Suha Kwak
TextME: Bridging Unseen Modalities Through Text Descriptions
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Expanding multimodal representations to novel modalities is constrained by reliance on large-scale paired datasets (e.g., text-image, text-audio, text-3D, text-molecule), which are costly and often infeasible in domains requiring expert annotation such as medical imaging and molecular analysis. We introduce TextME, the first text-only modality expansion framework, to the best of our knowledge, projecting diverse modalities into LLM embedding space as a unified anchor. Our approach exploits the geometric structure of pretrained contrastive encoders to enable zero-shot cross-modal transfer using only text descriptions, without paired supervision. We empirically validate that such consistent modality gaps exist across image, video, audio, 3D, X-ray, and molecular domains, demonstrating that text-only training can preserve substantial performance of pretrained encoders. We further show that our framework enables emergent cross-modal retrieval between modality pairs not explicitly aligned during training (e.g., audio-to-image, 3D-to-image). These results establish text-only training as a practical alternative to paired supervision for modality expansion.
Learned split-spectrum metalens for obstruction-free broadband imaging in the visible
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Obstructions such as raindrops, fences, or dust degrade captured images, especially when mechanical cleaning is infeasible. Conventional solutions to obstructions rely on a bulky compound optics array or computational inpainting, which compromise compactness or fidelity. Metalenses composed of subwavelength meta-atoms promise compact imaging, but simultaneous achievement of broadband and obstruction-free imaging remains a challenge, since a metalens that images distant scenes across a broadband spectrum cannot properly defocus near-depth occlusions. Here, we introduce a learned split-spectrum metalens that enables broadband obstruction-free imaging. Our approach divides the spectrum of each RGB channel into pass and stop bands with multi-band spectral filtering and learns the metalens to focus light from far objects through pass bands, while filtering focused near-depth light through stop bands. This optical signal is further enhanced using a neural network. Our learned split-spectrum metalens achieves broadband and obstruction-free imaging with relative PSNR gains of 32.29% and improves object detection and semantic segmentation accuracies with absolute gains of +13.54% mAP, +48.45% IoU, and +20.35% mIoU over a conventional hyperbolic design. This promises robust obstruction-free sensing and vision for space-constrained systems, such as mobile robots, drones, and endoscopes.
VIRO: Robust and Efficient Neuro-Symbolic Reasoning with Verification for Referring Expression Comprehension
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Referring Expression Comprehension (REC) aims to localize the image region corresponding to a natural-language query. Recent neuro-symbolic REC approaches leverage large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs) to perform compositional reasoning, decomposing queries 4 structured programs and executing them step-by-step. While such approaches achieve interpretable reasoning and strong zero-shot generalization, they assume that intermediate reasoning steps are accurate. However, this assumption causes cascading errors: false detections and invalid relations propagate through the reasoning chain, yielding high-confidence false positives even when no target is present in the image. To address this limitation, we introduce Verification-Integrated Reasoning Operators (VIRO), a neuro-symbolic framework that embeds lightweight operator-level verifiers within reasoning steps. Each operator executes and validates its output, such as object existence or spatial relationship, thereby allowing the system to robustly handle no-target cases when verification conditions are not met. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance, reaching 61.1% balanced accuracy across target-present and no-target settings, and demonstrates generalization to real-world egocentric data. Furthermore, VIRO shows superior computational efficiency in terms of throughput, high reliability with a program failure rate of less than 0.3%, and scalability through decoupled program generation from execution.
Part-Aware Bottom-Up Group Reasoning for Fine-Grained Social Interaction Detection
Nov 05, 2025
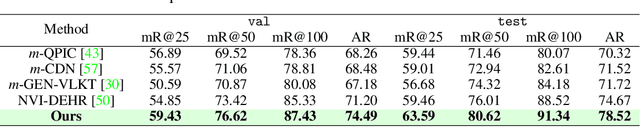

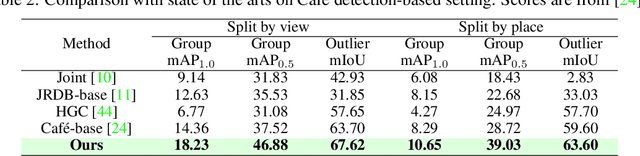
Abstract:Social interactions often emerge from subtle, fine-grained cues such as facial expressions, gaze, and gestures. However, existing methods for social interaction detection overlook such nuanced cues and primarily rely on holistic representations of individuals. Moreover, they directly detect social groups without explicitly modeling the underlying interactions between individuals. These drawbacks limit their ability to capture localized social signals and introduce ambiguity when group configurations should be inferred from social interactions grounded in nuanced cues. In this work, we propose a part-aware bottom-up group reasoning framework for fine-grained social interaction detection. The proposed method infers social groups and their interactions using body part features and their interpersonal relations. Our model first detects individuals and enhances their features using part-aware cues, and then infers group configuration by associating individuals via similarity-based reasoning, which considers not only spatial relations but also subtle social cues that signal interactions, leading to more accurate group inference. Experiments on the NVI dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms prior methods, achieving the new state of the art.
Improving Sound Source Localization with Joint Slot Attention on Image and Audio
Apr 21, 2025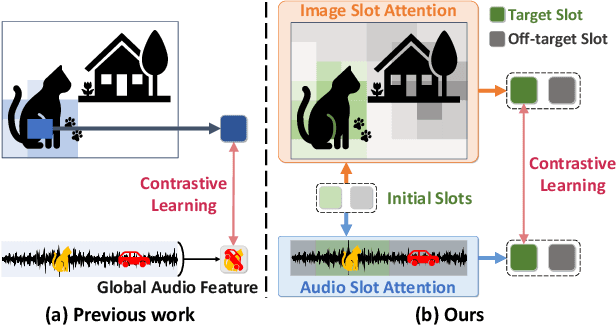
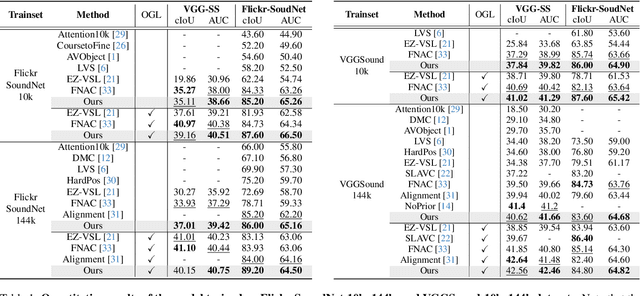
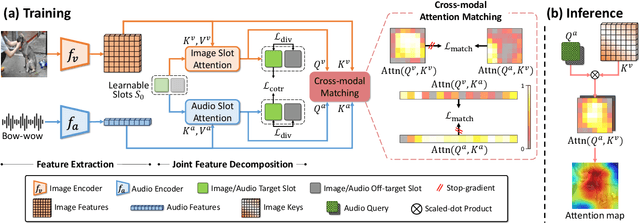
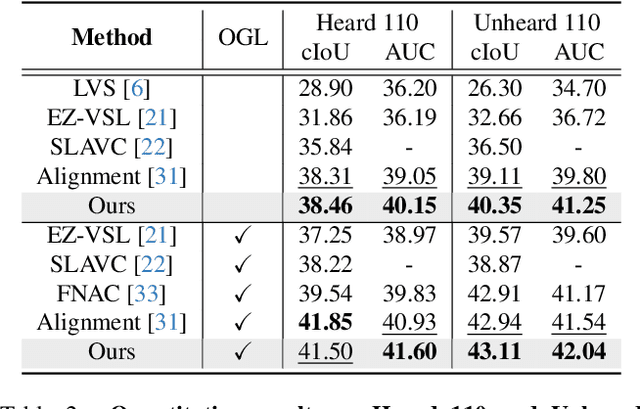
Abstract:Sound source localization (SSL) is the task of locating the source of sound within an image. Due to the lack of localization labels, the de facto standard in SSL has been to represent an image and audio as a single embedding vector each, and use them to learn SSL via contrastive learning. To this end, previous work samples one of local image features as the image embedding and aggregates all local audio features to obtain the audio embedding, which is far from optimal due to the presence of noise and background irrelevant to the actual target in the input. We present a novel SSL method that addresses this chronic issue by joint slot attention on image and audio. To be specific, two slots competitively attend image and audio features to decompose them into target and off-target representations, and only target representations of image and audio are used for contrastive learning. Also, we introduce cross-modal attention matching to further align local features of image and audio. Our method achieved the best in almost all settings on three public benchmarks for SSL, and substantially outperformed all the prior work in cross-modal retrieval.
DiCoTTA: Domain-invariant Learning for Continual Test-time Adaptation
Apr 07, 2025



Abstract:This paper studies continual test-time adaptation (CTTA), the task of adapting a model to constantly changing unseen domains in testing while preserving previously learned knowledge. Existing CTTA methods mostly focus on adaptation to the current test domain only, overlooking generalization to arbitrary test domains a model may face in the future. To tackle this limitation, we present a novel online domain-invariant learning framework for CTTA, dubbed DiCoTTA. DiCoTTA aims to learn feature representation to be invariant to both current and previous test domains on the fly during testing. To this end, we propose a new model architecture and a test-time adaptation strategy dedicated to learning domain-invariant features without corrupting semantic contents, along with a new data structure and optimization algorithm for effectively managing information from previous test domains. DiCoTTA achieved state-of-the-art performance on four public CTTA benchmarks. Moreover, it showed superior generalization to unseen test domains.
Learning Audio-guided Video Representation with Gated Attention for Video-Text Retrieval
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Video-text retrieval, the task of retrieving videos based on a textual query or vice versa, is of paramount importance for video understanding and multimodal information retrieval. Recent methods in this area rely primarily on visual and textual features and often ignore audio, although it helps enhance overall comprehension of video content. Moreover, traditional models that incorporate audio blindly utilize the audio input regardless of whether it is useful or not, resulting in suboptimal video representation. To address these limitations, we propose a novel video-text retrieval framework, Audio-guided VIdeo representation learning with GATEd attention (AVIGATE), that effectively leverages audio cues through a gated attention mechanism that selectively filters out uninformative audio signals. In addition, we propose an adaptive margin-based contrastive loss to deal with the inherently unclear positive-negative relationship between video and text, which facilitates learning better video-text alignment. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that AVIGATE achieves state-of-the-art performance on all the public benchmarks.
GENIUS: A Generative Framework for Universal Multimodal Search
Mar 25, 2025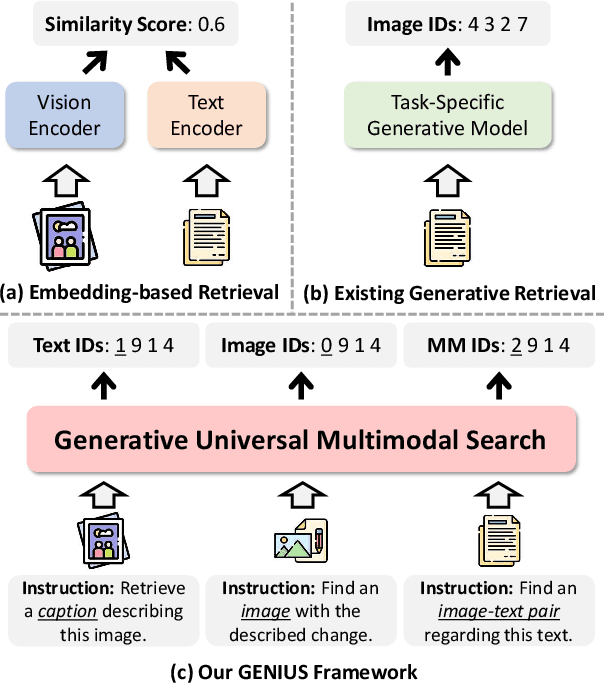
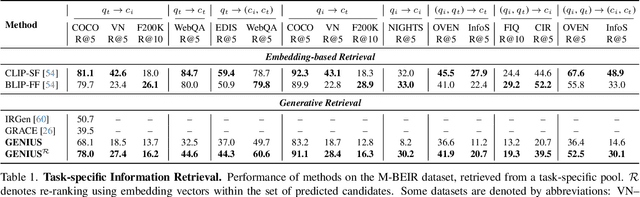
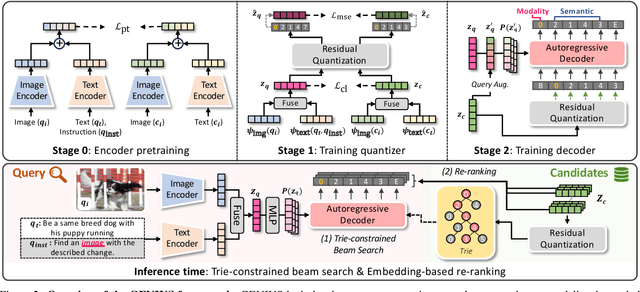
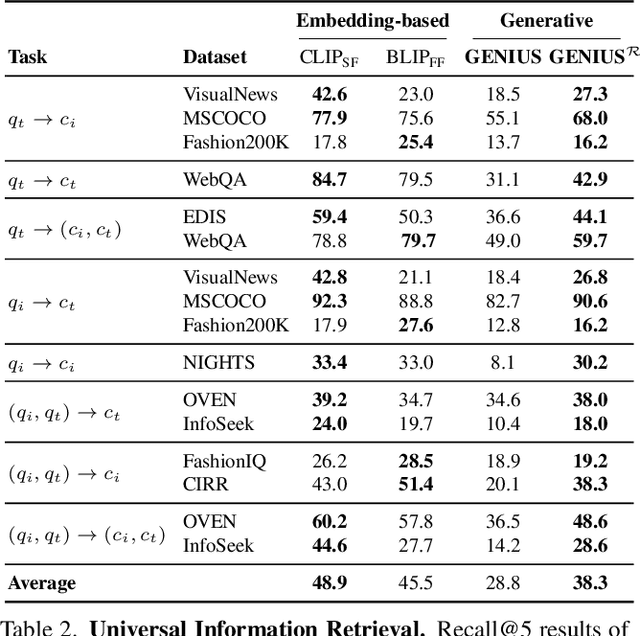
Abstract:Generative retrieval is an emerging approach in information retrieval that generates identifiers (IDs) of target data based on a query, providing an efficient alternative to traditional embedding-based retrieval methods. However, existing models are task-specific and fall short of embedding-based retrieval in performance. This paper proposes GENIUS, a universal generative retrieval framework supporting diverse tasks across multiple modalities and domains. At its core, GENIUS introduces modality-decoupled semantic quantization, transforming multimodal data into discrete IDs encoding both modality and semantics. Moreover, to enhance generalization, we propose a query augmentation that interpolates between a query and its target, allowing GENIUS to adapt to varied query forms. Evaluated on the M-BEIR benchmark, it surpasses prior generative methods by a clear margin. Unlike embedding-based retrieval, GENIUS consistently maintains high retrieval speed across database size, with competitive performance across multiple benchmarks. With additional re-ranking, GENIUS often achieves results close to those of embedding-based methods while preserving efficiency.
Enhancing Cost Efficiency in Active Learning with Candidate Set Query
Feb 10, 2025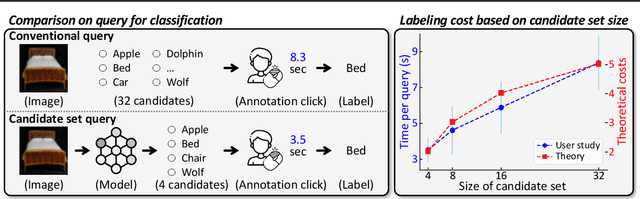

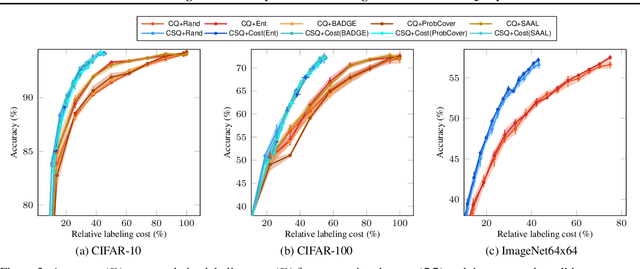
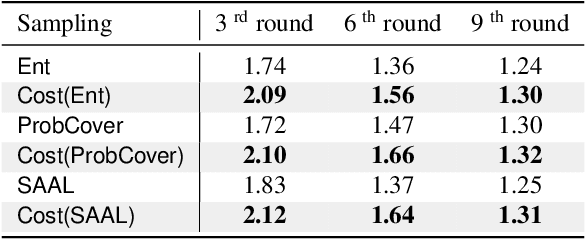
Abstract:This paper introduces a cost-efficient active learning (AL) framework for classification, featuring a novel query design called candidate set query. Unlike traditional AL queries requiring the oracle to examine all possible classes, our method narrows down the set of candidate classes likely to include the ground-truth class, significantly reducing the search space and labeling cost. Moreover, we leverage conformal prediction to dynamically generate small yet reliable candidate sets, adapting to model enhancement over successive AL rounds. To this end, we introduce an acquisition function designed to prioritize data points that offer high information gain at lower cost. Empirical evaluations on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and ImageNet64x64 demonstrate the effectiveness and scalability of our framework. Notably, it reduces labeling cost by 42% on ImageNet64x64.
Democratizing Text-to-Image Masked Generative Models with Compact Text-Aware One-Dimensional Tokens
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:Image tokenizers form the foundation of modern text-to-image generative models but are notoriously difficult to train. Furthermore, most existing text-to-image models rely on large-scale, high-quality private datasets, making them challenging to replicate. In this work, we introduce Text-Aware Transformer-based 1-Dimensional Tokenizer (TA-TiTok), an efficient and powerful image tokenizer that can utilize either discrete or continuous 1-dimensional tokens. TA-TiTok uniquely integrates textual information during the tokenizer decoding stage (i.e., de-tokenization), accelerating convergence and enhancing performance. TA-TiTok also benefits from a simplified, yet effective, one-stage training process, eliminating the need for the complex two-stage distillation used in previous 1-dimensional tokenizers. This design allows for seamless scalability to large datasets. Building on this, we introduce a family of text-to-image Masked Generative Models (MaskGen), trained exclusively on open data while achieving comparable performance to models trained on private data. We aim to release both the efficient, strong TA-TiTok tokenizers and the open-data, open-weight MaskGen models to promote broader access and democratize the field of text-to-image masked generative models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge