Seoyeon Kim
Learned split-spectrum metalens for obstruction-free broadband imaging in the visible
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Obstructions such as raindrops, fences, or dust degrade captured images, especially when mechanical cleaning is infeasible. Conventional solutions to obstructions rely on a bulky compound optics array or computational inpainting, which compromise compactness or fidelity. Metalenses composed of subwavelength meta-atoms promise compact imaging, but simultaneous achievement of broadband and obstruction-free imaging remains a challenge, since a metalens that images distant scenes across a broadband spectrum cannot properly defocus near-depth occlusions. Here, we introduce a learned split-spectrum metalens that enables broadband obstruction-free imaging. Our approach divides the spectrum of each RGB channel into pass and stop bands with multi-band spectral filtering and learns the metalens to focus light from far objects through pass bands, while filtering focused near-depth light through stop bands. This optical signal is further enhanced using a neural network. Our learned split-spectrum metalens achieves broadband and obstruction-free imaging with relative PSNR gains of 32.29% and improves object detection and semantic segmentation accuracies with absolute gains of +13.54% mAP, +48.45% IoU, and +20.35% mIoU over a conventional hyperbolic design. This promises robust obstruction-free sensing and vision for space-constrained systems, such as mobile robots, drones, and endoscopes.
SPRInG: Continual LLM Personalization via Selective Parametric Adaptation and Retrieval-Interpolated Generation
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Personalizing Large Language Models typically relies on static retrieval or one-time adaptation, assuming user preferences remain invariant over time. However, real-world interactions are dynamic, where user interests continuously evolve, posing a challenge for models to adapt to preference drift without catastrophic forgetting. Standard continual learning approaches often struggle in this context, as they indiscriminately update on noisy interaction streams, failing to distinguish genuine preference shifts from transient contexts. To address this, we introduce SPRInG, a novel semi-parametric framework designed for effective continual personalization. During training, SPRInG employs drift-driven selective adaptation, which utilizes a likelihood-based scoring function to identify high-novelty interactions. This allows the model to selectively update the user-specific adapter on drift signals while preserving hard-to-learn residuals in a replay buffer. During inference, we apply strict relevance gating and fuse parametric knowledge with retrieved history via logit interpolation. Experiments on the long-form personalized generation benchmark demonstrate that SPRInG outperforms existing baselines, validating its robustness for real-world continual personalization.
Rethinking Test-Time Scaling for Medical AI: Model and Task-Aware Strategies for LLMs and VLMs
Jun 16, 2025



Abstract:Test-time scaling has recently emerged as a promising approach for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models or vision-language models during inference. Although a variety of test-time scaling strategies have been proposed, and interest in their application to the medical domain is growing, many critical aspects remain underexplored, including their effectiveness for vision-language models and the identification of optimal strategies for different settings. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive investigation of test-time scaling in the medical domain. We evaluate its impact on both large language models and vision-language models, considering factors such as model size, inherent model characteristics, and task complexity. Finally, we assess the robustness of these strategies under user-driven factors, such as misleading information embedded in prompts. Our findings offer practical guidelines for the effective use of test-time scaling in medical applications and provide insights into how these strategies can be further refined to meet the reliability and interpretability demands of the medical domain.
Bootstrapping Top-down Information for Self-modulating Slot Attention
Nov 04, 2024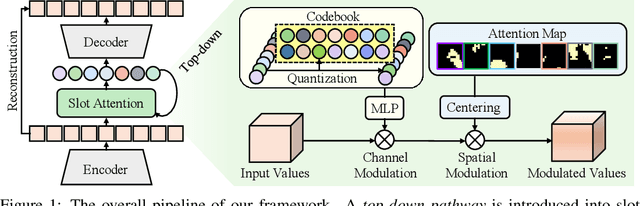
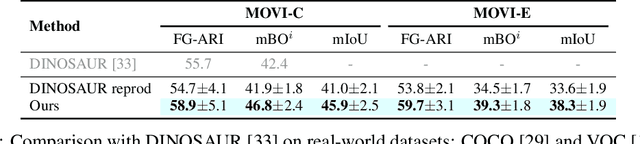

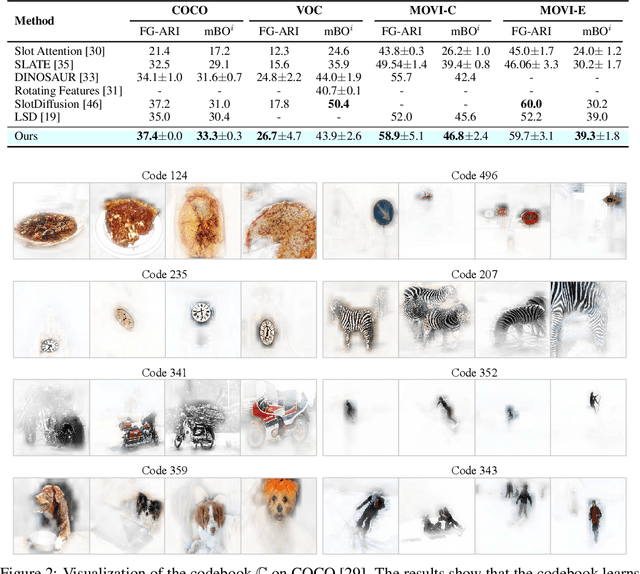
Abstract:Object-centric learning (OCL) aims to learn representations of individual objects within visual scenes without manual supervision, facilitating efficient and effective visual reasoning. Traditional OCL methods primarily employ bottom-up approaches that aggregate homogeneous visual features to represent objects. However, in complex visual environments, these methods often fall short due to the heterogeneous nature of visual features within an object. To address this, we propose a novel OCL framework incorporating a top-down pathway. This pathway first bootstraps the semantics of individual objects and then modulates the model to prioritize features relevant to these semantics. By dynamically modulating the model based on its own output, our top-down pathway enhances the representational quality of objects. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple synthetic and real-world object-discovery benchmarks.
Can Code-Switched Texts Activate a Knowledge Switch in LLMs? A Case Study on English-Korean Code-Switching
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:Code-switching (CS), a phenomenon where multilingual speakers alternate between languages in a discourse, can convey subtle cultural and linguistic nuances that can be otherwise lost in translation. Recent state-of-the-art multilingual large language models (LLMs) demonstrate excellent multilingual abilities in various aspects including understanding CS, but the power of CS in eliciting language-specific knowledge is yet to be discovered. Therefore, we investigate the effectiveness of code-switching on a wide range of multilingual LLMs in terms of knowledge activation, or the act of identifying and leveraging knowledge for reasoning. To facilitate the research, we first present EnKoQA, a synthetic English-Korean CS question-answering dataset. We provide a comprehensive analysis on a variety of multilingual LLMs by subdividing activation process into knowledge identification and knowledge leveraging. Our experiments demonstrate that compared to English text, CS can faithfully activate knowledge inside LLMs, especially on language-specific domains. In addition, the performance gap between CS and English is larger in models that show excellent monolingual abilities, suggesting that there exists a correlation with CS and Korean proficiency.
VerifiNER: Verification-augmented NER via Knowledge-grounded Reasoning with Large Language Models
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:Recent approaches in domain-specific named entity recognition (NER), such as biomedical NER, have shown remarkable advances. However, they still lack of faithfulness, producing erroneous predictions. We assume that knowledge of entities can be useful in verifying the correctness of the predictions. Despite the usefulness of knowledge, resolving such errors with knowledge is nontrivial, since the knowledge itself does not directly indicate the ground-truth label. To this end, we propose VerifiNER, a post-hoc verification framework that identifies errors from existing NER methods using knowledge and revises them into more faithful predictions. Our framework leverages the reasoning abilities of large language models to adequately ground on knowledge and the contextual information in the verification process. We validate effectiveness of VerifiNER through extensive experiments on biomedical datasets. The results suggest that VerifiNER can successfully verify errors from existing models as a model-agnostic approach. Further analyses on out-of-domain and low-resource settings show the usefulness of VerifiNER on real-world applications.
Commonsense-augmented Memory Construction and Management in Long-term Conversations via Context-aware Persona Refinement
Jan 29, 2024



Abstract:Memorizing and utilizing speakers' personas is a common practice for response generation in long-term conversations. Yet, human-authored datasets often provide uninformative persona sentences that hinder response quality. This paper presents a novel framework that leverages commonsense-based persona expansion to address such issues in long-term conversation. While prior work focuses on not producing personas that contradict others, we focus on transforming contradictory personas into sentences that contain rich speaker information, by refining them based on their contextual backgrounds with designed strategies. As the pioneer of persona expansion in multi-session settings, our framework facilitates better response generation via human-like persona refinement. The supplementary video of our work is available at https://caffeine-15bbf.web.app/.
RISCLIP: Referring Image Segmentation Framework using CLIP
Jun 14, 2023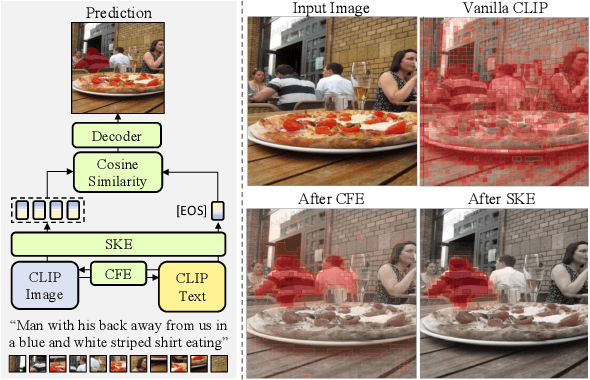



Abstract:Recent advances in computer vision and natural language processing have naturally led to active research in multi-modal tasks, including Referring Image Segmentation (RIS). Recent approaches have advanced the frontier of RIS by impressive margins, but they require an additional pretraining stage on external visual grounding datasets to achieve the state-of-the-art performances. We attempt to break free from this requirement by effectively adapting Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) to RIS. We propose a novel framework that residually adapts frozen CLIP features to RIS with Fusion Adapters and Backbone Adapters. Freezing CLIP preserves the backbone's rich, general image-text alignment knowledge, whilst Fusion Adapters introduce multi-modal communication and Backbone Adapters inject new knowledge useful in solving RIS. Our method reaches a new state of the art on three major RIS benchmarks. We attain such performance without additional pretraining and thereby absolve the necessity of extra training and data preparation. Source code and model weights will be available upon publication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge