Minsu Cho
Vision-aligned Latent Reasoning for Multi-modal Large Language Model
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Despite recent advancements in Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) on diverse understanding tasks, these models struggle to solve problems which require extensive multi-step reasoning. This is primarily due to the progressive dilution of visual information during long-context generation, which hinders their ability to fully exploit test-time scaling. To address this issue, we introduce Vision-aligned Latent Reasoning (VaLR), a simple, yet effective reasoning framework that dynamically generates vision-aligned latent tokens before each Chain of Thought reasoning step, guiding the model to reason based on perceptual cues in the latent space. Specifically, VaLR is trained to preserve visual knowledge during reasoning by aligning intermediate embeddings of MLLM with those from vision encoders. Empirical results demonstrate that VaLR consistently outperforms existing approaches across a wide range of benchmarks requiring long-context understanding or precise visual perception, while exhibiting test-time scaling behavior not observed in prior MLLMs. In particular, VaLR improves the performance significantly from 33.0% to 52.9% on VSI-Bench, achieving a 19.9%p gain over Qwen2.5-VL.
MV-SAM: Multi-view Promptable Segmentation using Pointmap Guidance
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Promptable segmentation has emerged as a powerful paradigm in computer vision, enabling users to guide models in parsing complex scenes with prompts such as clicks, boxes, or textual cues. Recent advances, exemplified by the Segment Anything Model (SAM), have extended this paradigm to videos and multi-view images. However, the lack of 3D awareness often leads to inconsistent results, necessitating costly per-scene optimization to enforce 3D consistency. In this work, we introduce MV-SAM, a framework for multi-view segmentation that achieves 3D consistency using pointmaps -- 3D points reconstructed from unposed images by recent visual geometry models. Leveraging the pixel-point one-to-one correspondence of pointmaps, MV-SAM lifts images and prompts into 3D space, eliminating the need for explicit 3D networks or annotated 3D data. Specifically, MV-SAM extends SAM by lifting image embeddings from its pretrained encoder into 3D point embeddings, which are decoded by a transformer using cross-attention with 3D prompt embeddings. This design aligns 2D interactions with 3D geometry, enabling the model to implicitly learn consistent masks across views through 3D positional embeddings. Trained on the SA-1B dataset, our method generalizes well across domains, outperforming SAM2-Video and achieving comparable performance with per-scene optimization baselines on NVOS, SPIn-NeRF, ScanNet++, uCo3D, and DL3DV benchmarks. Code will be released.
DextER: Language-driven Dexterous Grasp Generation with Embodied Reasoning
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Language-driven dexterous grasp generation requires the models to understand task semantics, 3D geometry, and complex hand-object interactions. While vision-language models have been applied to this problem, existing approaches directly map observations to grasp parameters without intermediate reasoning about physical interactions. We present DextER, Dexterous Grasp Generation with Embodied Reasoning, which introduces contact-based embodied reasoning for multi-finger manipulation. Our key insight is that predicting which hand links contact where on the object surface provides an embodiment-aware intermediate representation bridging task semantics with physical constraints. DextER autoregressively generates embodied contact tokens specifying which finger links contact where on the object surface, followed by grasp tokens encoding the hand configuration. On DexGYS, DextER achieves 67.14% success rate, outperforming state-of-the-art by 3.83%p with 96.4% improvement in intention alignment. We also demonstrate steerable generation through partial contact specification, providing fine-grained control over grasp synthesis.
Affostruction: 3D Affordance Grounding with Generative Reconstruction
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of affordance grounding from RGBD images of an object, which aims to localize surface regions corresponding to a text query that describes an action on the object. While existing methods predict affordance regions only on visible surfaces, we propose Affostruction, a generative framework that reconstructs complete geometry from partial observations and grounds affordances on the full shape including unobserved regions. We make three core contributions: generative multi-view reconstruction via sparse voxel fusion that extrapolates unseen geometry while maintaining constant token complexity, flow-based affordance grounding that captures inherent ambiguity in affordance distributions, and affordance-driven active view selection that leverages predicted affordances for intelligent viewpoint sampling. Affostruction achieves 19.1 aIoU on affordance grounding (40.4\% improvement) and 32.67 IoU for 3D reconstruction (67.7\% improvement), enabling accurate affordance prediction on complete shapes.
Quantile Rendering: Efficiently Embedding High-dimensional Feature on 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 24, 2025

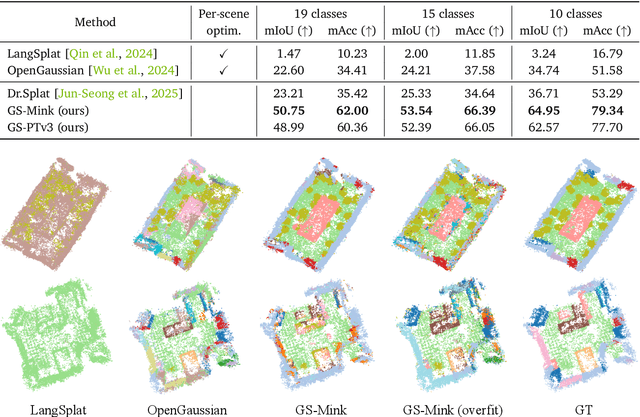

Abstract:Recent advancements in computer vision have successfully extended Open-vocabulary segmentation (OVS) to the 3D domain by leveraging 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS). Despite this progress, efficiently rendering the high-dimensional features required for open-vocabulary queries poses a significant challenge. Existing methods employ codebooks or feature compression, causing information loss, thereby degrading segmentation quality. To address this limitation, we introduce Quantile Rendering (Q-Render), a novel rendering strategy for 3D Gaussians that efficiently handles high-dimensional features while maintaining high fidelity. Unlike conventional volume rendering, which densely samples all 3D Gaussians intersecting each ray, Q-Render sparsely samples only those with dominant influence along the ray. By integrating Q-Render into a generalizable 3D neural network, we also propose Gaussian Splatting Network (GS-Net), which predicts Gaussian features in a generalizable manner. Extensive experiments on ScanNet and LeRF demonstrate that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods, while enabling real-time rendering with an approximate ~43.7x speedup on 512-D feature maps. Code will be made publicly available.
PanoGrounder: Bridging 2D and 3D with Panoramic Scene Representations for VLM-based 3D Visual Grounding
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:3D Visual Grounding (3DVG) is a critical bridge from vision-language perception to robotics, requiring both language understanding and 3D scene reasoning. Traditional supervised models leverage explicit 3D geometry but exhibit limited generalization, owing to the scarcity of 3D vision-language datasets and the limited reasoning capabilities compared to modern vision-language models (VLMs). We propose PanoGrounder, a generalizable 3DVG framework that couples multi-modal panoramic representation with pretrained 2D VLMs for strong vision-language reasoning. Panoramic renderings, augmented with 3D semantic and geometric features, serve as an intermediate representation between 2D and 3D, and offer two major benefits: (i) they can be directly fed to VLMs with minimal adaptation and (ii) they retain long-range object-to-object relations thanks to their 360-degree field of view. We devise a three-stage pipeline that places a compact set of panoramic viewpoints considering the scene layout and geometry, grounds a text query on each panoramic rendering with a VLM, and fuses per-view predictions into a single 3D bounding box via lifting. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on ScanRefer and Nr3D, and demonstrates superior generalization to unseen 3D datasets and text rephrasings.
Part-Aware Bottom-Up Group Reasoning for Fine-Grained Social Interaction Detection
Nov 05, 2025
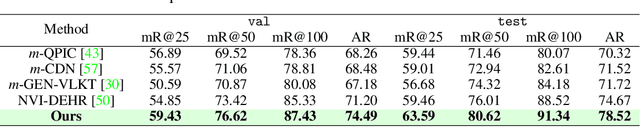

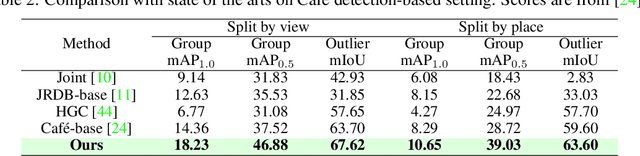
Abstract:Social interactions often emerge from subtle, fine-grained cues such as facial expressions, gaze, and gestures. However, existing methods for social interaction detection overlook such nuanced cues and primarily rely on holistic representations of individuals. Moreover, they directly detect social groups without explicitly modeling the underlying interactions between individuals. These drawbacks limit their ability to capture localized social signals and introduce ambiguity when group configurations should be inferred from social interactions grounded in nuanced cues. In this work, we propose a part-aware bottom-up group reasoning framework for fine-grained social interaction detection. The proposed method infers social groups and their interactions using body part features and their interpersonal relations. Our model first detects individuals and enhances their features using part-aware cues, and then infers group configuration by associating individuals via similarity-based reasoning, which considers not only spatial relations but also subtle social cues that signal interactions, leading to more accurate group inference. Experiments on the NVI dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms prior methods, achieving the new state of the art.
Few-Shot Pattern Detection via Template Matching and Regression
Aug 25, 2025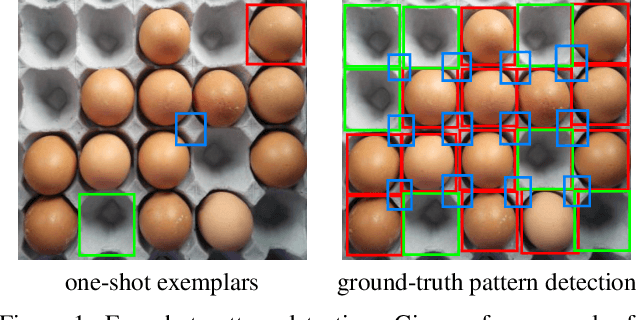

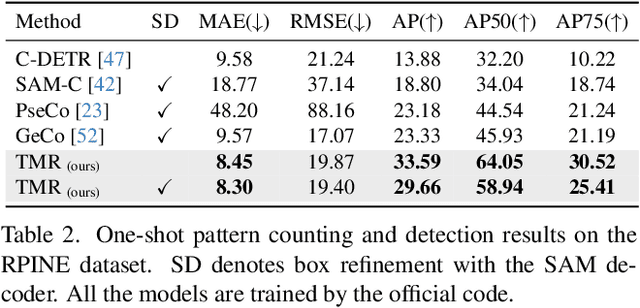
Abstract:We address the problem of few-shot pattern detection, which aims to detect all instances of a given pattern, typically represented by a few exemplars, from an input image. Although similar problems have been studied in few-shot object counting and detection (FSCD), previous methods and their benchmarks have narrowed patterns of interest to object categories and often fail to localize non-object patterns. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective detector based on template matching and regression, dubbed TMR. While previous FSCD methods typically represent target exemplars as spatially collapsed prototypes and lose structural information, we revisit classic template matching and regression. It effectively preserves and leverages the spatial layout of exemplars through a minimalistic structure with a small number of learnable convolutional or projection layers on top of a frozen backbone We also introduce a new dataset, dubbed RPINE, which covers a wider range of patterns than existing object-centric datasets. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on the three benchmarks, RPINE, FSCD-147, and FSCD-LVIS, and demonstrates strong generalization in cross-dataset evaluation.
Affogato: Learning Open-Vocabulary Affordance Grounding with Automated Data Generation at Scale
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Affordance grounding-localizing object regions based on natural language descriptions of interactions-is a critical challenge for enabling intelligent agents to understand and interact with their environments. However, this task remains challenging due to the need for fine-grained part-level localization, the ambiguity arising from multiple valid interaction regions, and the scarcity of large-scale datasets. In this work, we introduce Affogato, a large-scale benchmark comprising 150K instances, annotated with open-vocabulary text descriptions and corresponding 3D affordance heatmaps across a diverse set of objects and interactions. Building on this benchmark, we develop simple yet effective vision-language models that leverage pretrained part-aware vision backbones and a text-conditional heatmap decoder. Our models trained with the Affogato dataset achieve promising performance on the existing 2D and 3D benchmarks, and notably, exhibit effectiveness in open-vocabulary cross-domain generalization. The Affogato dataset is shared in public: https://huggingface.co/datasets/project-affogato/affogato
Harnessing the Power of Training-Free Techniques in Text-to-2D Generation for Text-to-3D Generation via Score Distillation Sampling
May 26, 2025Abstract:Recent studies show that simple training-free techniques can dramatically improve the quality of text-to-2D generation outputs, e.g. Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) or FreeU. However, these training-free techniques have been underexplored in the lens of Score Distillation Sampling (SDS), which is a popular and effective technique to leverage the power of pretrained text-to-2D diffusion models for various tasks. In this paper, we aim to shed light on the effect such training-free techniques have on SDS, via a particular application of text-to-3D generation via 2D lifting. We present our findings, which show that varying the scales of CFG presents a trade-off between object size and surface smoothness, while varying the scales of FreeU presents a trade-off between texture details and geometric errors. Based on these findings, we provide insights into how we can effectively harness training-free techniques for SDS, via a strategic scaling of such techniques in a dynamic manner with respect to the timestep or optimization iteration step. We show that using our proposed scheme strikes a favorable balance between texture details and surface smoothness in text-to-3D generations, while preserving the size of the output and mitigating the occurrence of geometric defects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge