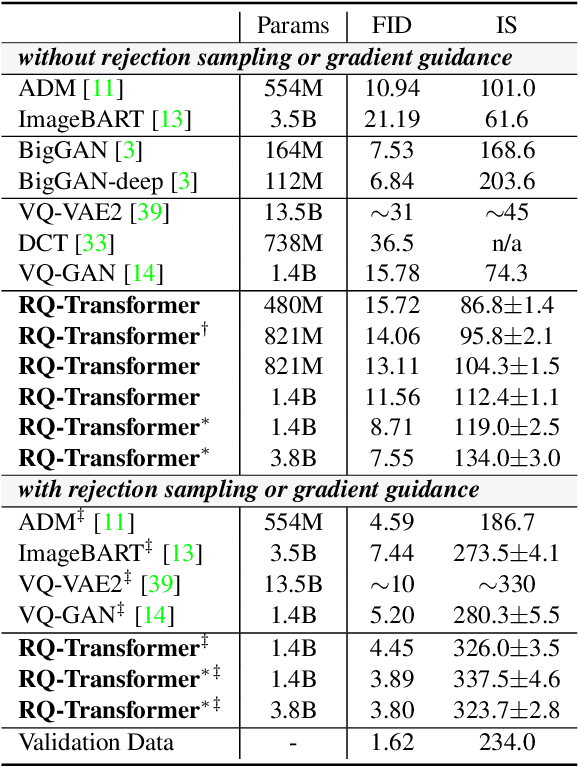
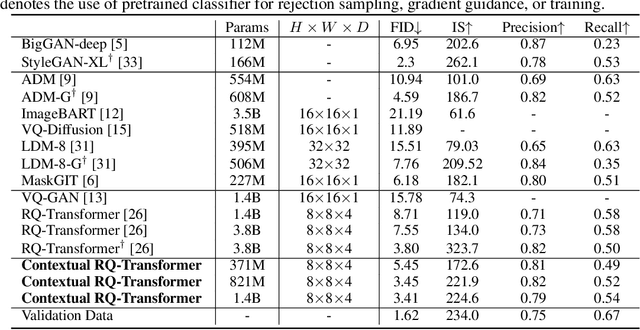
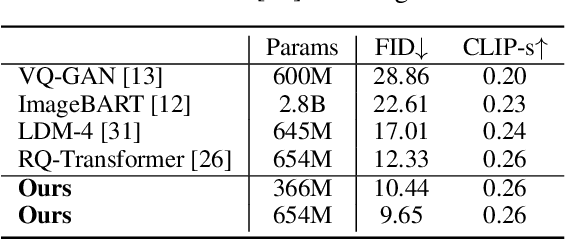
Abstract:For autoregressive (AR) modeling of high-resolution images, vector quantization (VQ) represents an image as a sequence of discrete codes. A short sequence length is important for an AR model to reduce its computational costs to consider long-range interactions of codes. However, we postulate that previous VQ cannot shorten the code sequence and generate high-fidelity images together in terms of the rate-distortion trade-off. In this study, we propose the two-stage framework, which consists of Residual-Quantized VAE (RQ-VAE) and RQ-Transformer, to effectively generate high-resolution images. Given a fixed codebook size, RQ-VAE can precisely approximate a feature map of an image and represent the image as a stacked map of discrete codes. Then, RQ-Transformer learns to predict the quantized feature vector at the next position by predicting the next stack of codes. Thanks to the precise approximation of RQ-VAE, we can represent a 256$\times$256 image as 8$\times$8 resolution of the feature map, and RQ-Transformer can efficiently reduce the computational costs. Consequently, our framework outperforms the existing AR models on various benchmarks of unconditional and conditional image generation. Our approach also has a significantly faster sampling speed than previous AR models to generate high-quality images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge