Jicheol Park
Improving Sound Source Localization with Joint Slot Attention on Image and Audio
Apr 21, 2025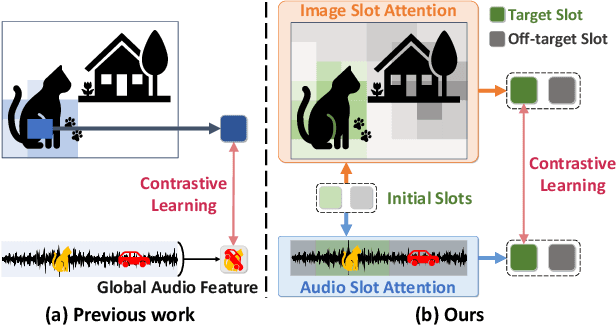
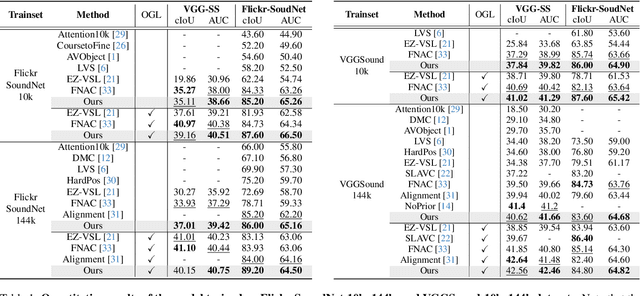
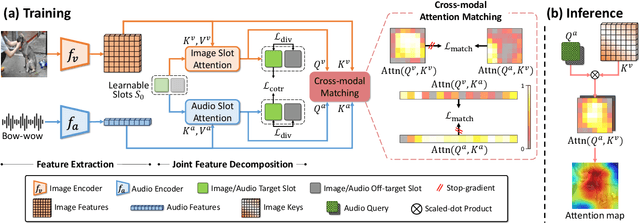
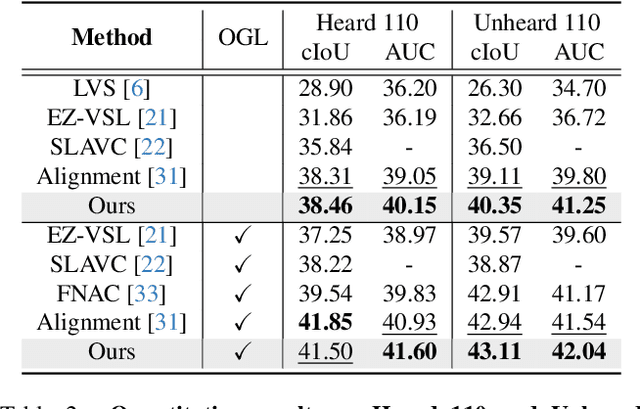
Abstract:Sound source localization (SSL) is the task of locating the source of sound within an image. Due to the lack of localization labels, the de facto standard in SSL has been to represent an image and audio as a single embedding vector each, and use them to learn SSL via contrastive learning. To this end, previous work samples one of local image features as the image embedding and aggregates all local audio features to obtain the audio embedding, which is far from optimal due to the presence of noise and background irrelevant to the actual target in the input. We present a novel SSL method that addresses this chronic issue by joint slot attention on image and audio. To be specific, two slots competitively attend image and audio features to decompose them into target and off-target representations, and only target representations of image and audio are used for contrastive learning. Also, we introduce cross-modal attention matching to further align local features of image and audio. Our method achieved the best in almost all settings on three public benchmarks for SSL, and substantially outperformed all the prior work in cross-modal retrieval.
Learning Audio-guided Video Representation with Gated Attention for Video-Text Retrieval
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Video-text retrieval, the task of retrieving videos based on a textual query or vice versa, is of paramount importance for video understanding and multimodal information retrieval. Recent methods in this area rely primarily on visual and textual features and often ignore audio, although it helps enhance overall comprehension of video content. Moreover, traditional models that incorporate audio blindly utilize the audio input regardless of whether it is useful or not, resulting in suboptimal video representation. To address these limitations, we propose a novel video-text retrieval framework, Audio-guided VIdeo representation learning with GATEd attention (AVIGATE), that effectively leverages audio cues through a gated attention mechanism that selectively filters out uninformative audio signals. In addition, we propose an adaptive margin-based contrastive loss to deal with the inherently unclear positive-negative relationship between video and text, which facilitates learning better video-text alignment. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that AVIGATE achieves state-of-the-art performance on all the public benchmarks.
Improving Text-based Person Search via Part-level Cross-modal Correspondence
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:Text-based person search is the task of finding person images that are the most relevant to the natural language text description given as query. The main challenge of this task is a large gap between the target images and text queries, which makes it difficult to establish correspondence and distinguish subtle differences across people. To address this challenge, we introduce an efficient encoder-decoder model that extracts coarse-to-fine embedding vectors which are semantically aligned across the two modalities without supervision for the alignment. There is another challenge of learning to capture fine-grained information with only person IDs as supervision, where similar body parts of different individuals are considered different due to the lack of part-level supervision. To tackle this, we propose a novel ranking loss, dubbed commonality-based margin ranking loss, which quantifies the degree of commonality of each body part and reflects it during the learning of fine-grained body part details. As a consequence, it enables our method to achieve the best records on three public benchmarks.
ASMR: Learning Attribute-Based Person Search with Adaptive Semantic Margin Regularizer
Aug 10, 2021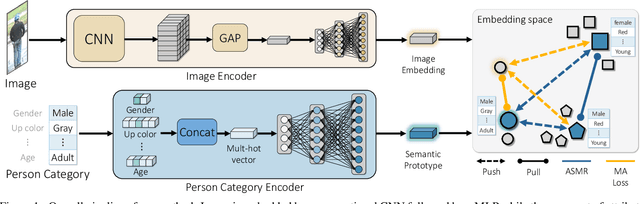
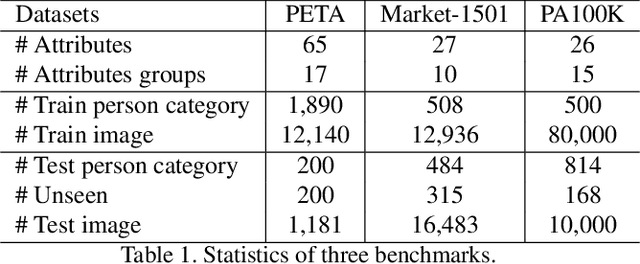
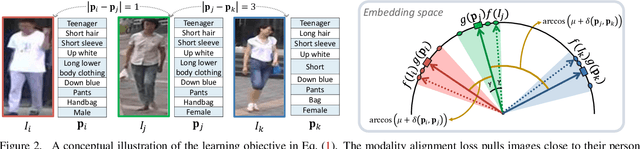
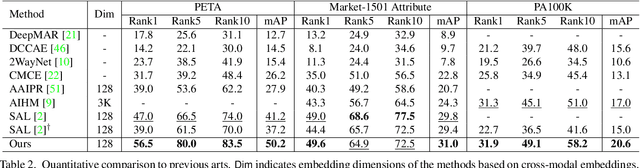
Abstract:Attribute-based person search is the task of finding person images that are best matched with a set of text attributes given as query. The main challenge of this task is the large modality gap between attributes and images. To reduce the gap, we present a new loss for learning cross-modal embeddings in the context of attribute-based person search. We regard a set of attributes as a category of people sharing the same traits. In a joint embedding space of the two modalities, our loss pulls images close to their person categories for modality alignment. More importantly, it pushes apart a pair of person categories by a margin determined adaptively by their semantic distance, where the distance metric is learned end-to-end so that the loss considers importance of each attribute when relating person categories. Our loss guided by the adaptive semantic margin leads to more discriminative and semantically well-arranged distributions of person images. As a consequence, it enables a simple embedding model to achieve state-of-the-art records on public benchmarks without bells and whistles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge